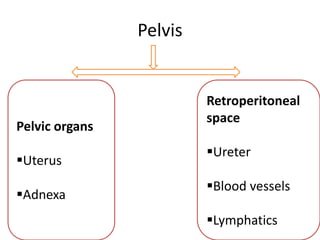
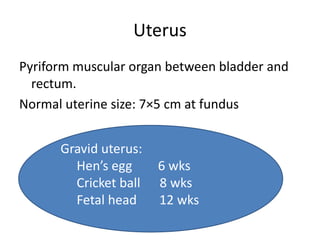
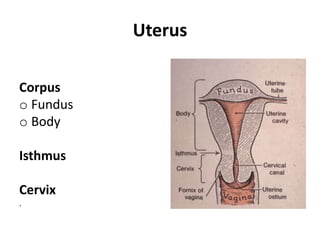
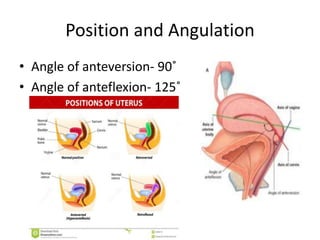
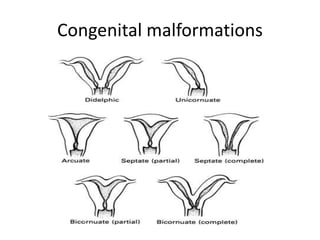
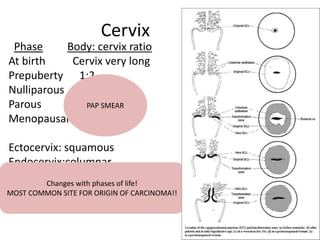
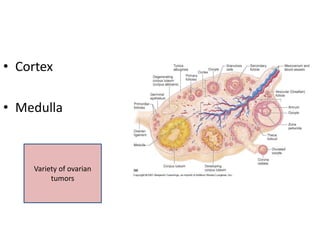
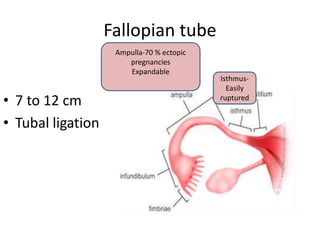
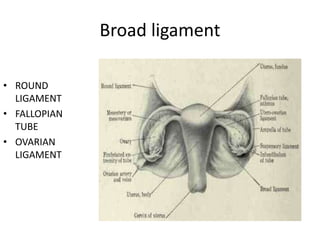
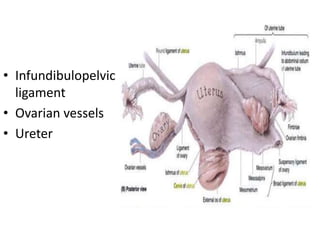
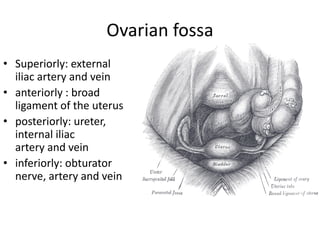
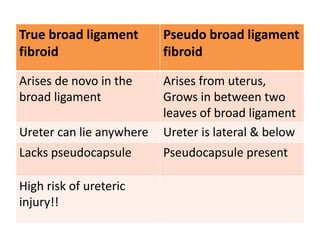
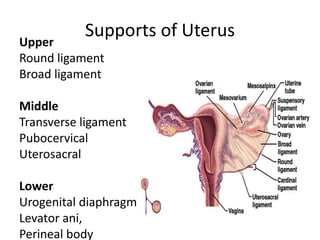
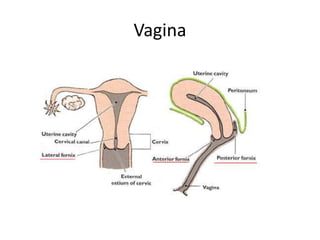
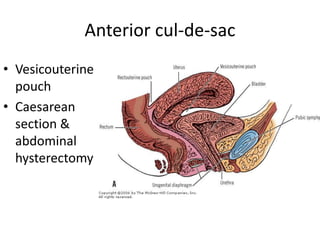
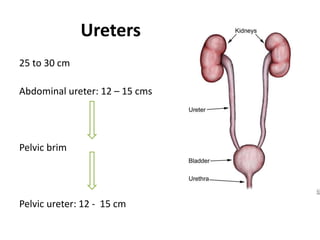
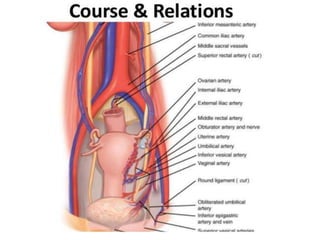
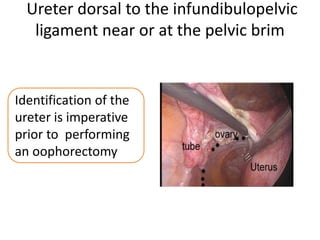
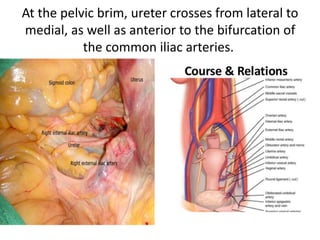
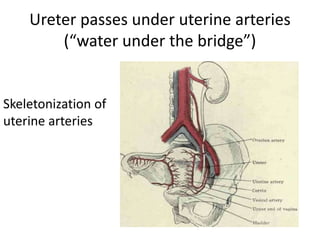
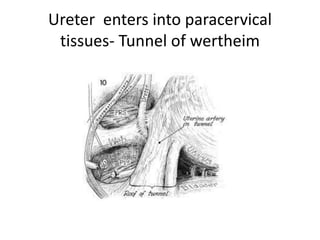
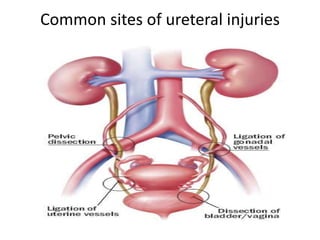
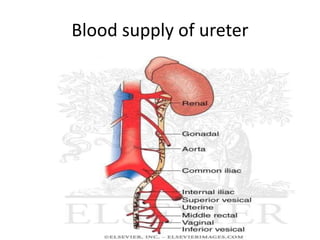
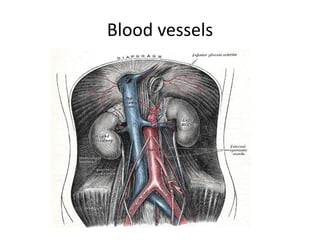
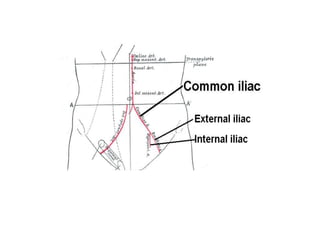
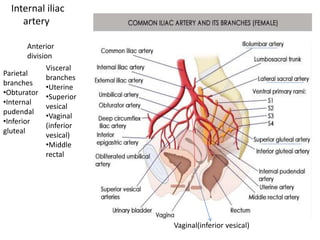
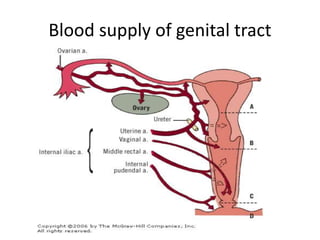
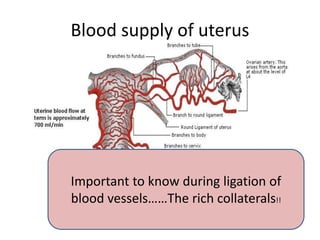
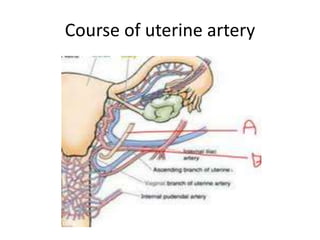
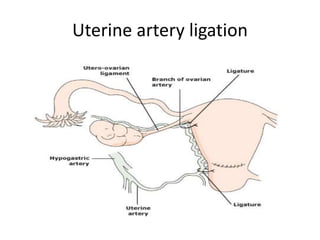
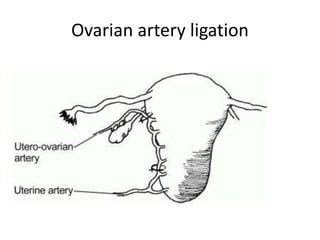
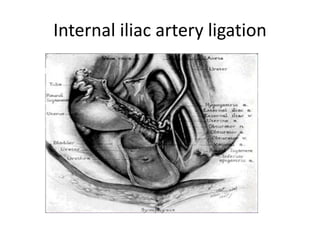
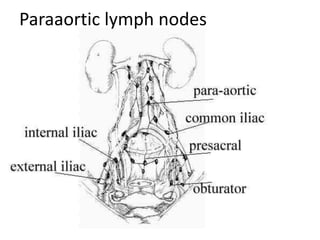
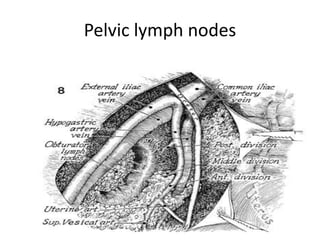
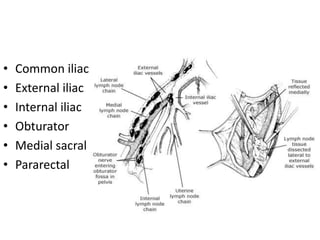
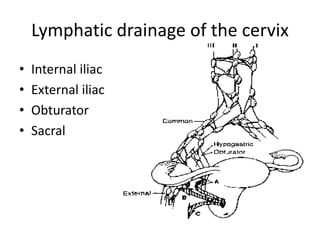
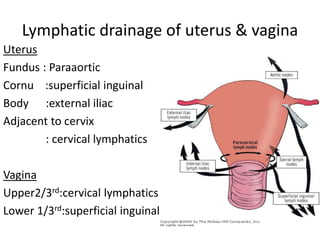
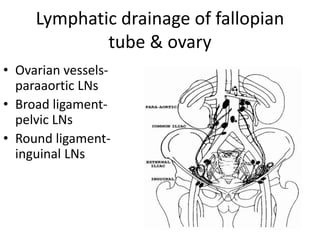
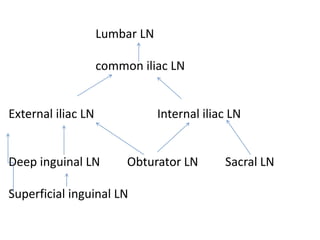
This document provides an overview of pelvic anatomy including the pelvis, pelvic organs, uterus, cervix, adnexa, broad ligament, vagina, retroperitoneal structures, blood vessels, lymphatics, and congenital malformations. It describes the size, shape, position and layers of the uterus and cervix. It details the structures of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, broad ligament and their blood supply. It outlines the course and tributaries of the internal iliac artery. It maps the lymphatic drainage pathways of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes and ovaries.