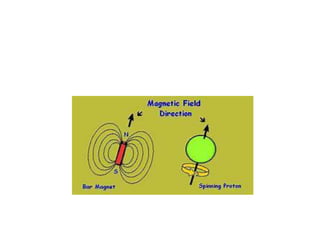
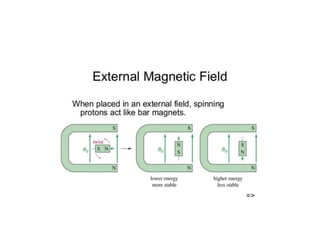
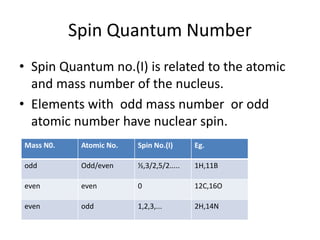
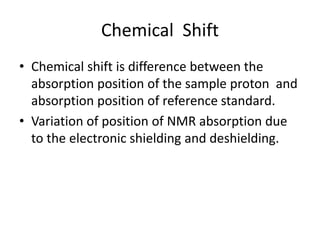
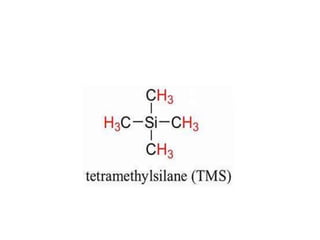
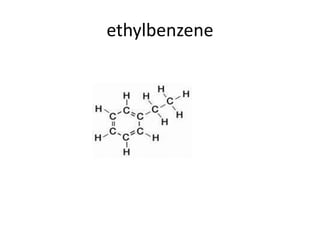
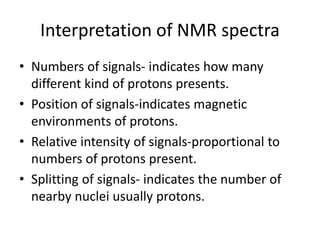
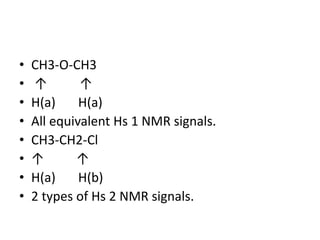
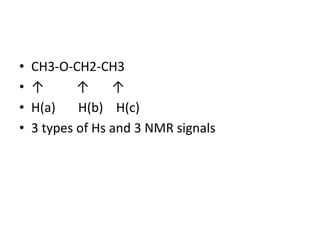
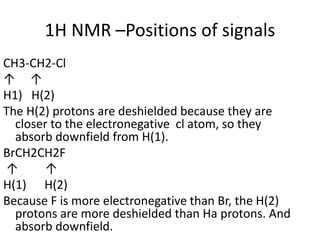
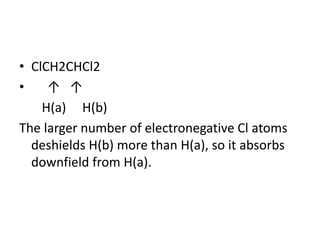
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy involves absorbing radio frequency radiation by atomic nuclei in a magnetic field. NMR can be used to study the magnetic properties and local chemical environments of different nuclei, deduce molecular structure, and identify atoms in neighboring groups. The number and positions of NMR signals provide information about the number of different proton types in a molecule and their magnetic shielding. Signal intensities correlate with proton numbers, and splitting patterns indicate neighboring protons. NMR has applications in materials science, chemical analysis, studying hydrogen bonding and drug design.