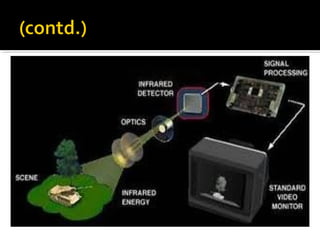
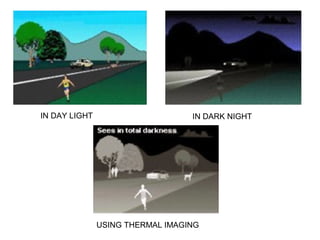
This document discusses the history and development of night vision technology from its origins in WWII to modern applications. It describes how early night vision devices used searchlights but had disadvantages, leading to advancements like image intensification tubes and thermal imaging. The document outlines the generations of night vision and how they provide improved amplification and resolution. It discusses uses of night vision in the military, law enforcement, automobiles and other areas, concluding that night vision has come a long way from its military origins to help people today.