Embed presentation
Downloaded 520 times



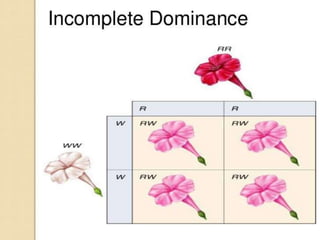




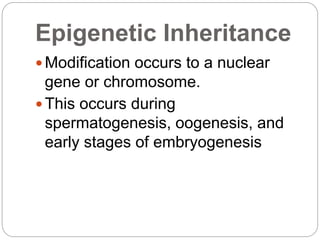
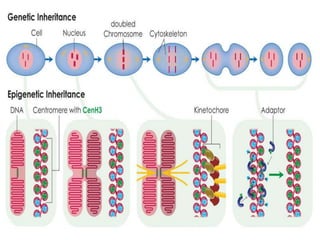
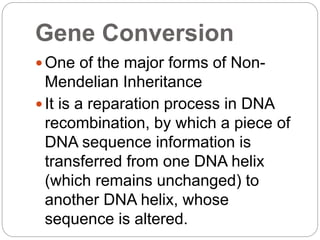
This document discusses several forms of non-Mendelian inheritance including incomplete dominance where traits show a combined phenotype, co-dominance where offspring exhibit both parental traits together, multiple alleles where more than two alleles can code for a trait, maternal and paternal effects where the parent's environment or genotype influences the offspring's phenotype, epigenetic inheritance involving modification to genes or chromosomes early in development, and gene conversion being a DNA recombination process that transfers sequence information between DNA helices.










