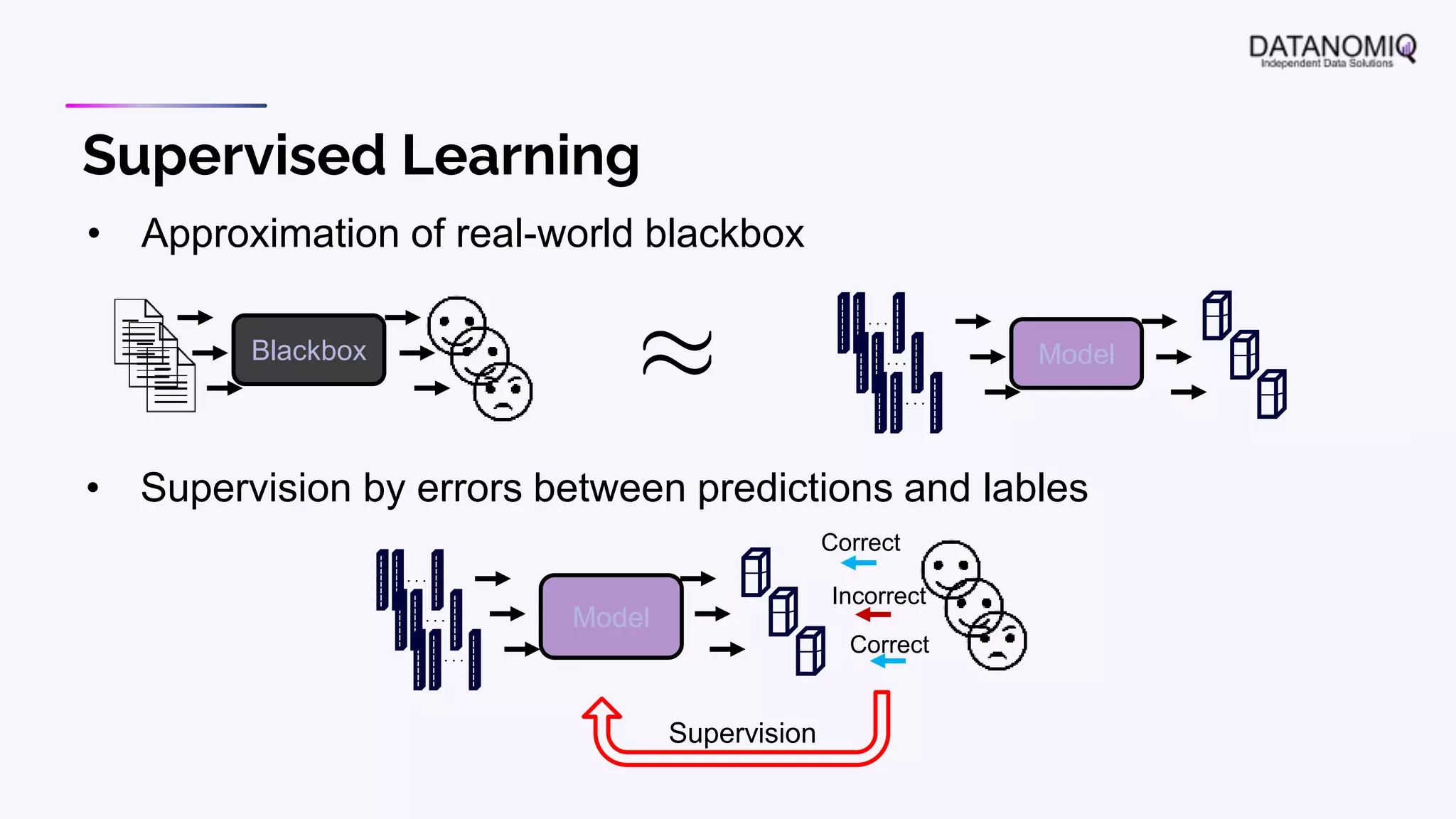
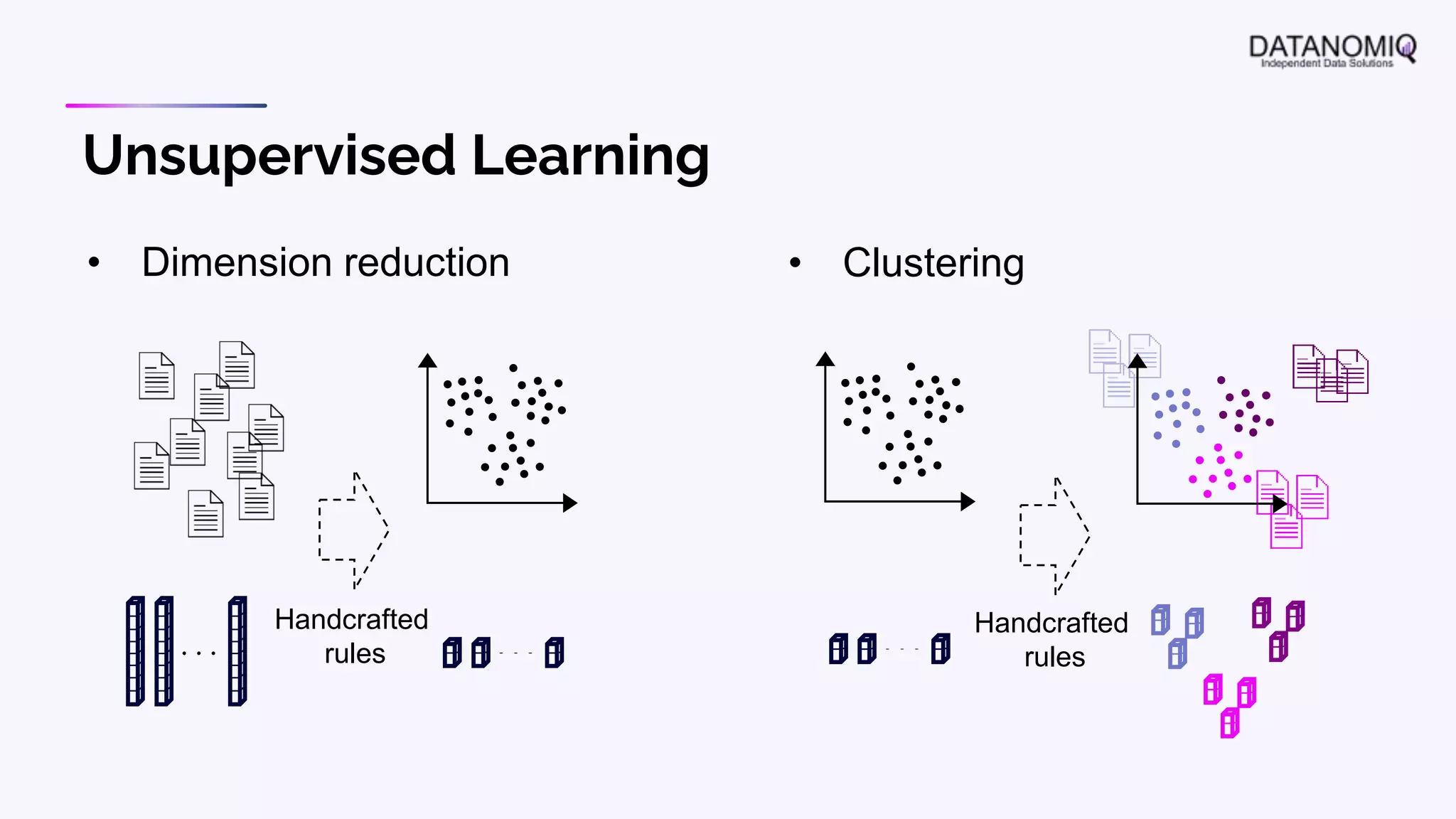
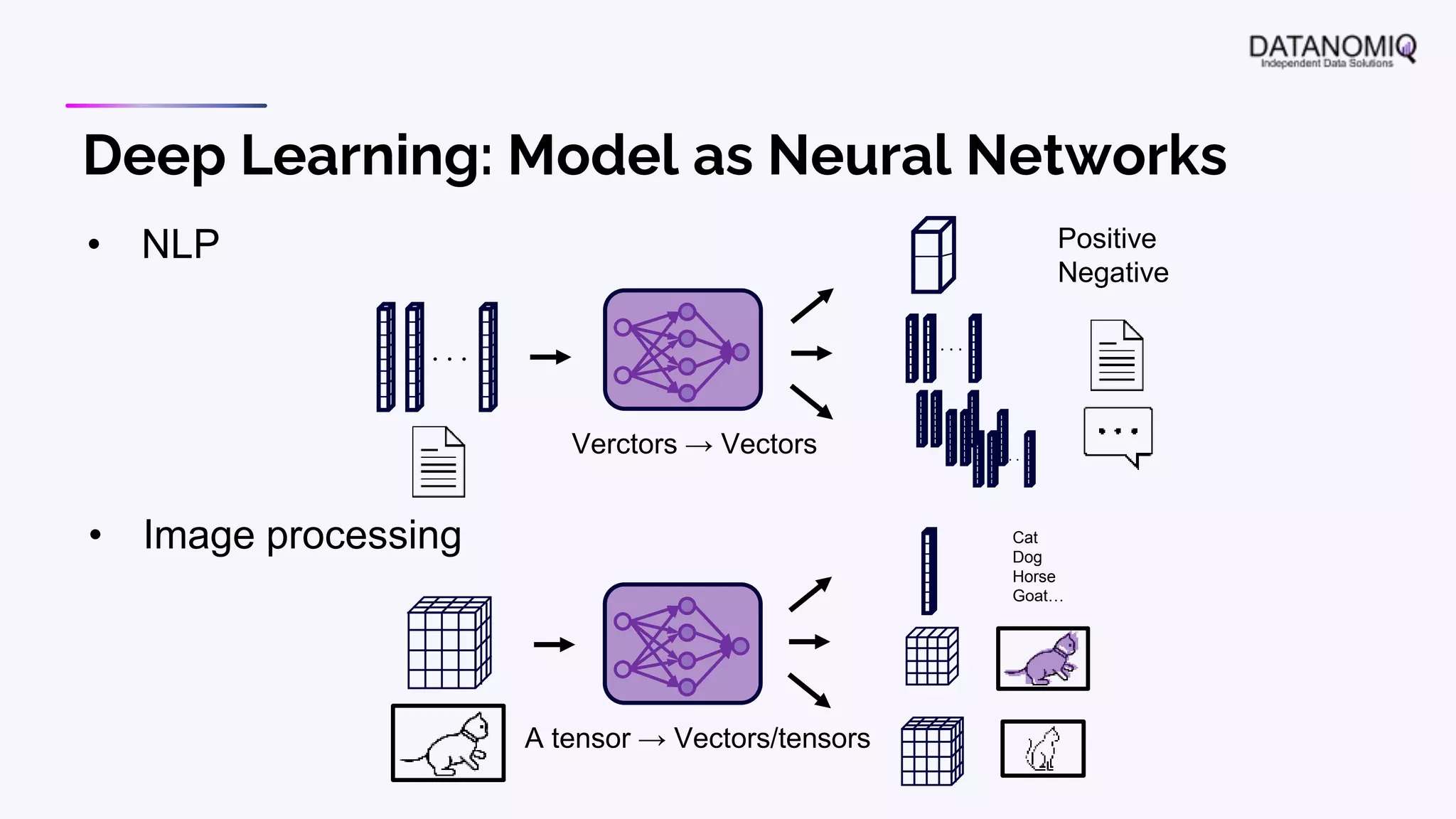
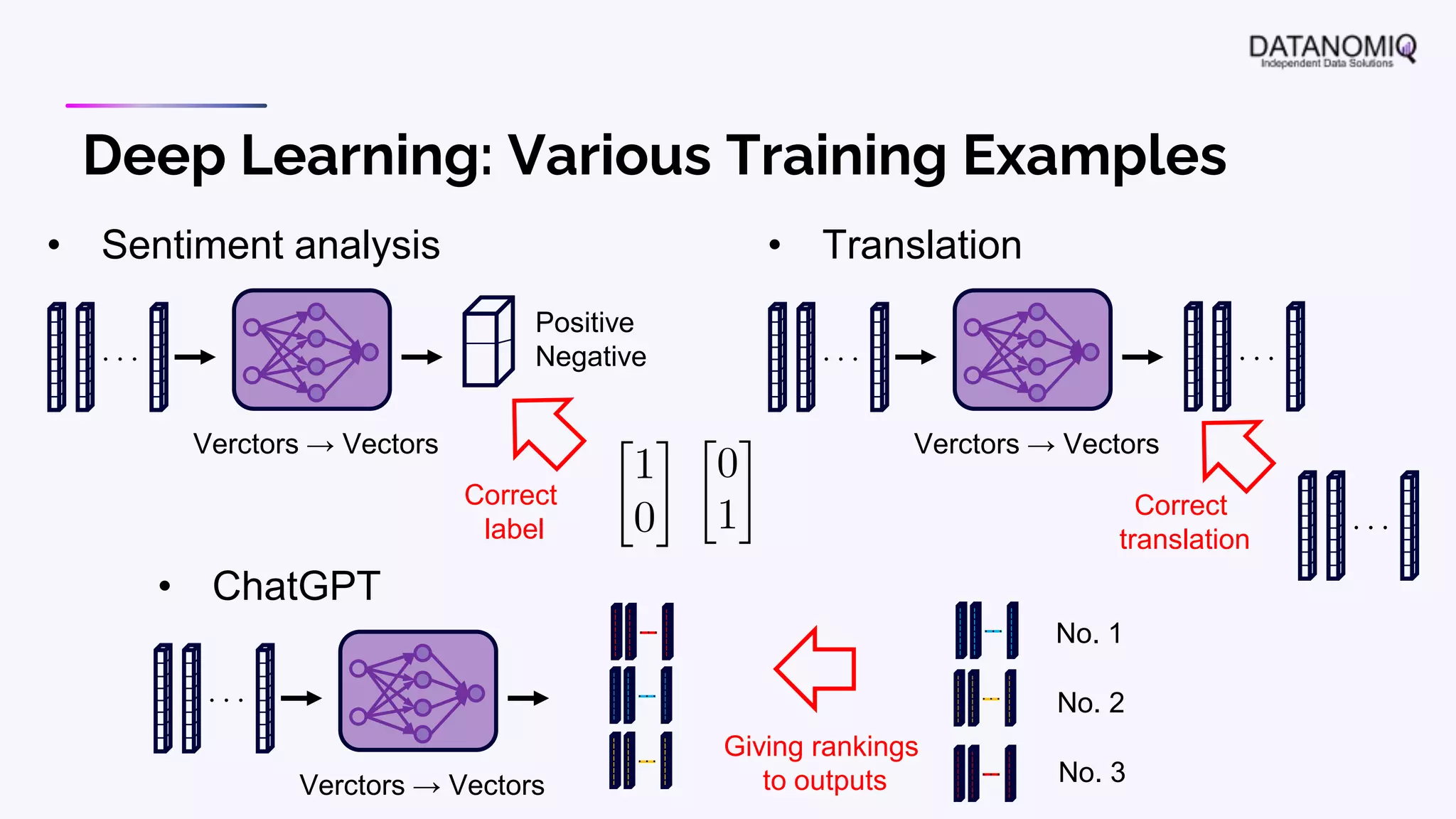
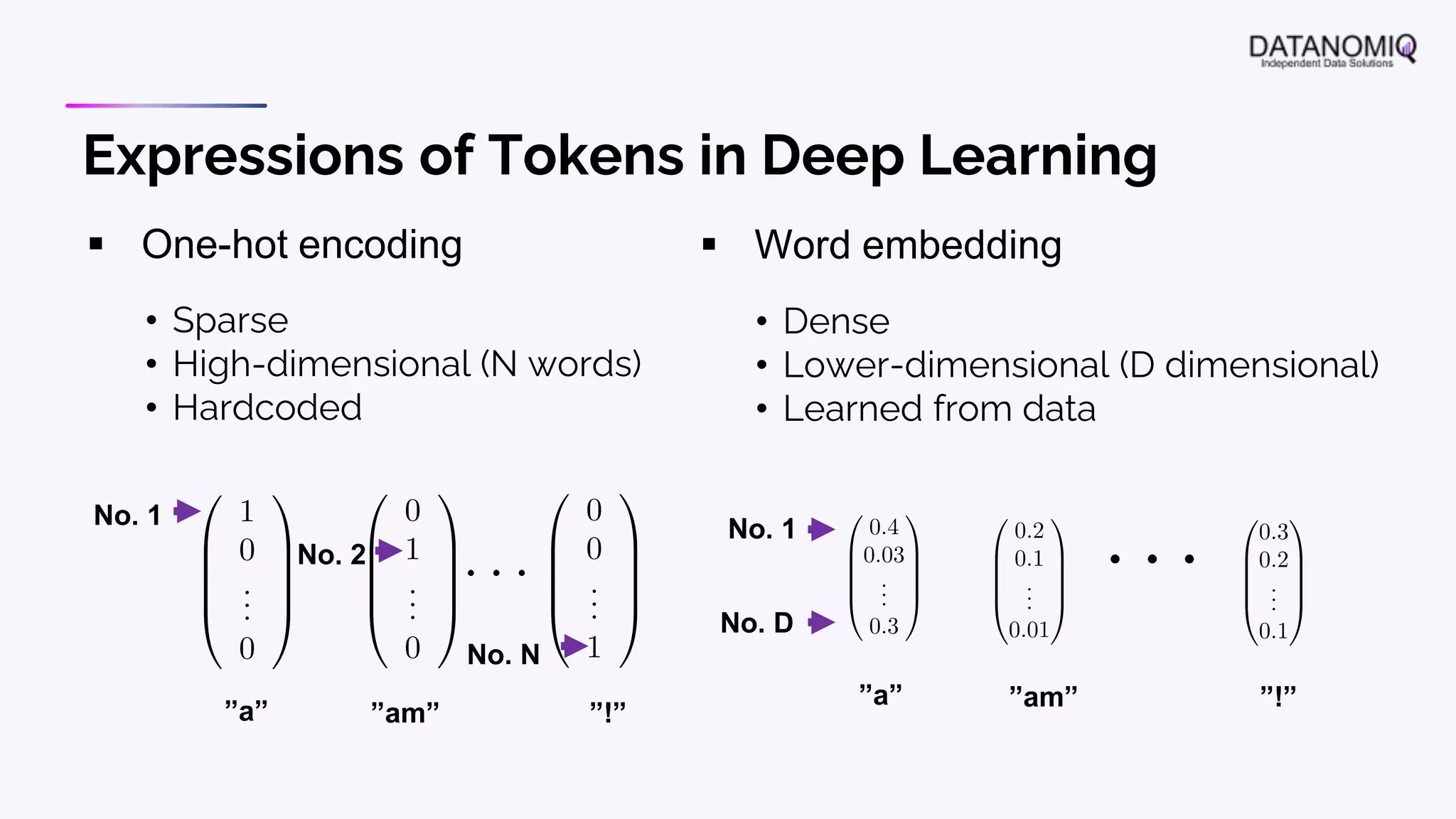
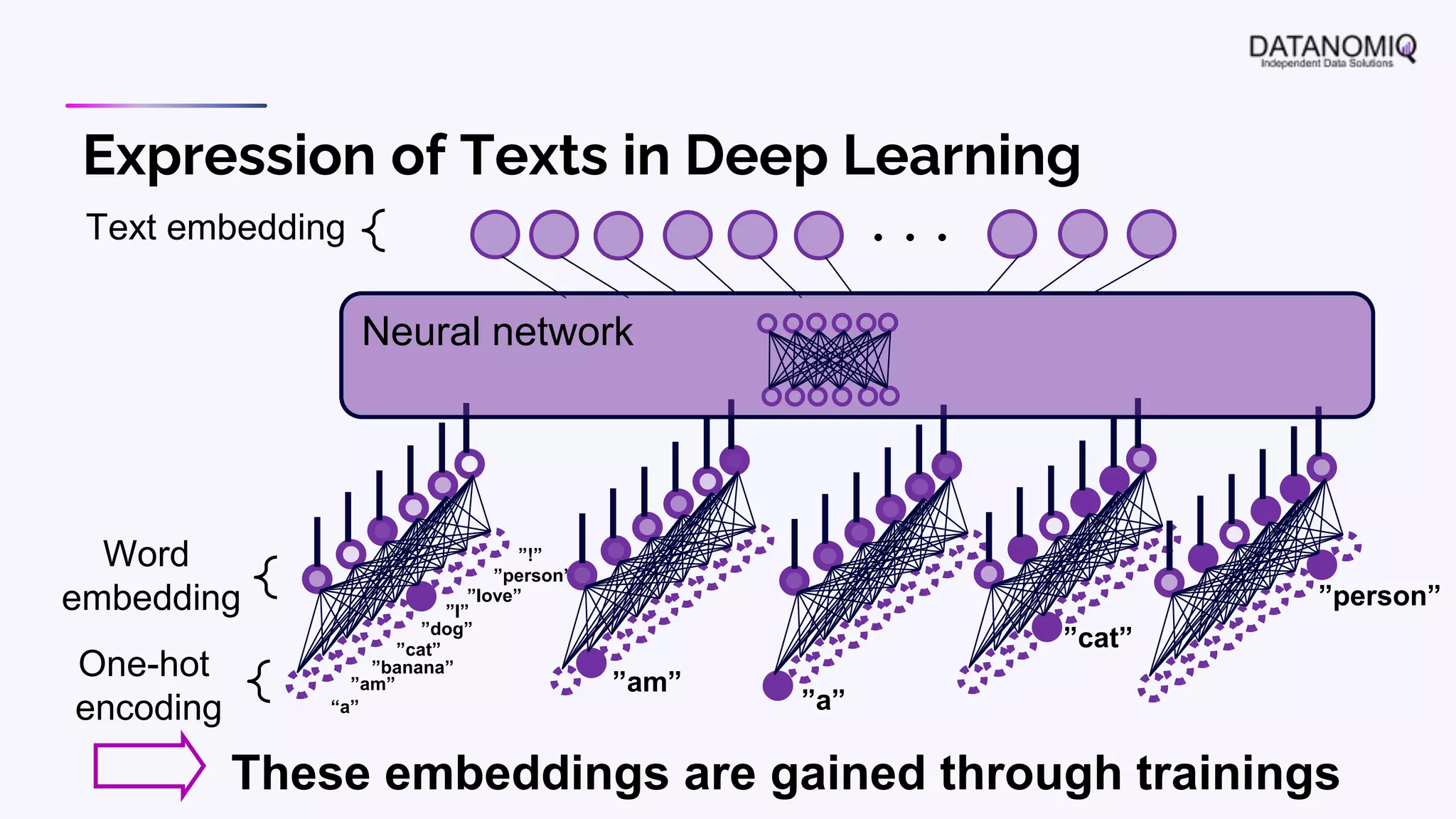
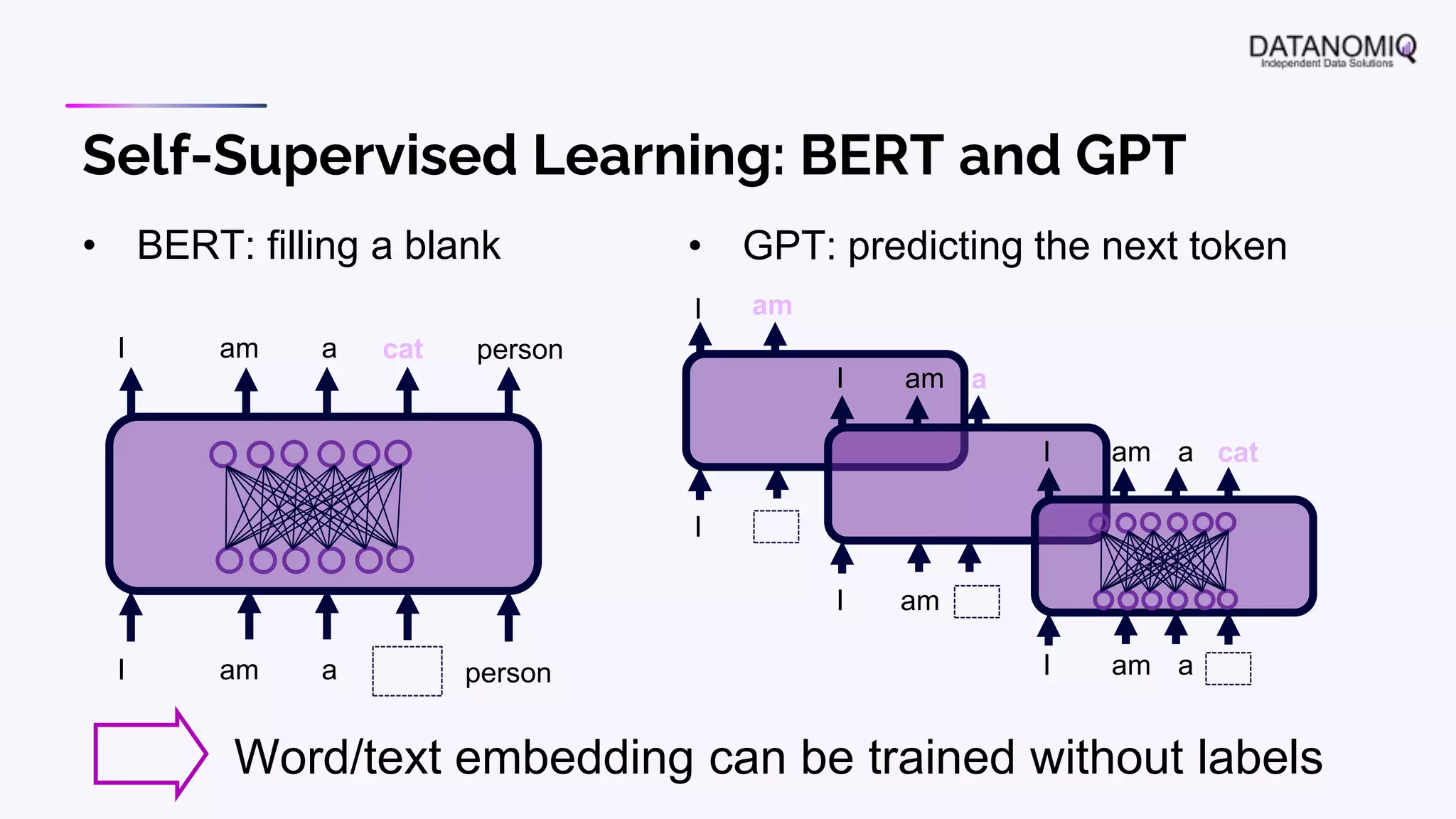
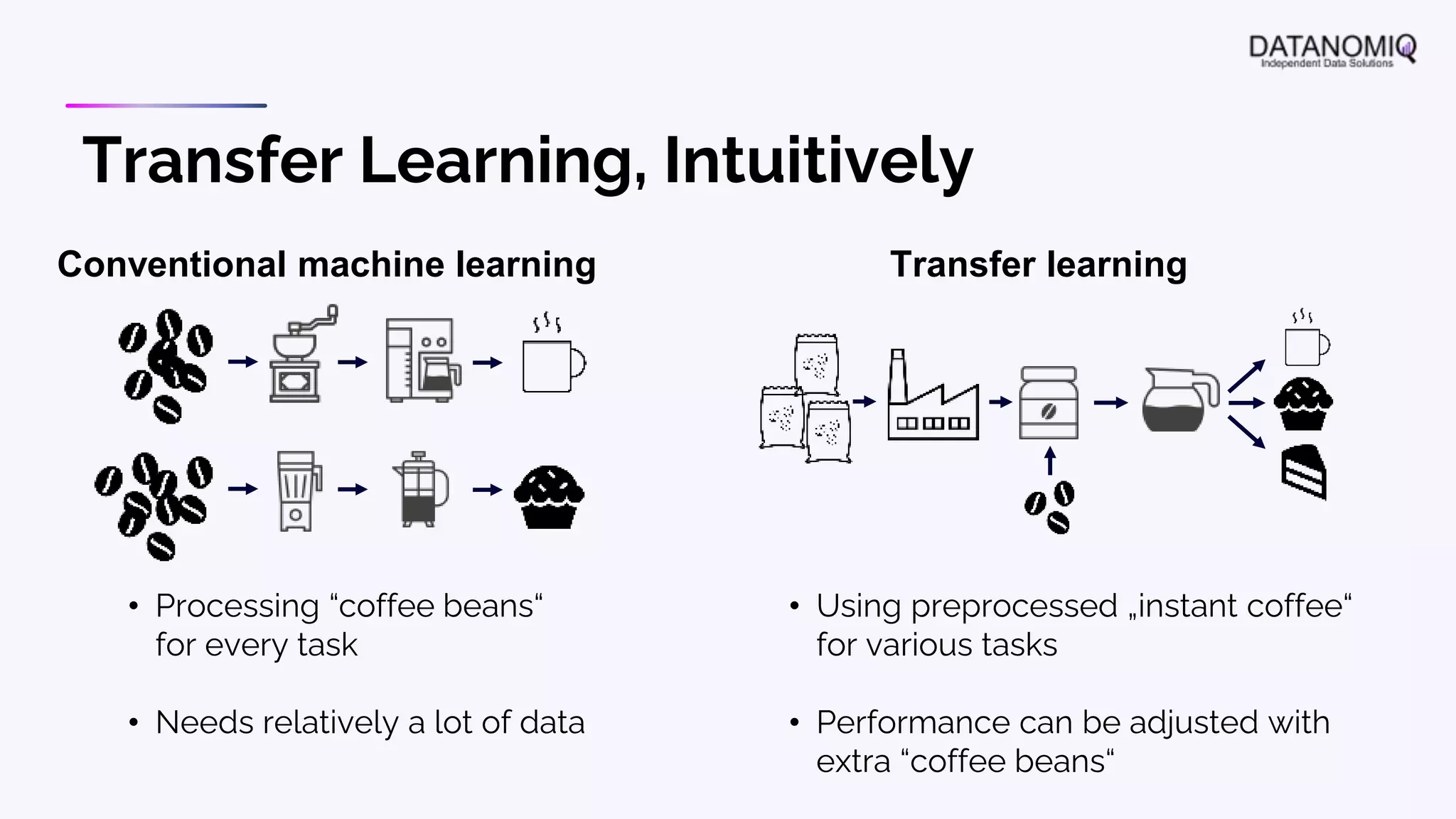
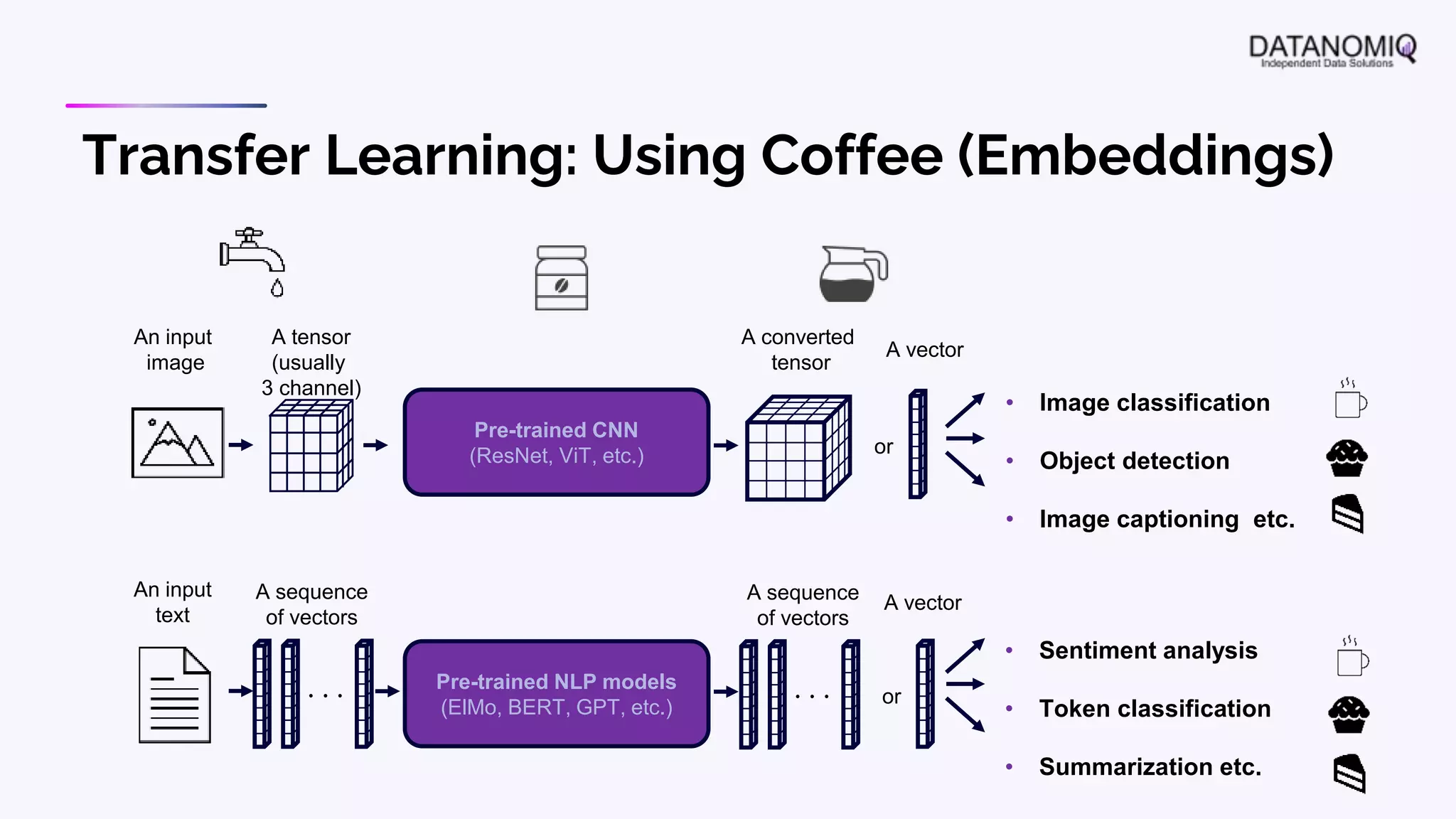
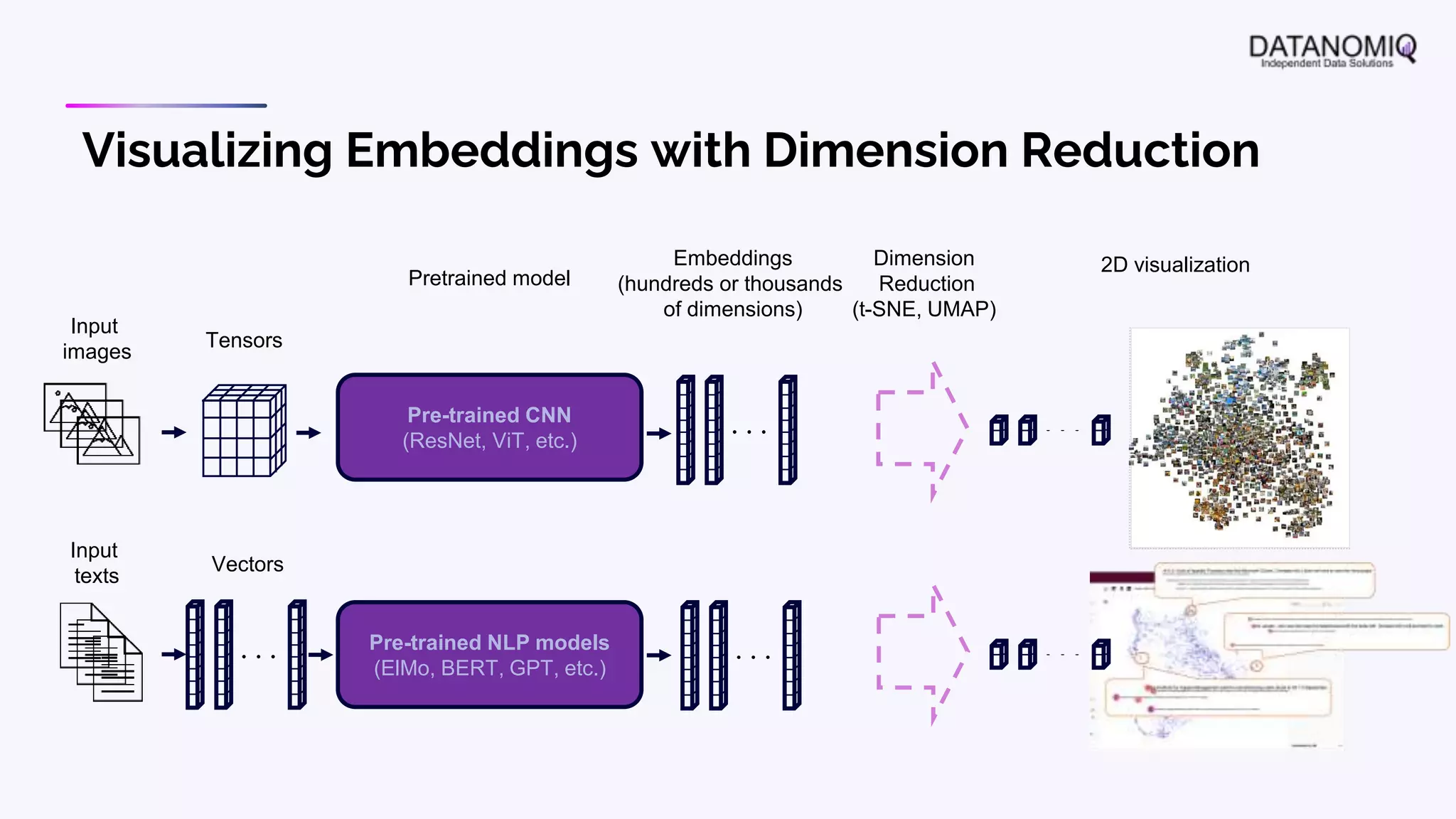
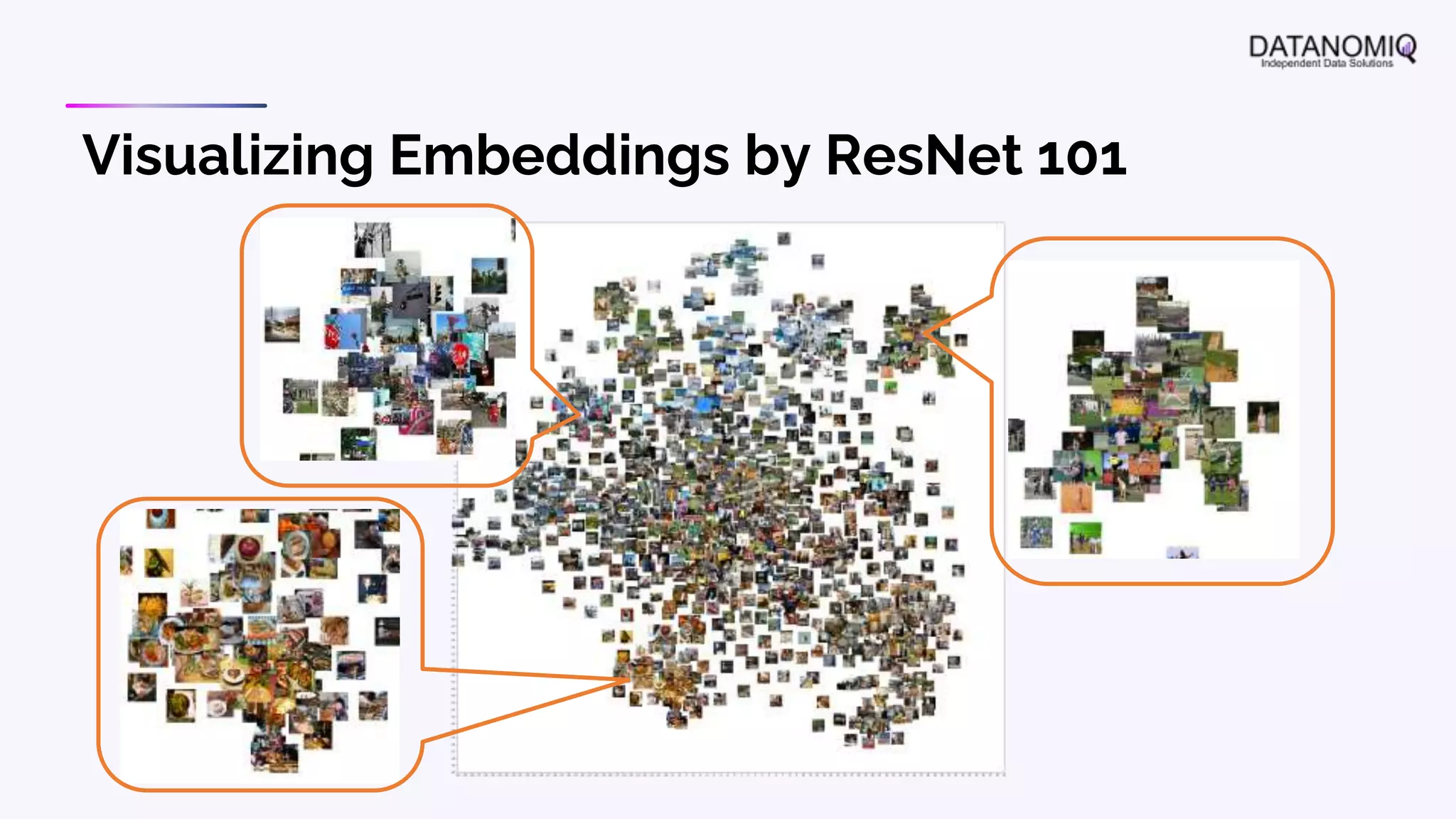
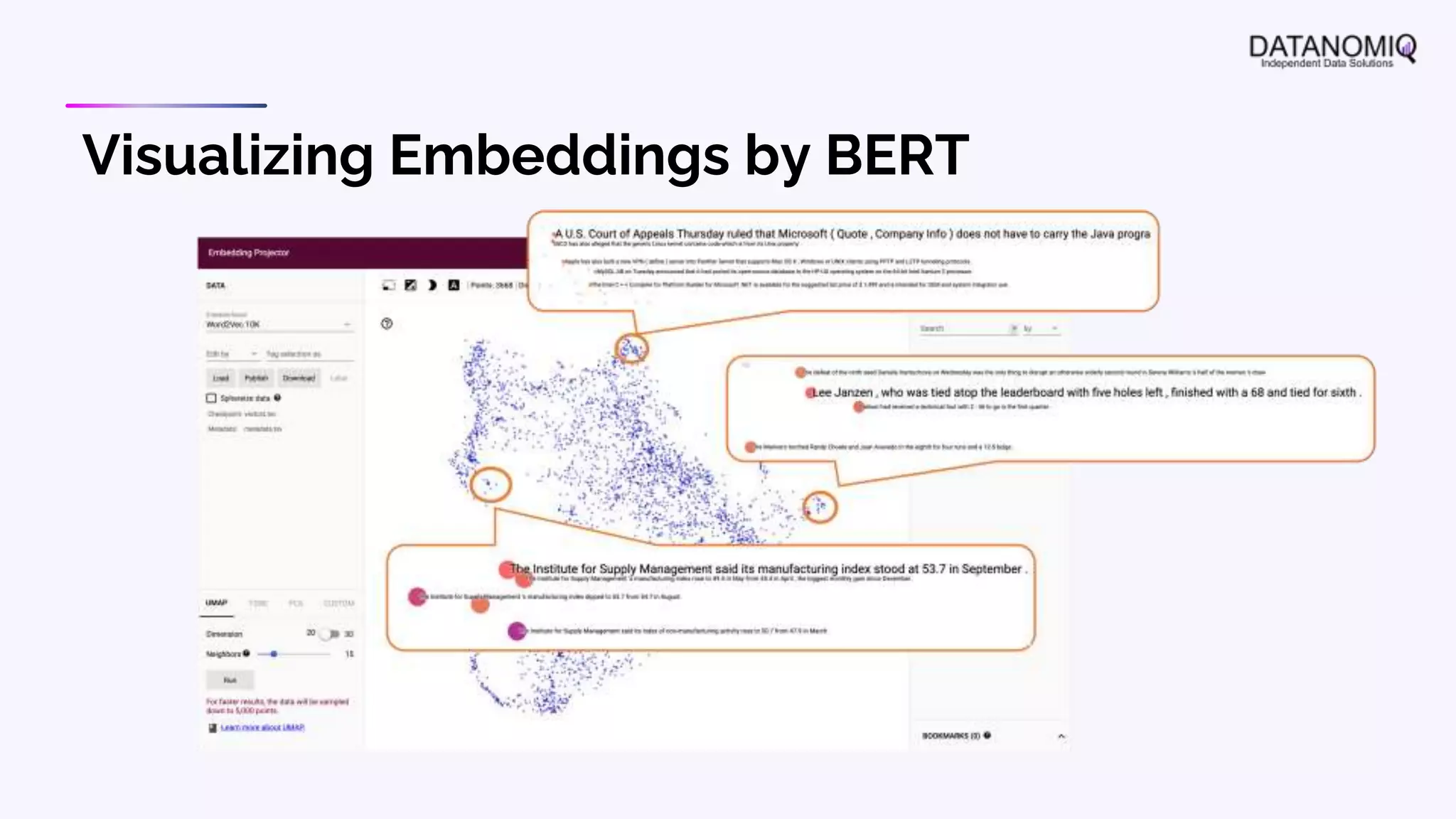
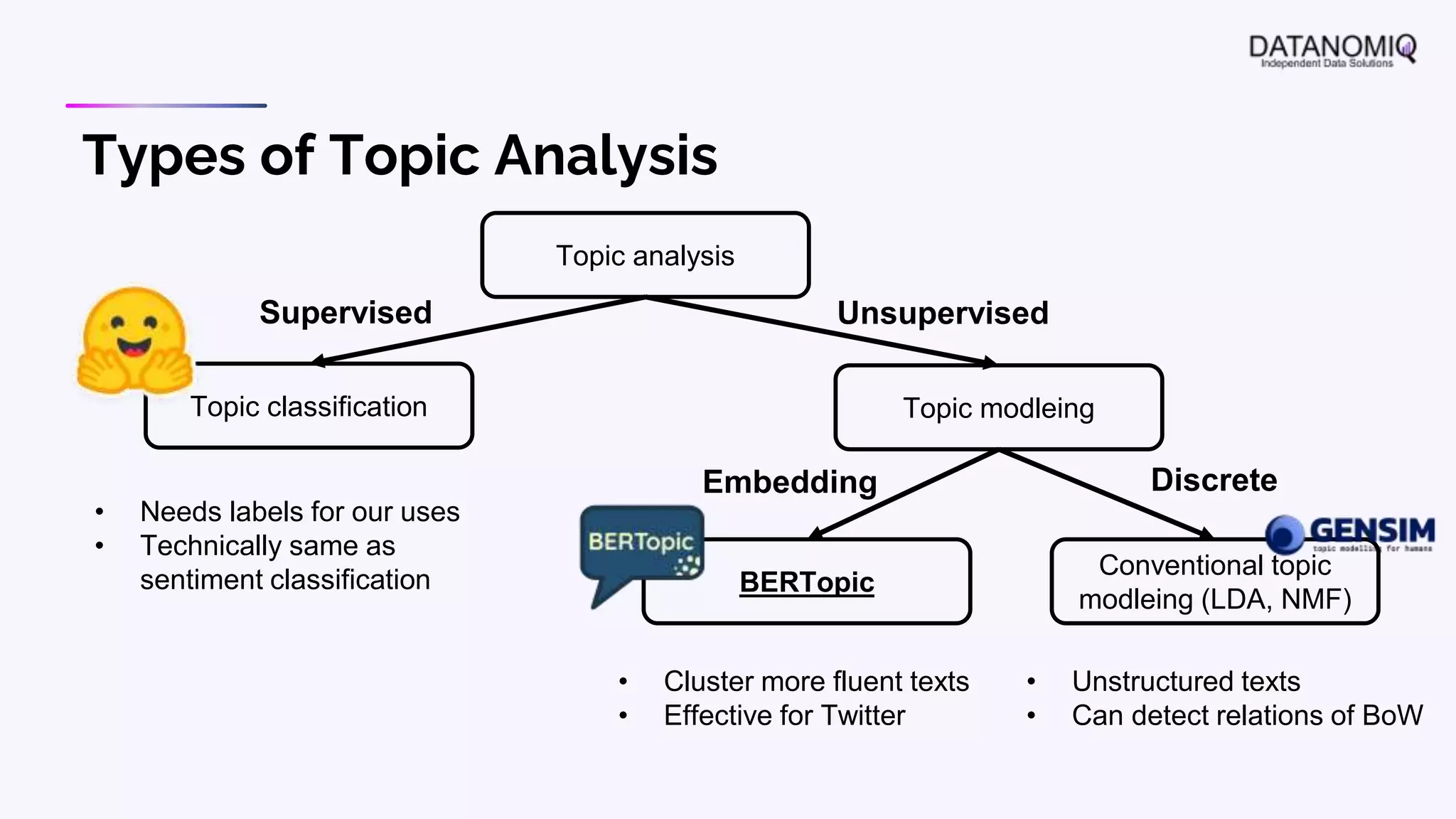
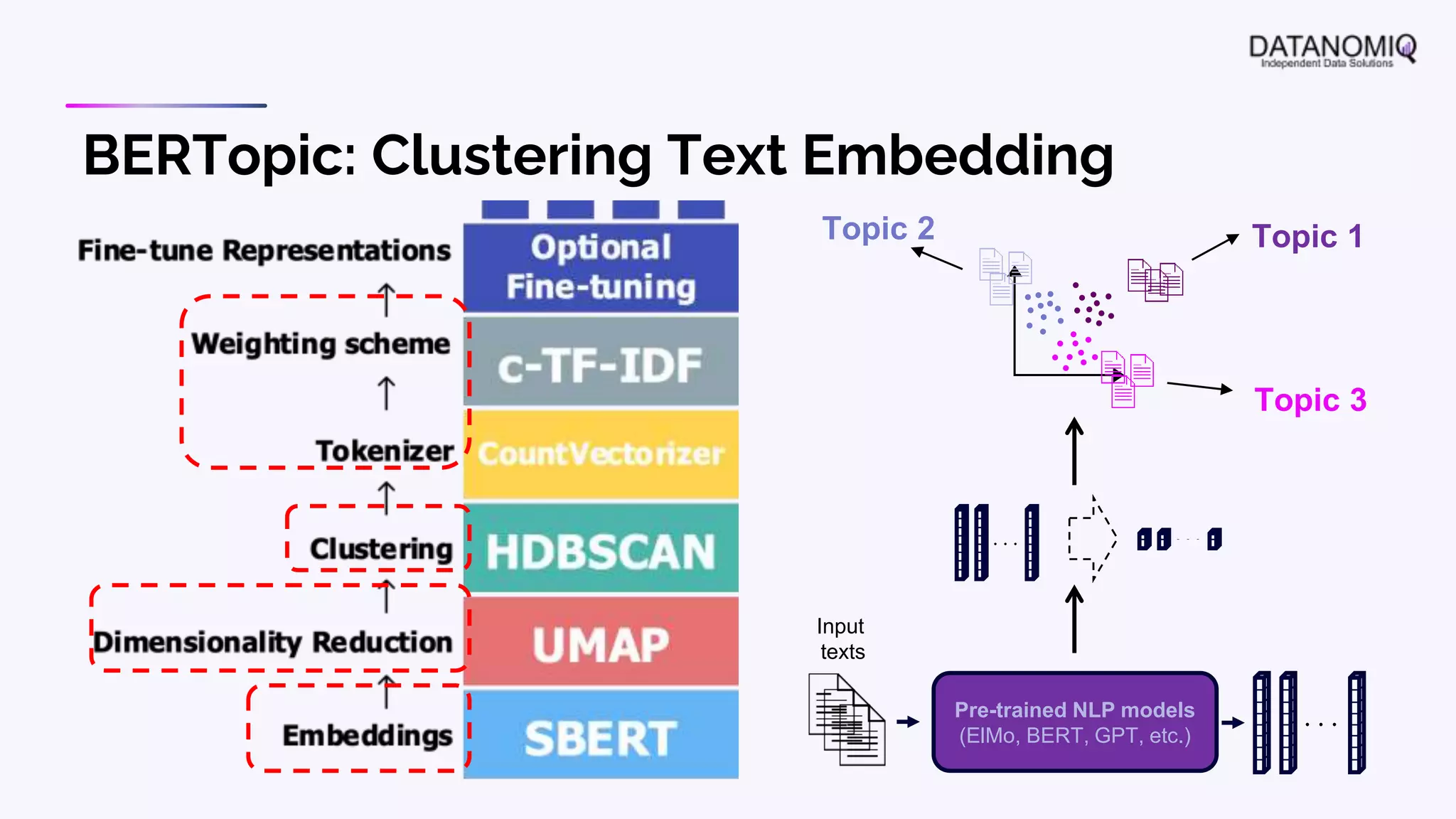
The document discusses various aspects of natural language processing (NLP) using deep learning techniques, emphasizing supervised and unsupervised learning methods, including transfer learning and the use of pre-trained models. It covers concepts such as word embeddings, token embeddings, and methods for visualizing embeddings through dimensionality reduction. Additionally, it explores topic analysis and classification, outlining approaches like BERT and traditional topic modeling techniques.