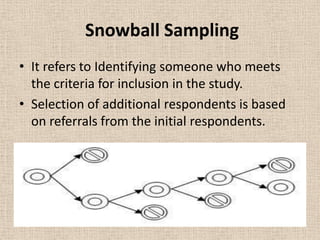
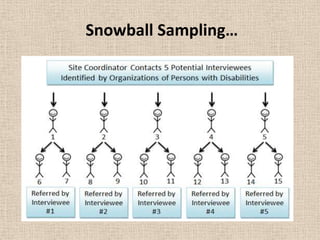
This document discusses different types of non-probability sampling methods. It describes convenience sampling as selecting samples that are readily available without rigorous sampling methods. Judgemental sampling involves selecting samples based on the researcher's judgement when little is known about the population. Quota sampling determines the sample size and quotas for different population categories in advance. Snowball sampling identifies initial respondents who meet criteria and selects additional respondents through their referrals.