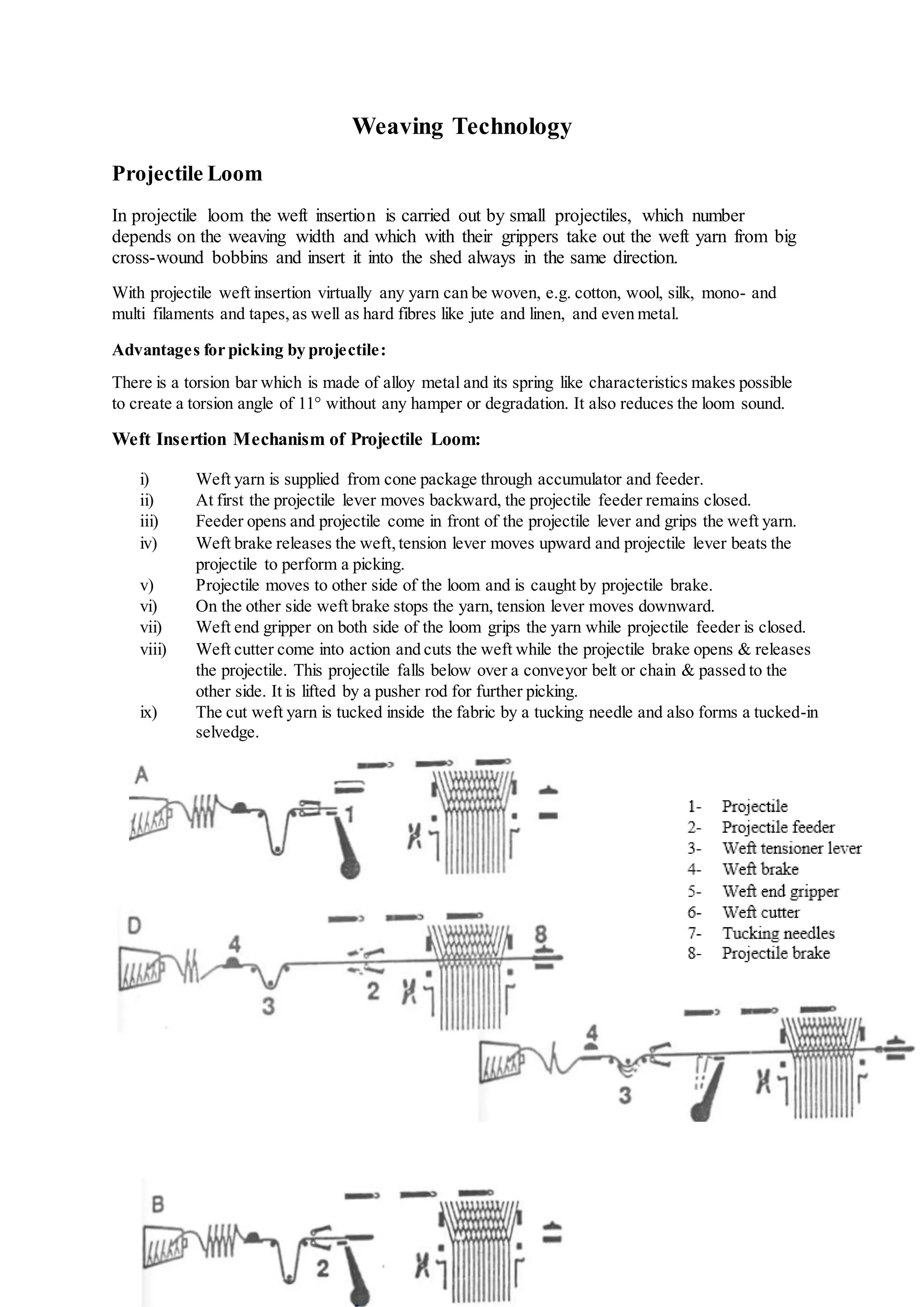
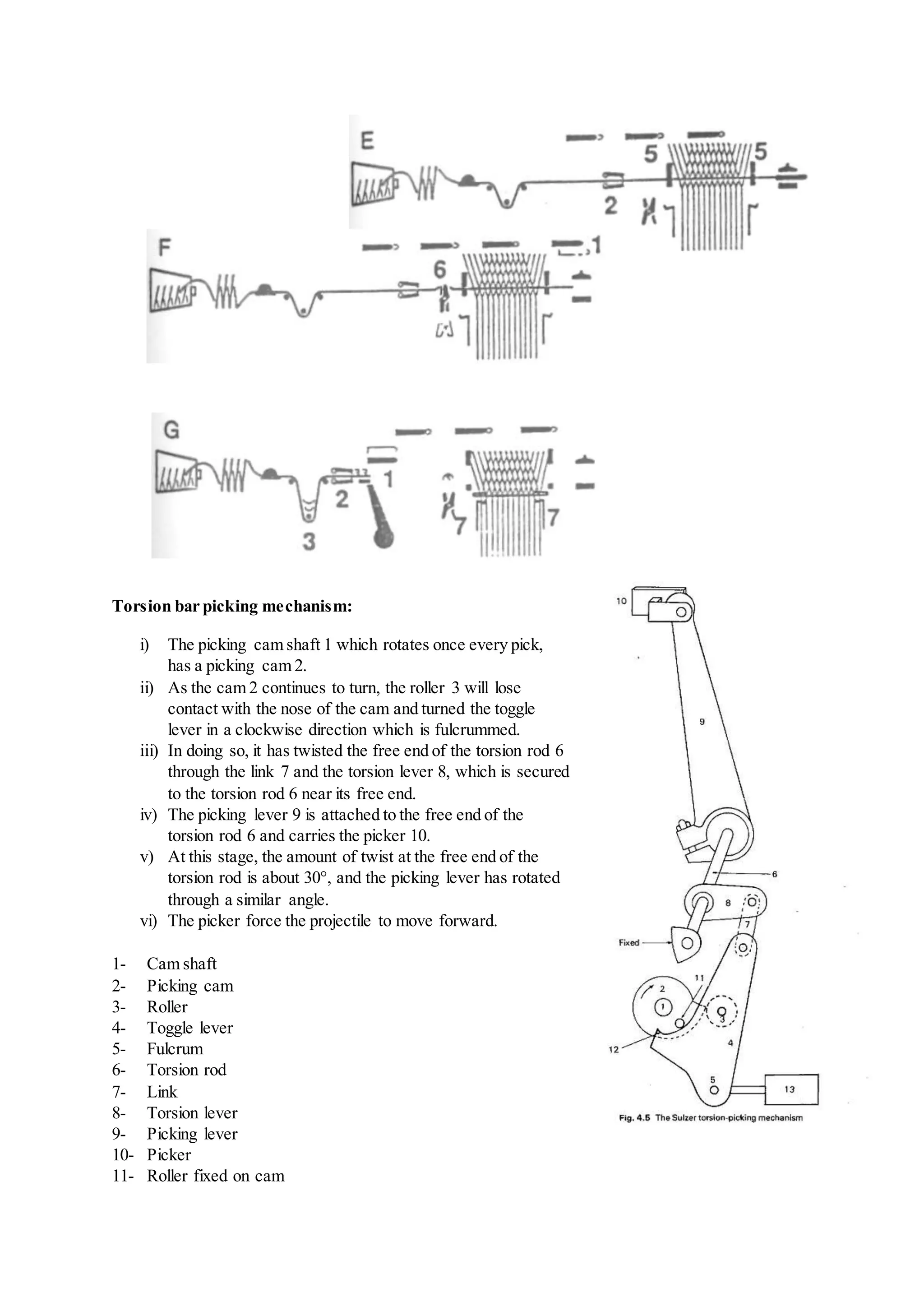
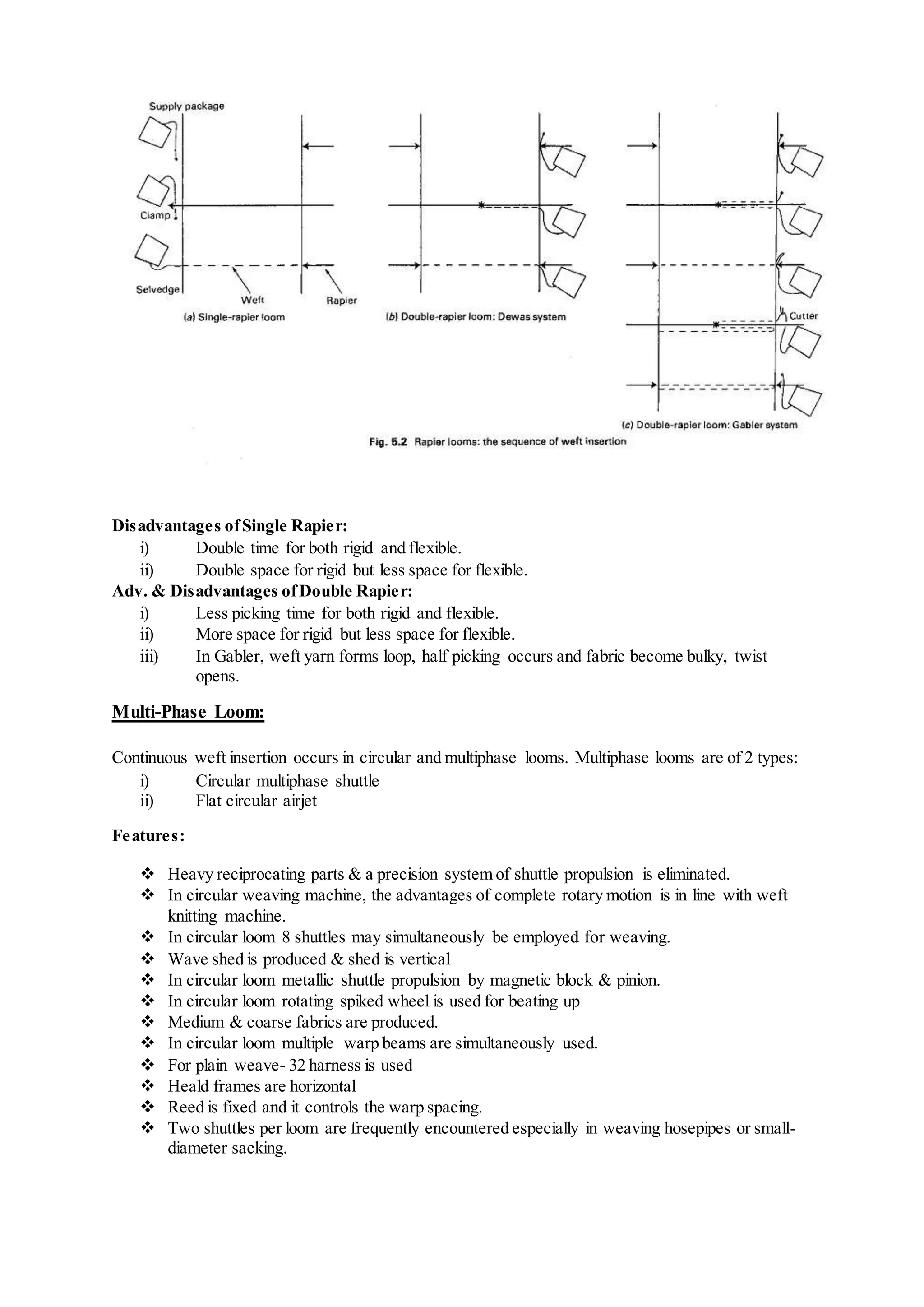
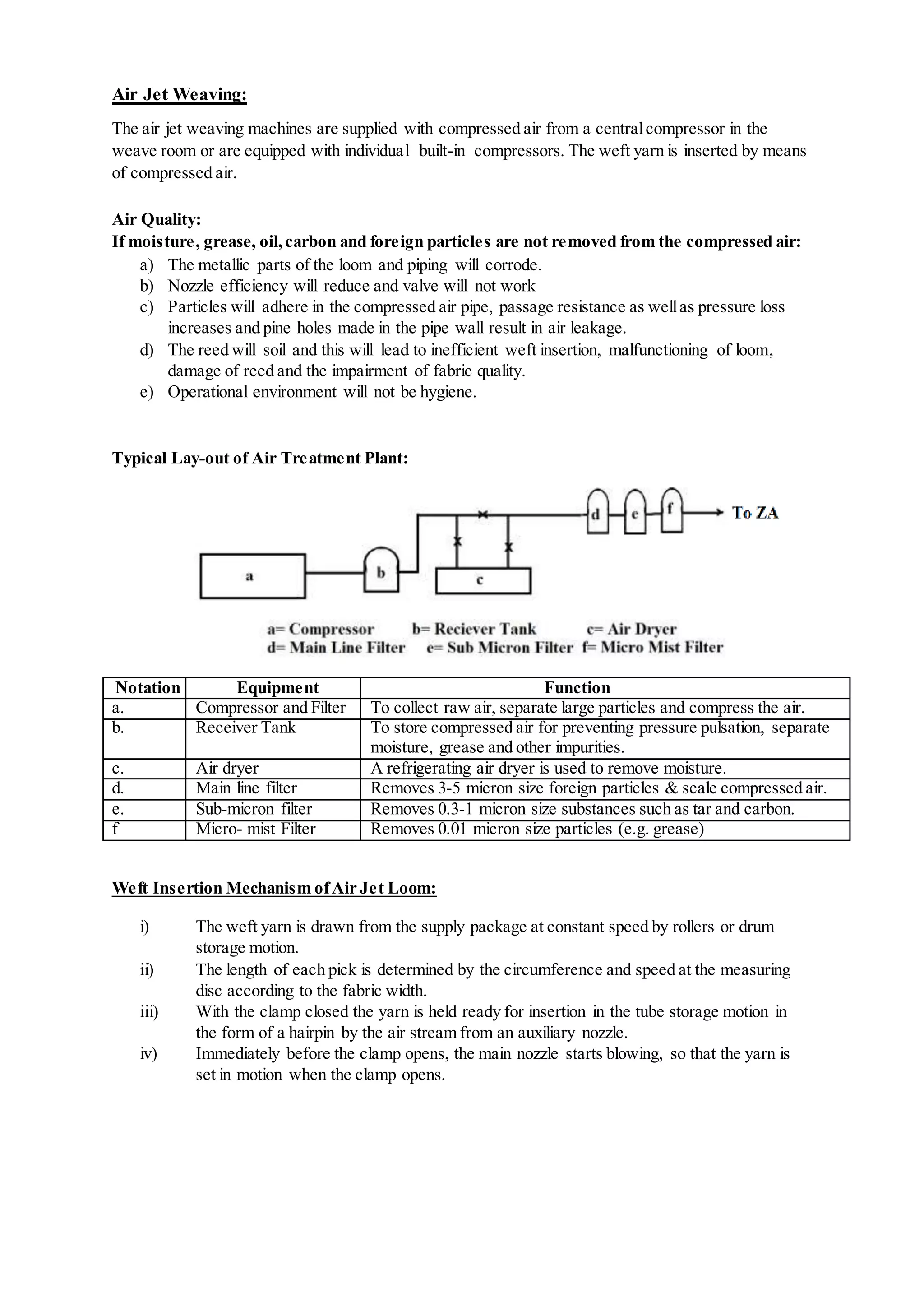
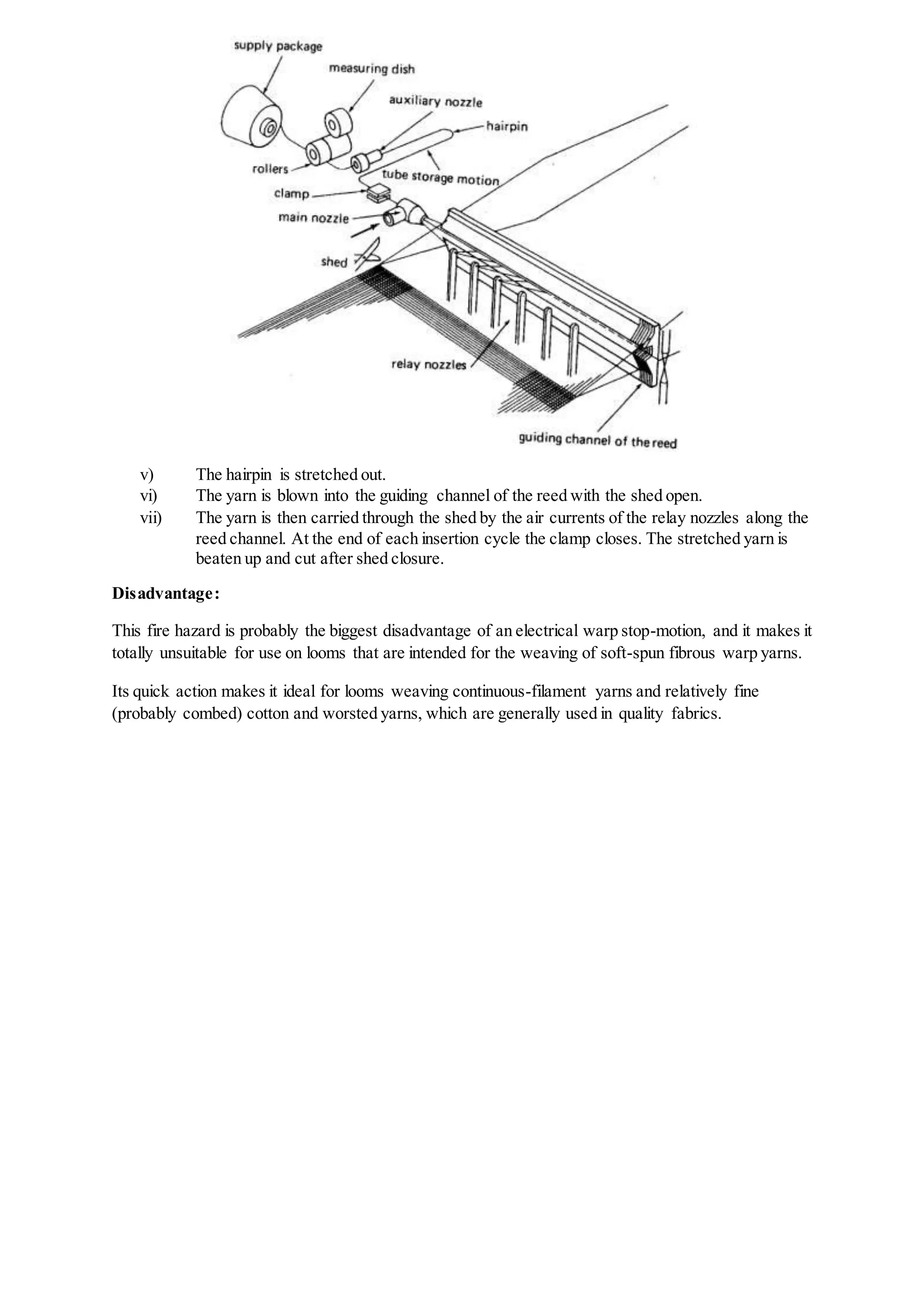
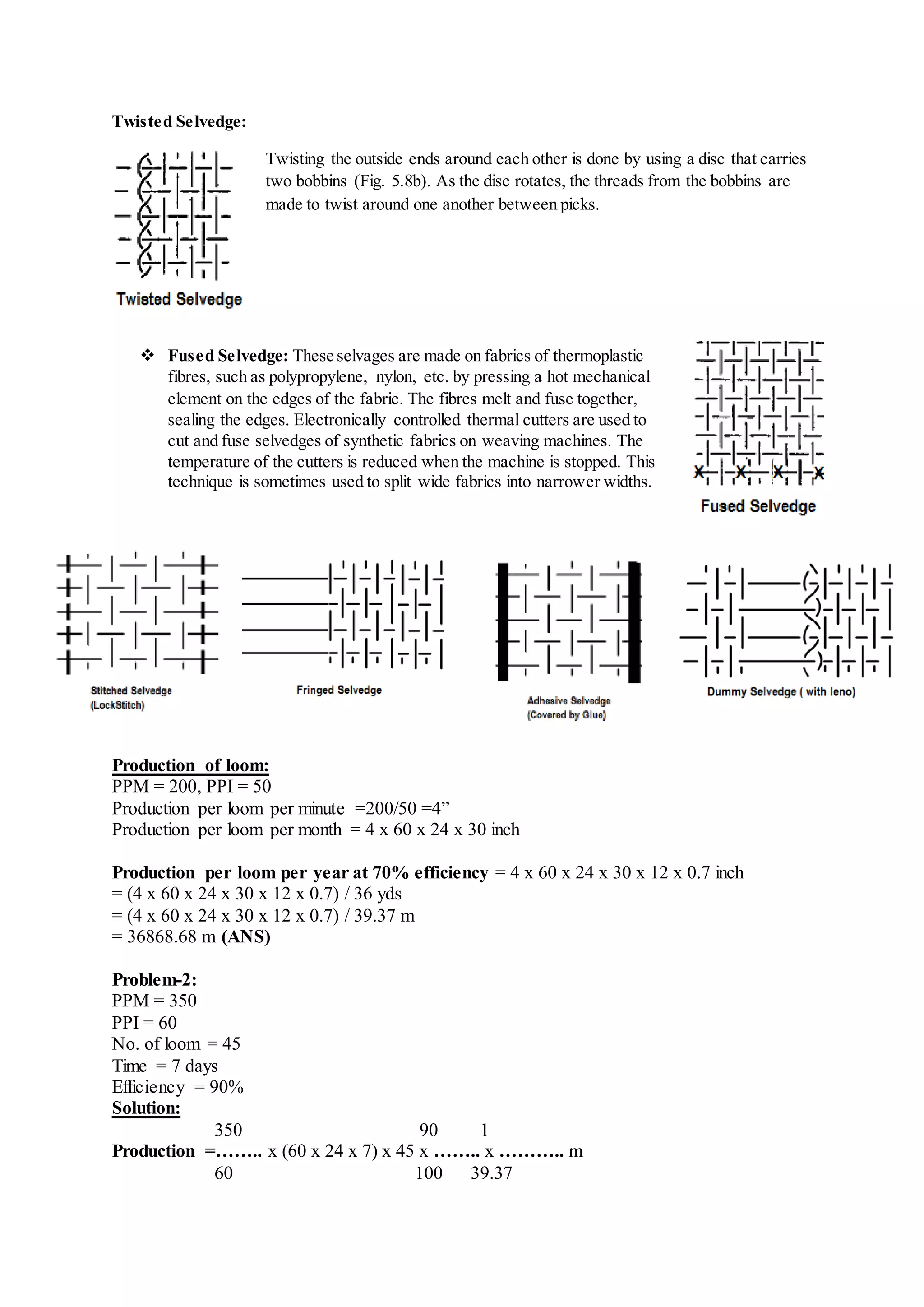
The document discusses different types of looms and their weft insertion mechanisms, including projectile looms, rapier looms, air jet looms, and multiphase looms. It describes the torsion bar picking mechanism of projectile looms and covers topics like weft insertion, selvedges, classifications of double rapier looms, air treatment systems for air jet looms, and calculations for fabric and yarn production.