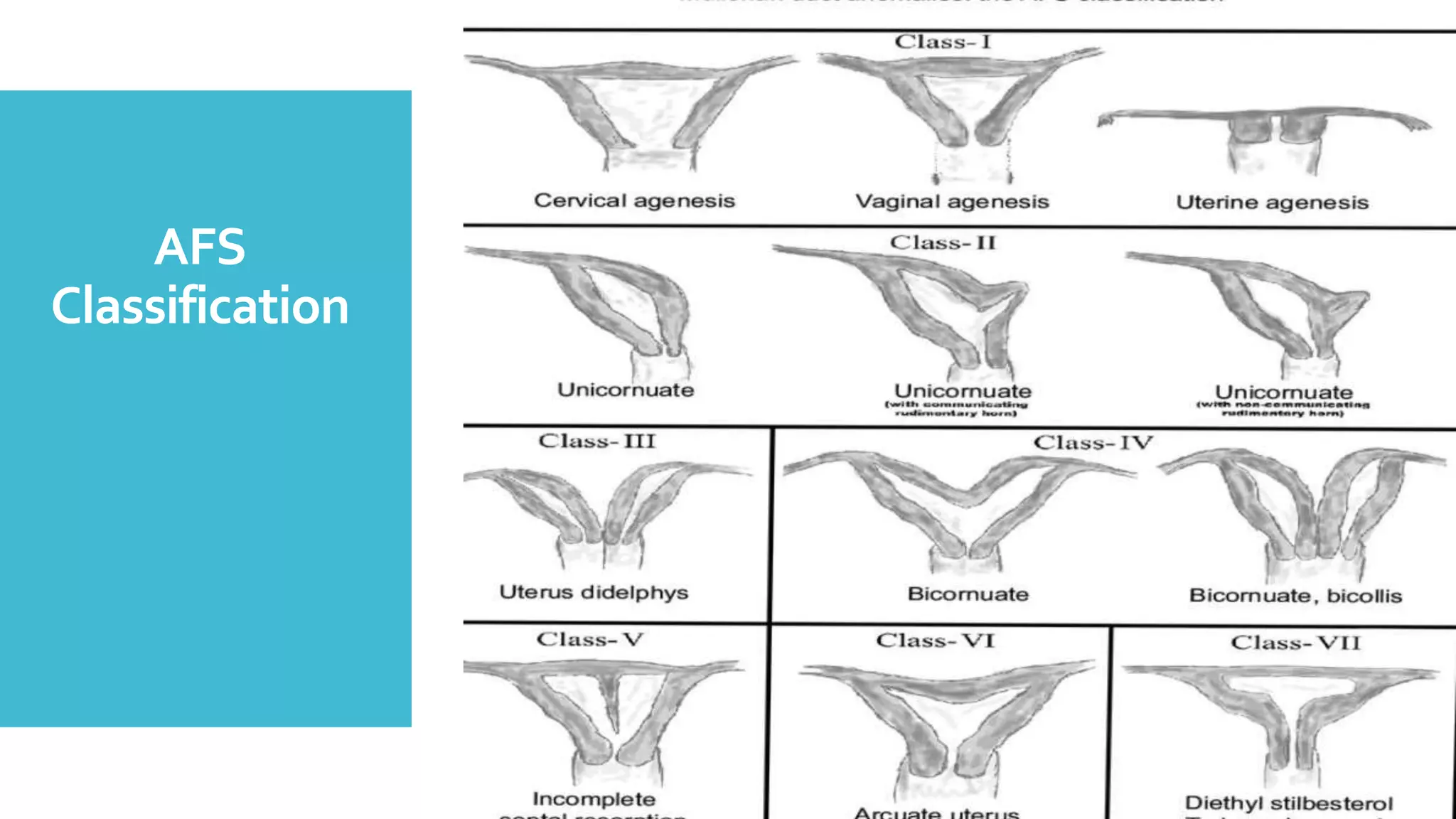
Uterine malformations occur due to abnormal development of the Mullerian ducts during embryogenesis. Common types include septate uterus (35%), bicornuate uterus (26%), and arcuate uterus (18%). Uterine malformations can lead to infertility, dysmenorrhea, recurrent miscarriage, preterm birth, and obstructed labor due to the abnormal uterine anatomy. Diagnosis involves hysteroscopy, ultrasound, or MRI to visualize the internal and external uterine architecture. Surgical correction through hysteroscopic or abdominal metroplasty may be recommended for otherwise unexplained fertility or pregnancy complications.