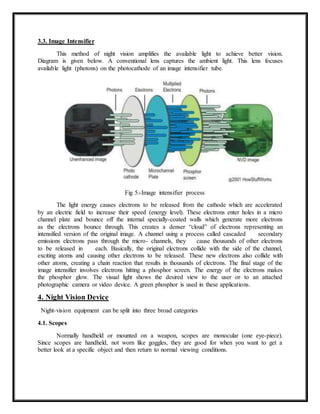
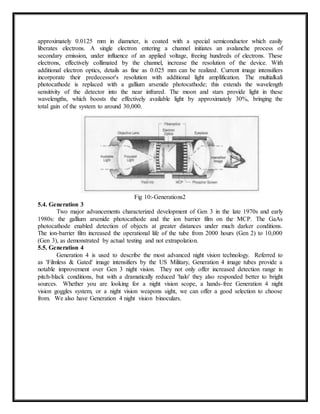
This document provides an overview of night vision technology. It discusses the two main types: 1) thermal imaging, which detects infrared light emitted as heat from objects, and 2) image intensification, which amplifies available light. Several generations of night vision devices are described, from early Generation 0 systems requiring infrared illumination, to modern Generations 2-3 that use microchannel plates and gallium arsenide to improve light sensitivity and gain. Common night vision applications include military, law enforcement, hunting and security. The document provides details on how different night vision components like image intensifier tubes work to capture light and amplify images for low-light viewing.