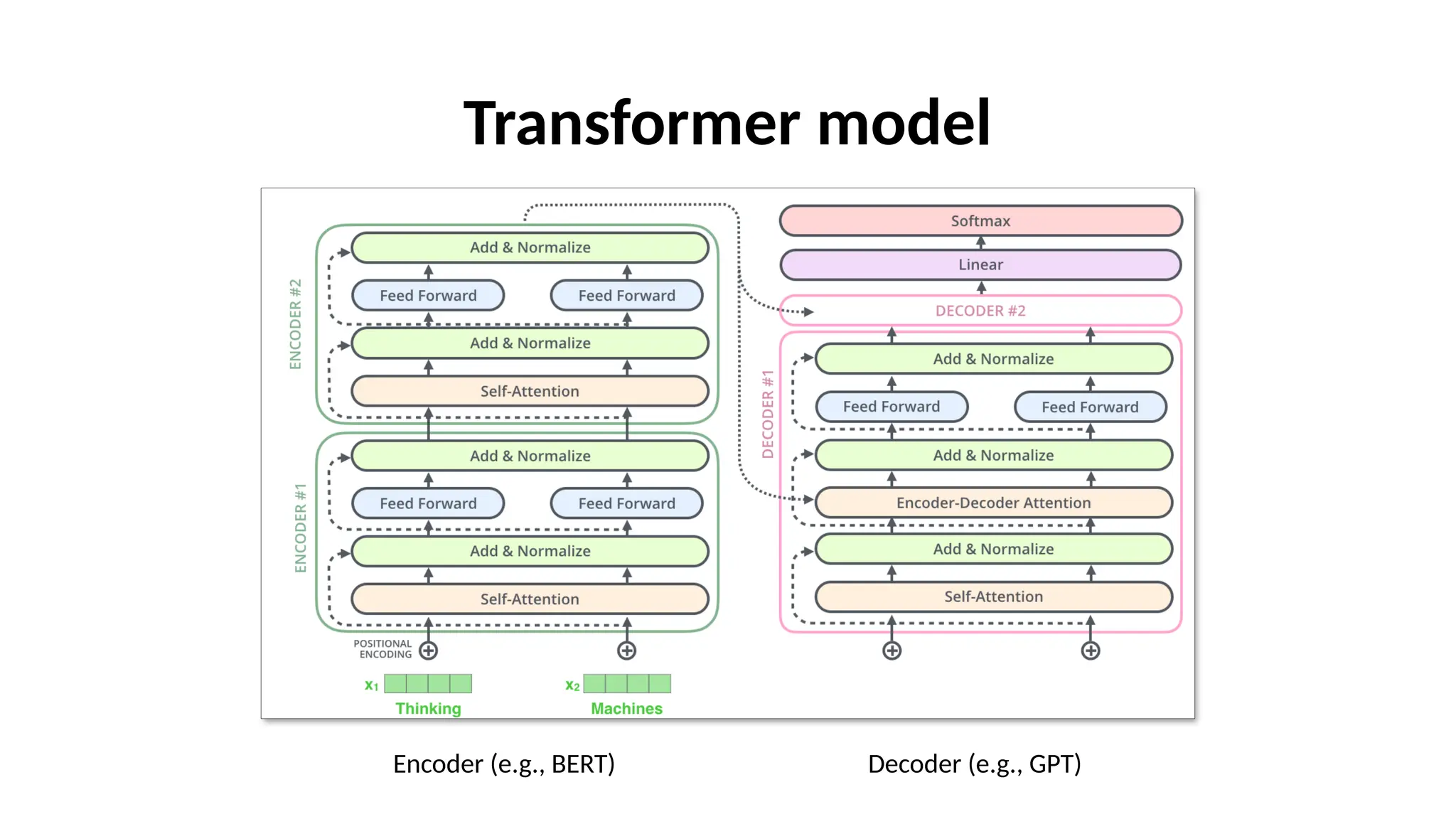
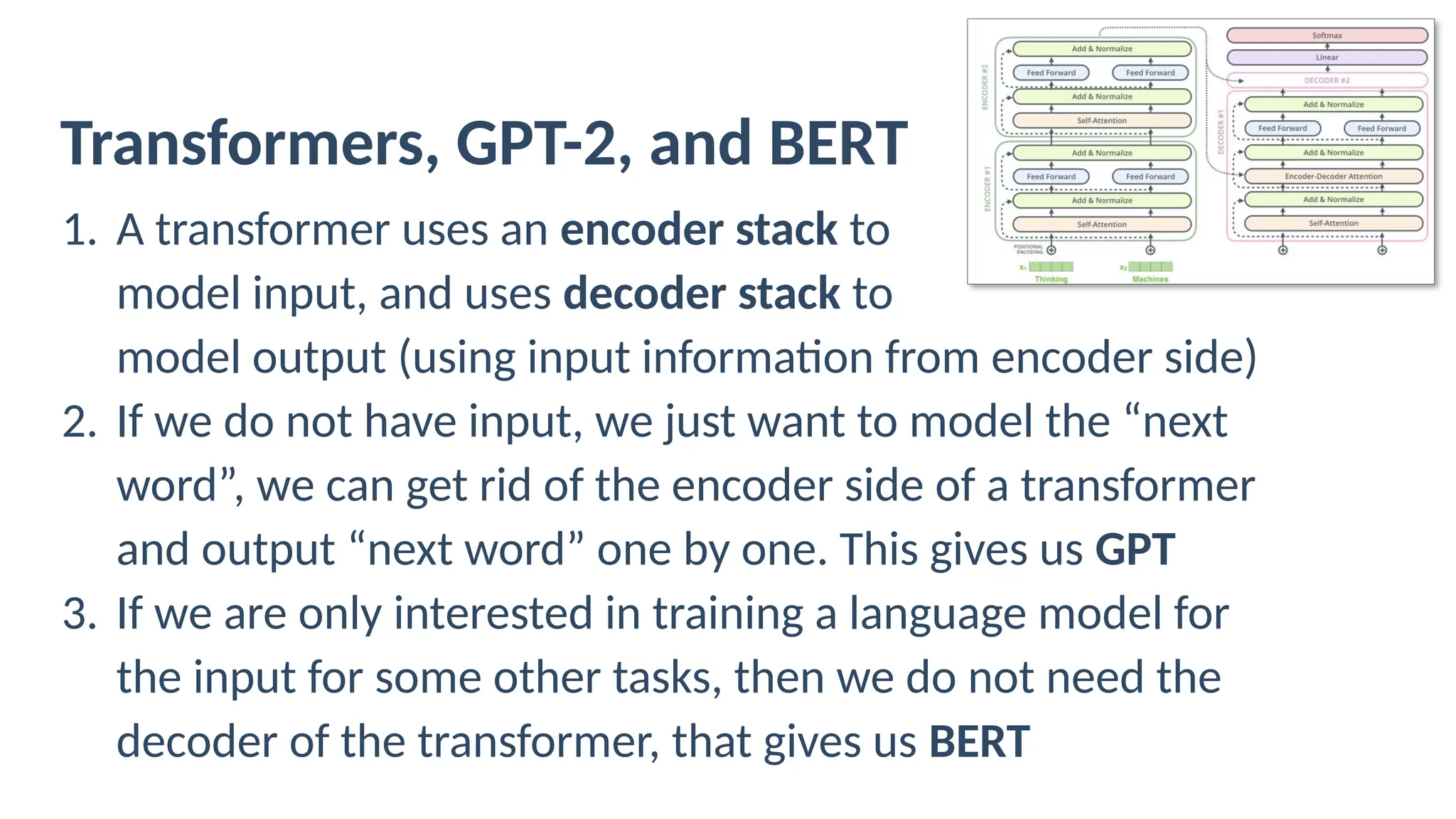
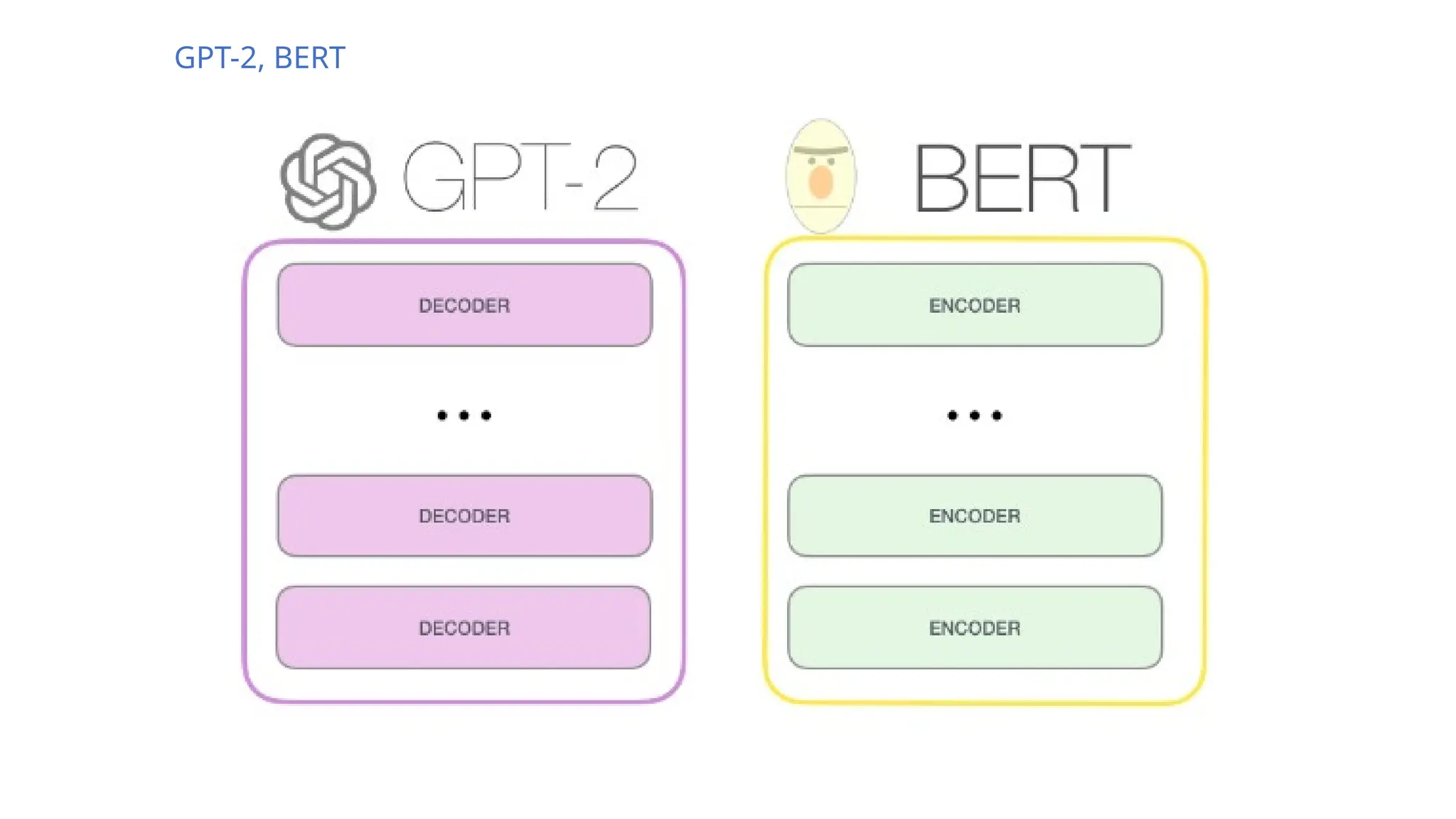
The document discusses the evolution of neural models for language processing, focusing on RNNs, LSTMs, and Transformers. It highlights how Transformers improve contextual understanding by utilizing both left and right word contexts and incorporating features like attention, using encoders (e.g., BERT) and decoders (e.g., GPT). Furthermore, it explains the training process involving unsupervised pretraining and supervised fine-tuning, along with examples of commonly used pretrained models such as BERT and GPT-3.