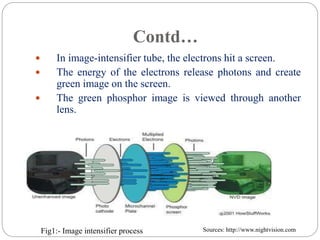
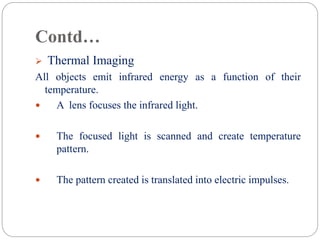
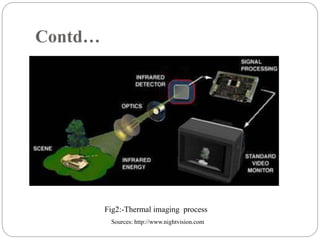
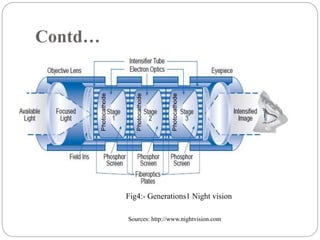
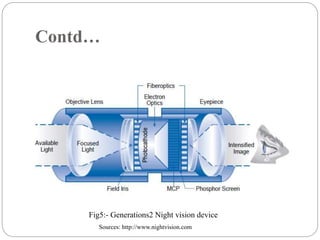
The document discusses night vision technology. It describes the two types of night vision as biological and technical. Technical night vision works using either image intensification or thermal imaging. It discusses the components and process of image intensification tubes. It also outlines the different generations of night vision devices and their capabilities. Applications of night vision technology include military, hunting, wildlife observation, and security. The document concludes that night vision has advanced significantly since the 1940s and has both defensive and scientific applications.