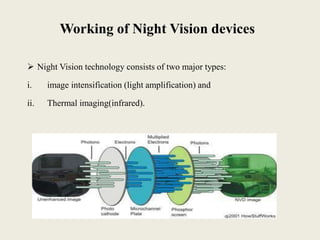
This document discusses night vision technology. It describes how night vision devices work by either amplifying available light through image intensification or detecting infrared radiation through thermal imaging. Night vision devices are classified into generations based on improvements in image resolution and light amplification. Generation 3 devices offer the best performance with gallium arsenide photocathodes and microchannel plates providing high resolution images. Night vision has military and civilian applications in low-light conditions for tasks such as navigation, surveillance and hunting.