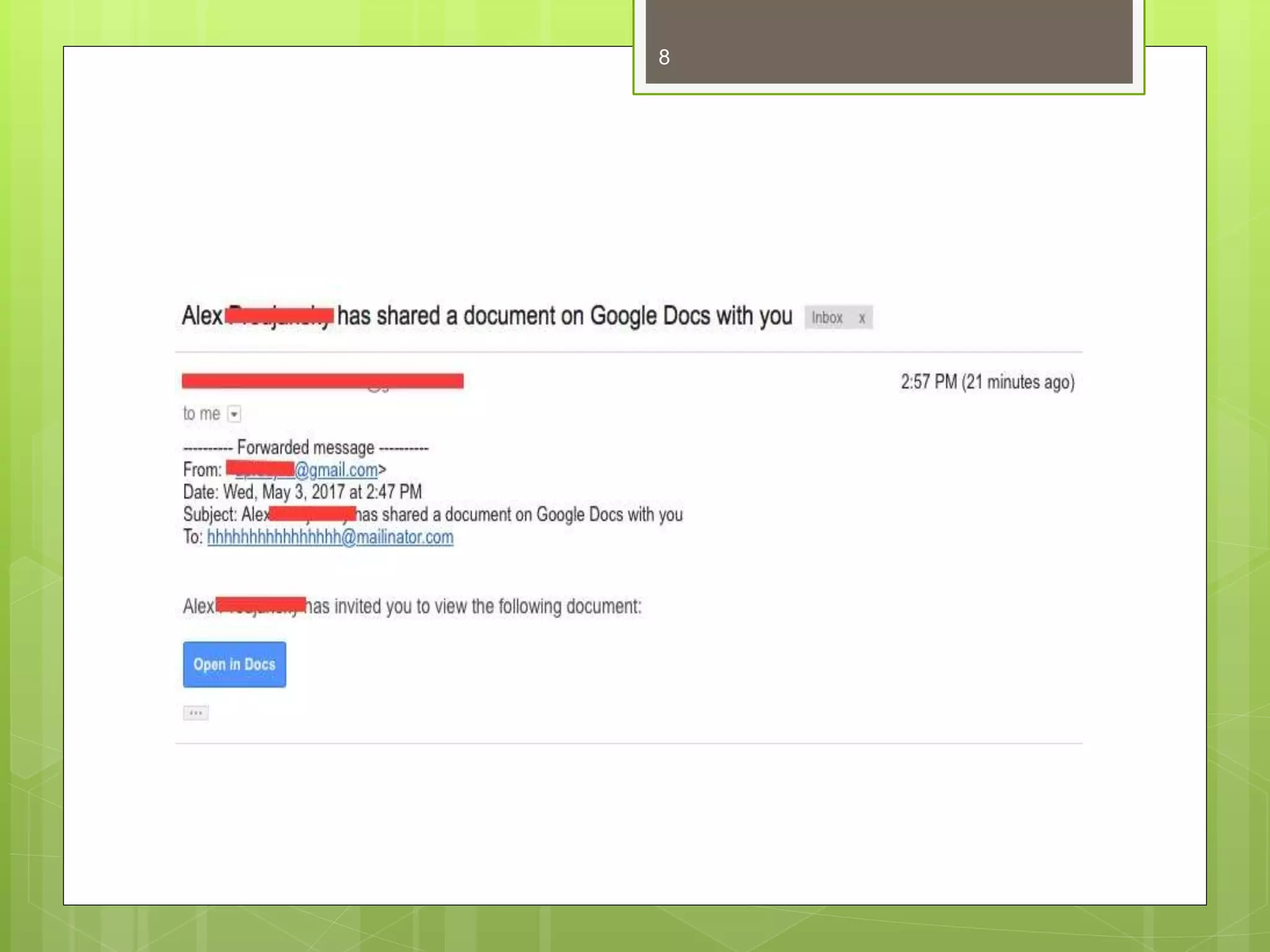
This document discusses computer security, privacy, and ecommerce. It defines computer security as protecting systems from damage or unauthorized access. Common cyber attacks like malware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks are described along with methods to prevent them like anti-malware software and extra bandwidth. The document also defines computer privacy as an individual's right to choose what information is shared, and discusses maintaining privacy through separate user accounts and encrypted files. Ecommerce is defined as the buying and selling of goods online, and the main types including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, and consumer-to-consumer are outlined. The advantages and disadvantages of ecommerce are briefly discussed.