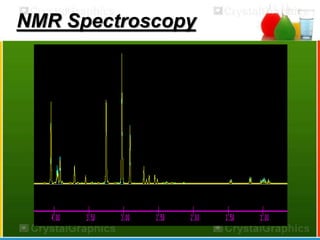
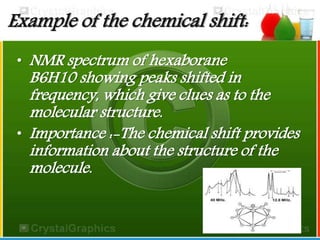
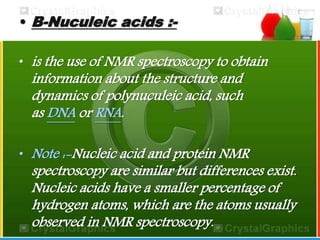
The document discusses nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, which exploits the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei. It explains basic NMR techniques, how NMR relies on nuclear magnetic resonance, and its importance in providing structural information about molecules. The document also discusses chemical shifts, spin-spin coupling, NMR analysis applications including quantitative NMR and solid state NMR, and the history and some websites related to NMR.