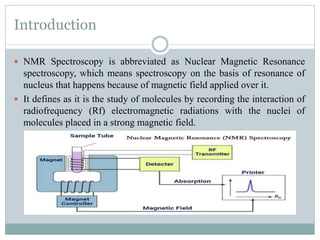
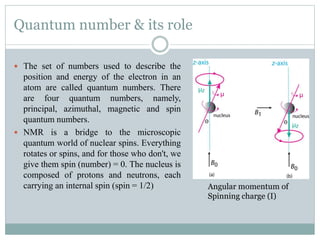
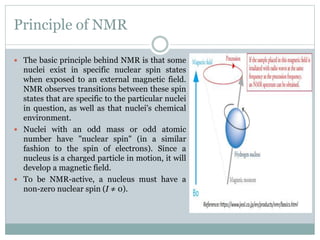
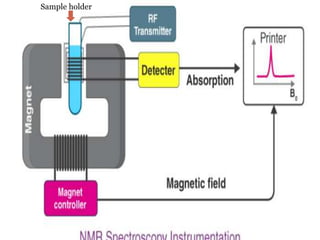
NMR spectroscopy involves applying a strong magnetic field to atomic nuclei and observing the electromagnetic radiation absorbed and emitted during transitions between nuclear spin energy levels. It provides information about the structure of molecules by detecting hydrogen and carbon isotopes. The first NMR spectrum was published in 1946 by Bloch and Purcell, who received the Nobel Prize for their work developing NMR spectroscopy. It has become an important tool for organic chemists to determine molecular structure.