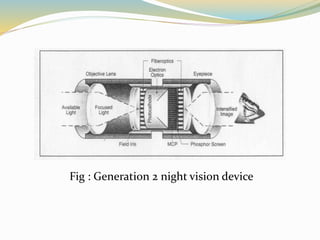
This document provides an overview of night vision technology. It begins with introducing the basics of how night vision works by detecting infrared light. It then describes the processes of thermal imaging and image enhancement that allow night vision devices to amplify weak light sources and display an image. The document outlines the generations of night vision devices and their improvements in amplification and lifespan. It discusses common night vision applications in military, wildlife observation, security, and more. Finally, it notes the advantages of long-distance vision in darkness and disadvantages like low image quality and high cost.