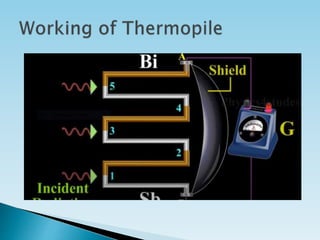
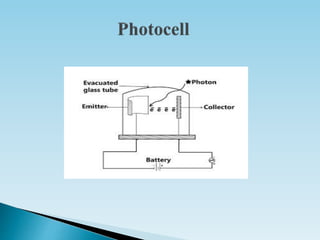
This document discusses actinometry, which is a technique used to determine the number of photons in a beam of light or absorbed per unit time. It defines quantum yield as the number of moles of product formed per Einstein of light absorbed. An actinometer is a chemical system or physical device that determines the rate of photon absorption. There are two main types of actinometers - physical detectors such as thermopiles and photocells, and chemical actinometers which measure radiation intensity through chemical reaction yields, such as the uranyl oxalate actinometer discussed in the document.