Embed presentation
Download to read offline








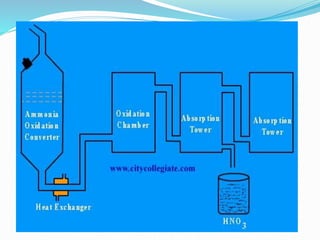







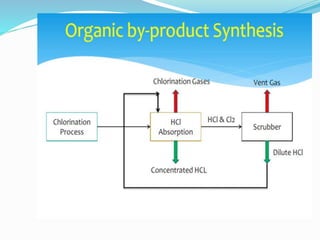

This document discusses nitric acid and hydrochloric acid (HCl). It describes the preparation and uses of nitric acid, including in fertilizers, plastics, dyes, and explosives. The disadvantages of nitric acid are that it is highly corrosive and can damage lungs if inhaled or the throat and stomach if swallowed. The document then introduces HCl as a clear, colorless, and corrosive acid found in gastric acid. Methods of producing HCl include burning elements, reactions of organic byproducts and metallic chlorides with sulfuric acid, waste incineration, and decomposition of hydrated heavy metals.

















