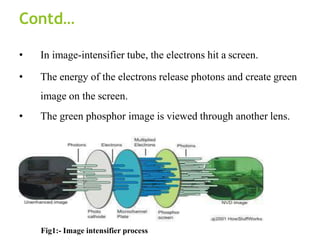
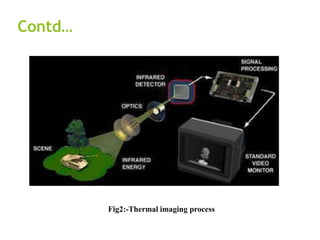
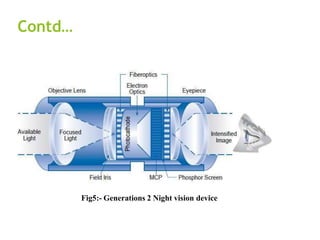
The document discusses the history and technology of night vision. It describes how night vision works using either image intensification or thermal imaging to detect low levels of light invisible to the human eye and amplify it into a visible image. Night vision devices are categorized into generations based on their amplification abilities and components. They have military, hunting, wildlife observation, security, and hidden object detection applications.