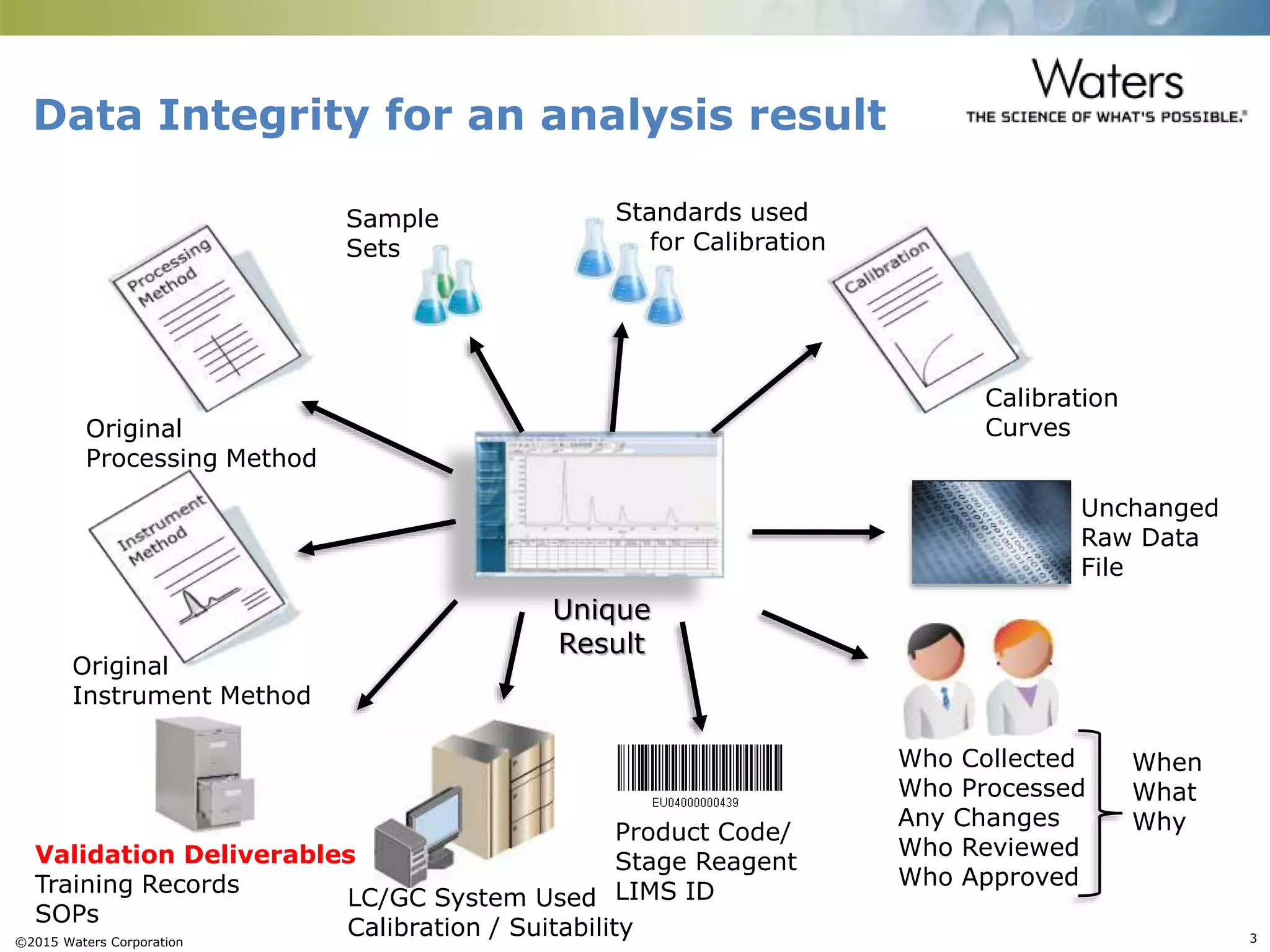
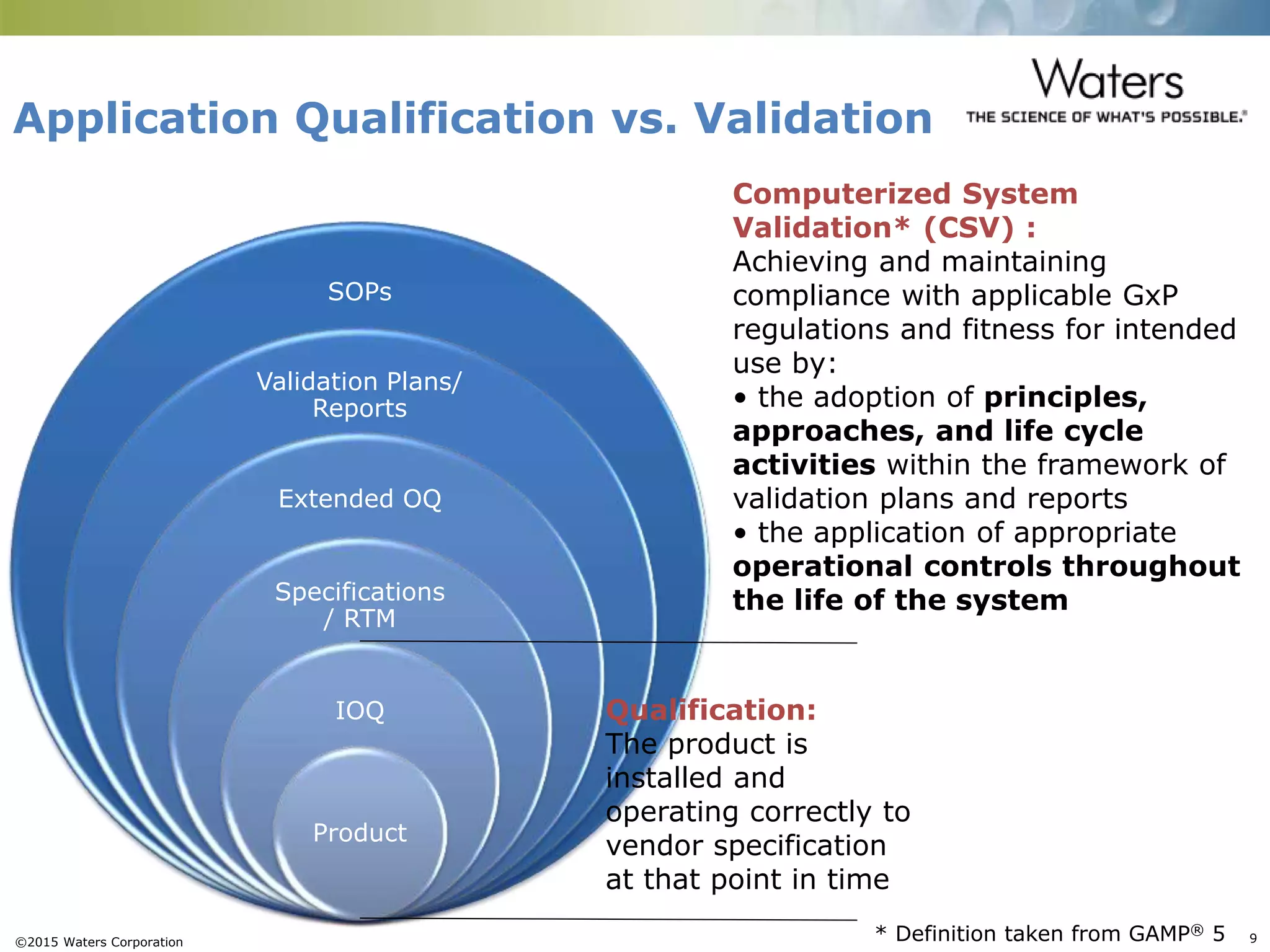
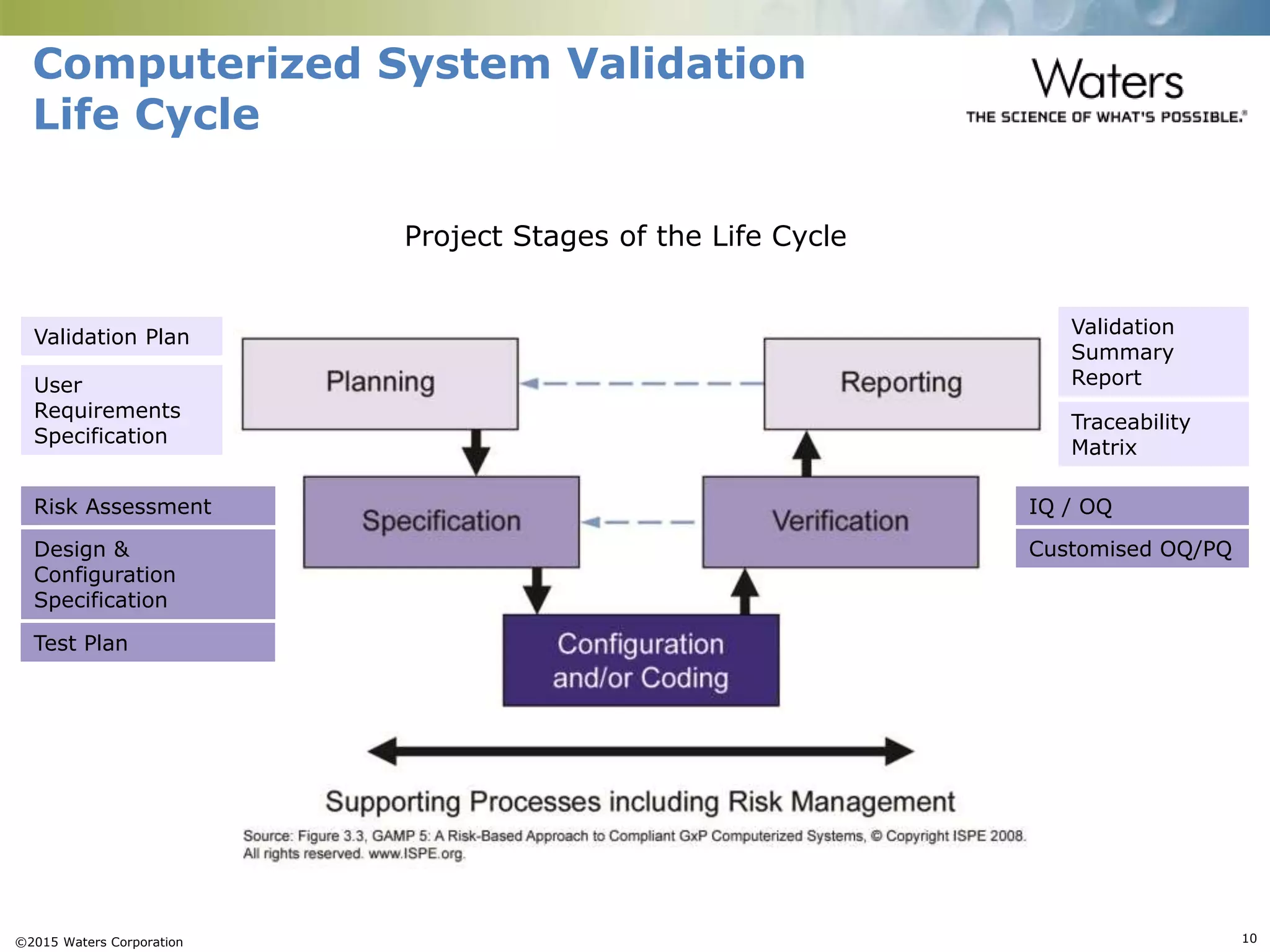
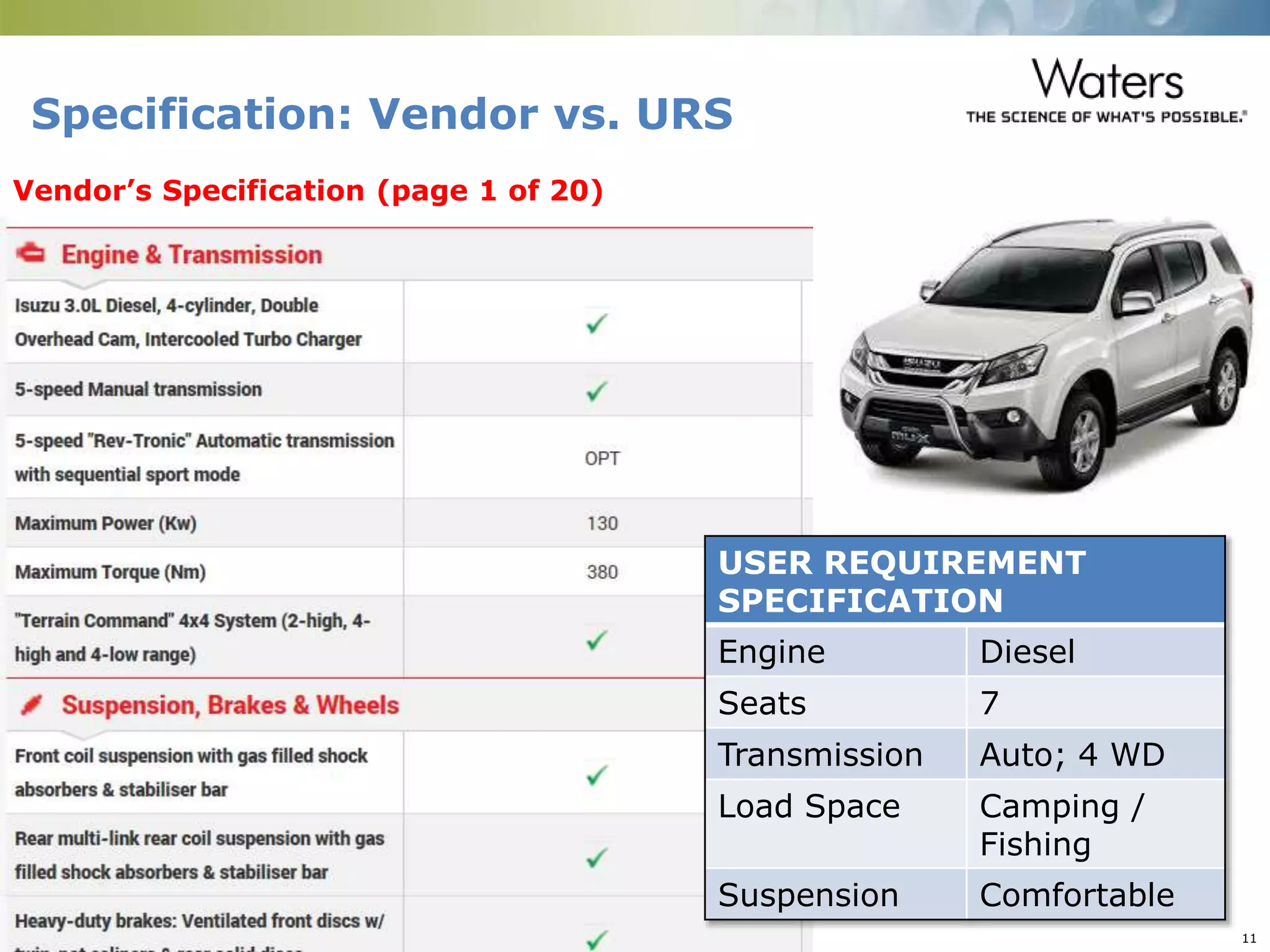
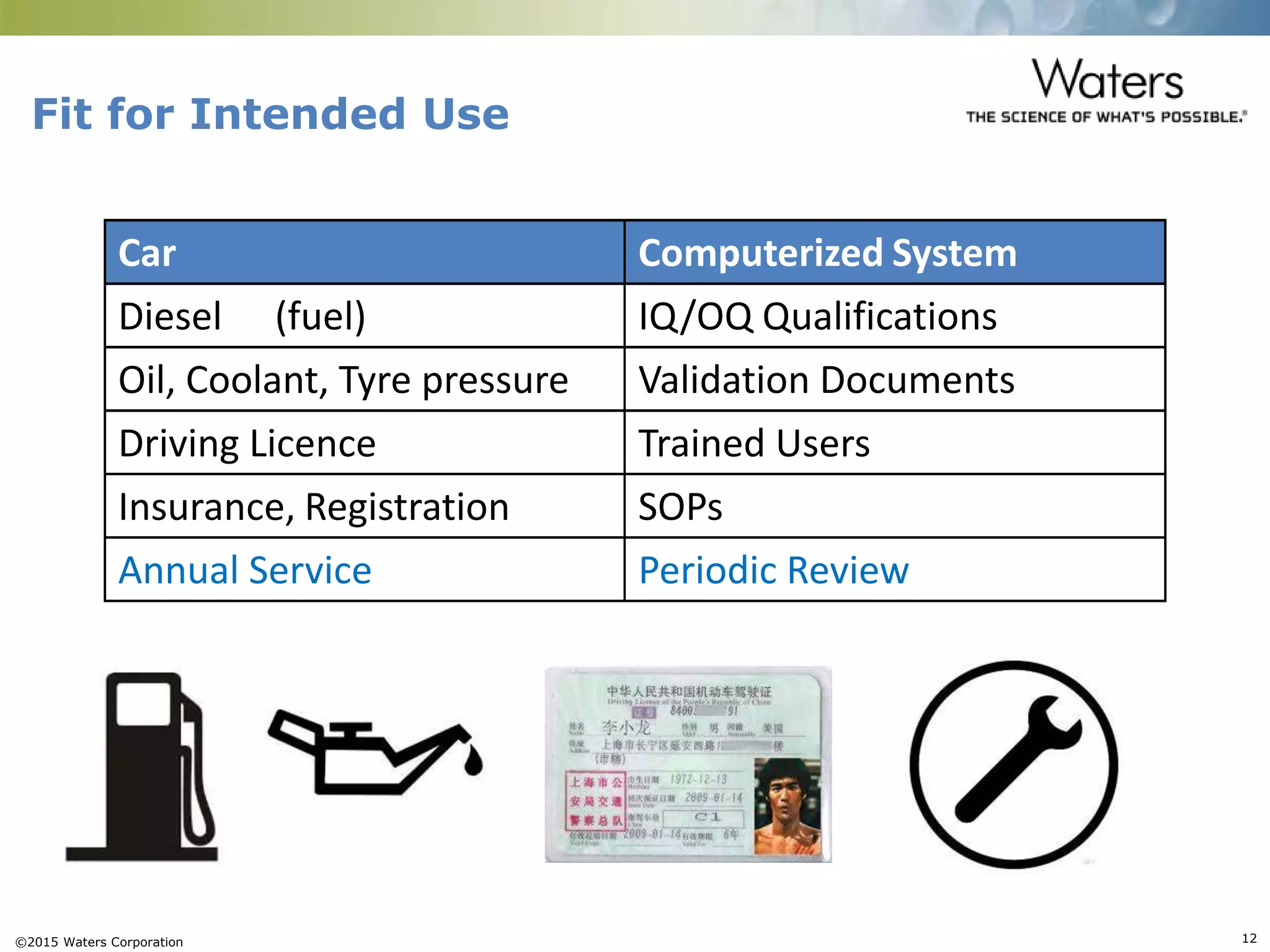
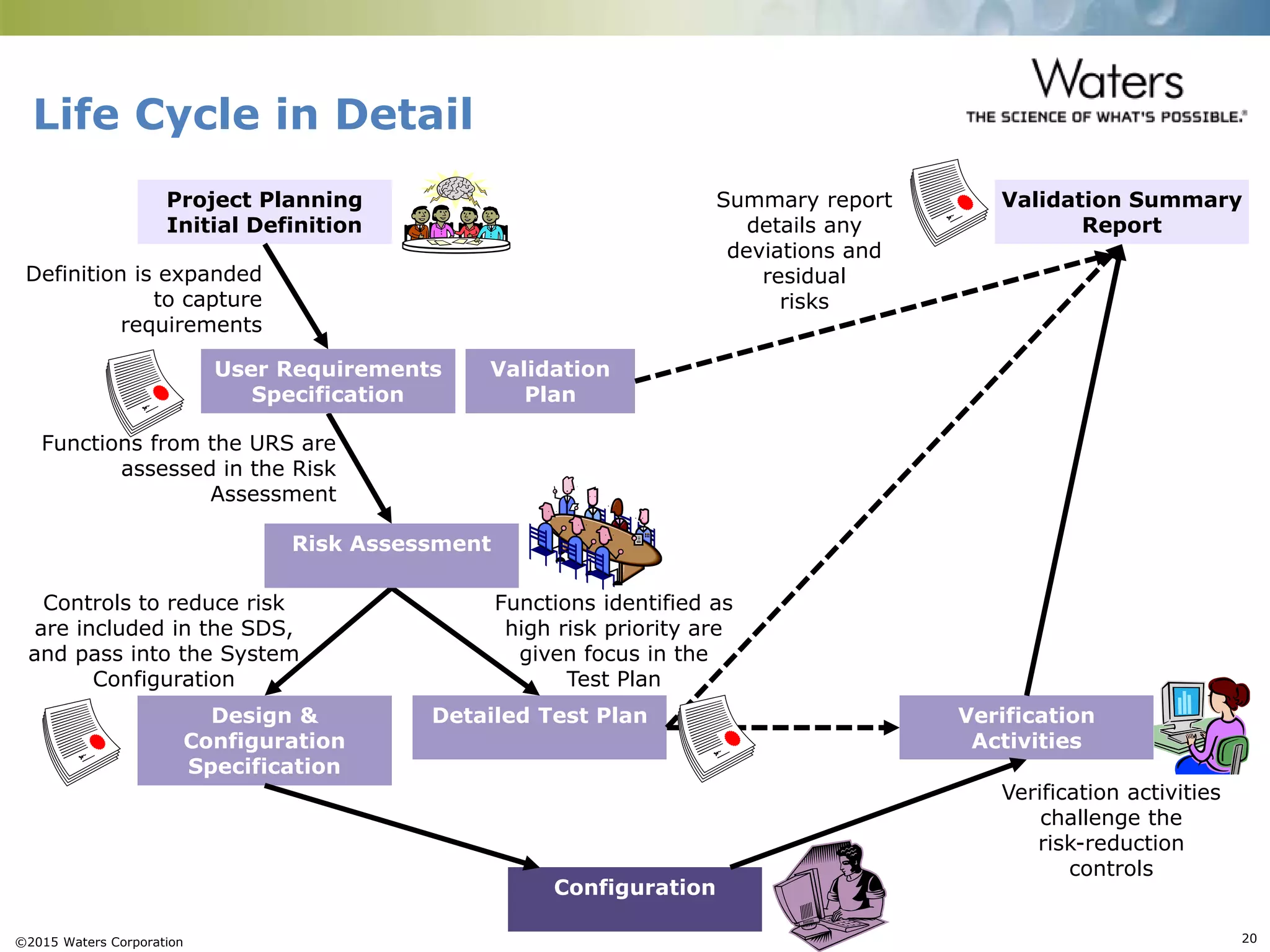
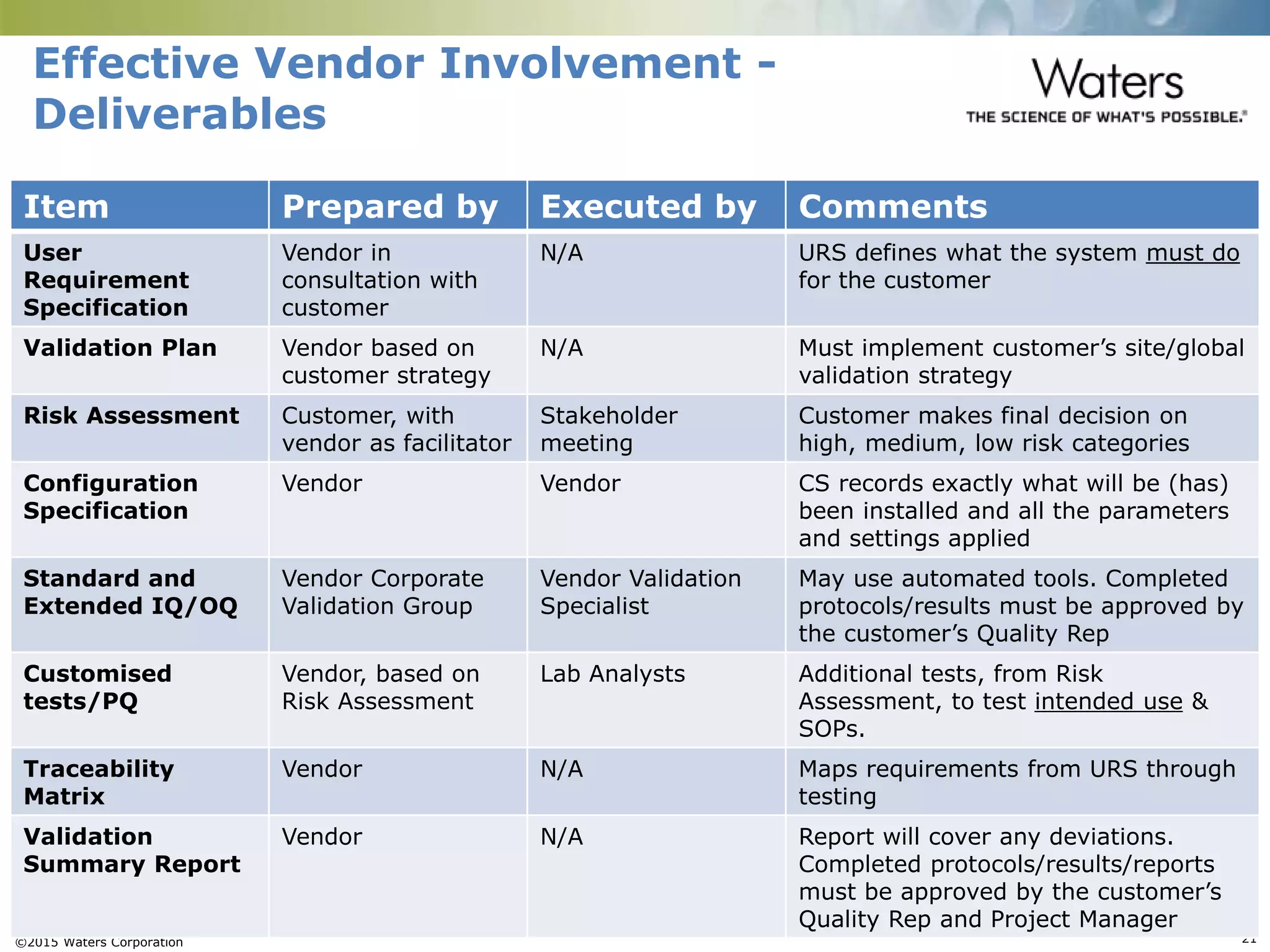
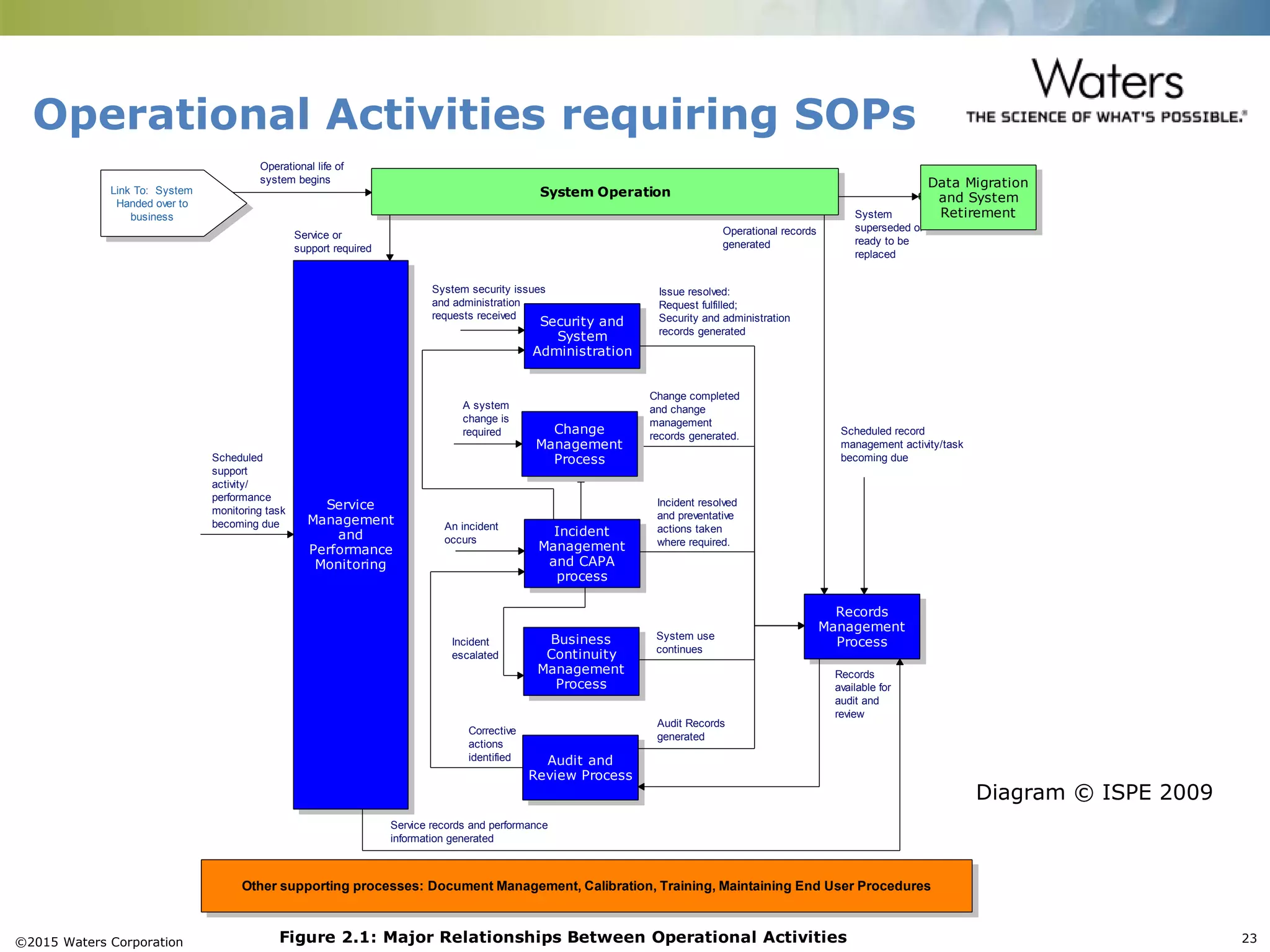
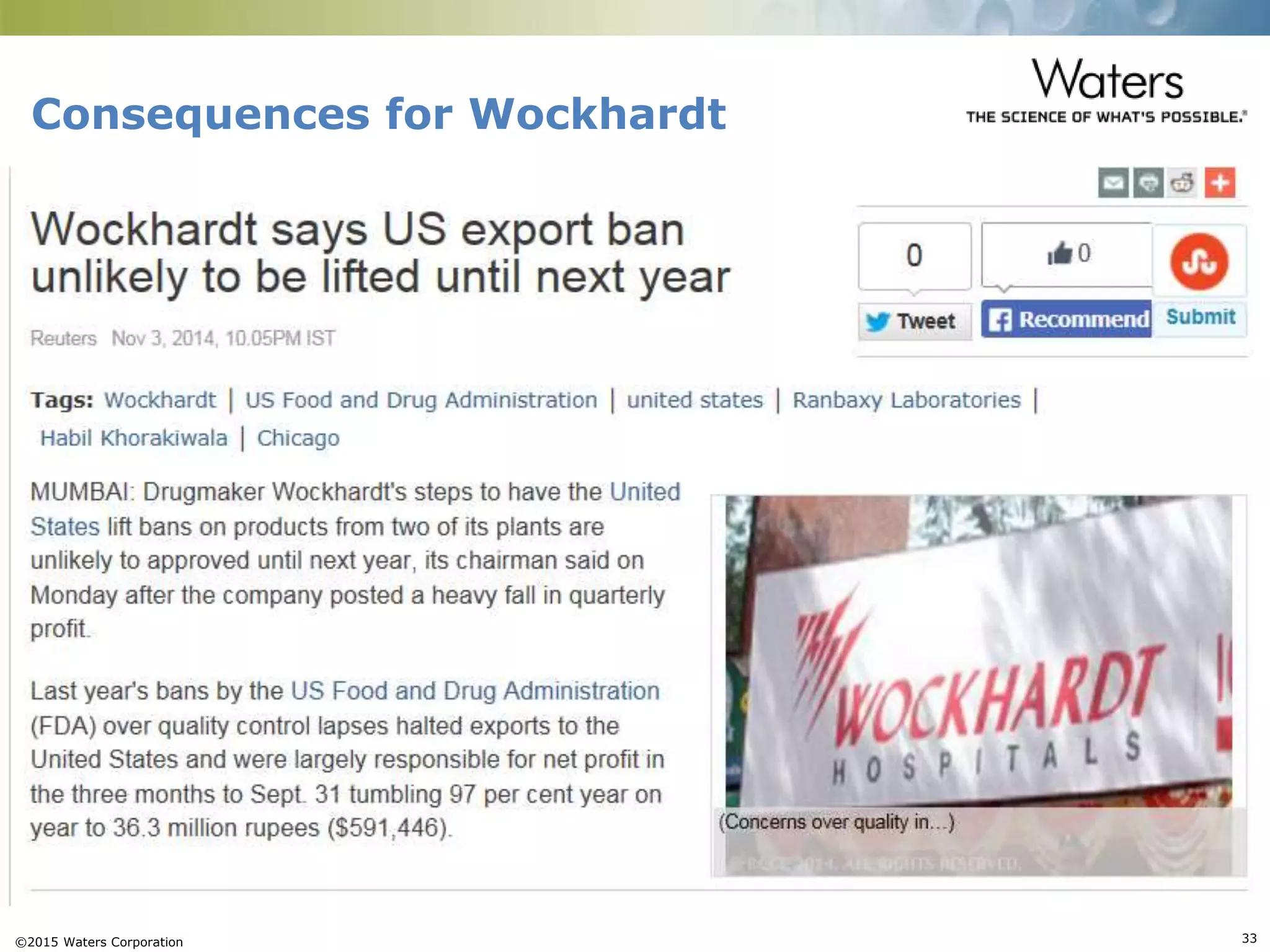
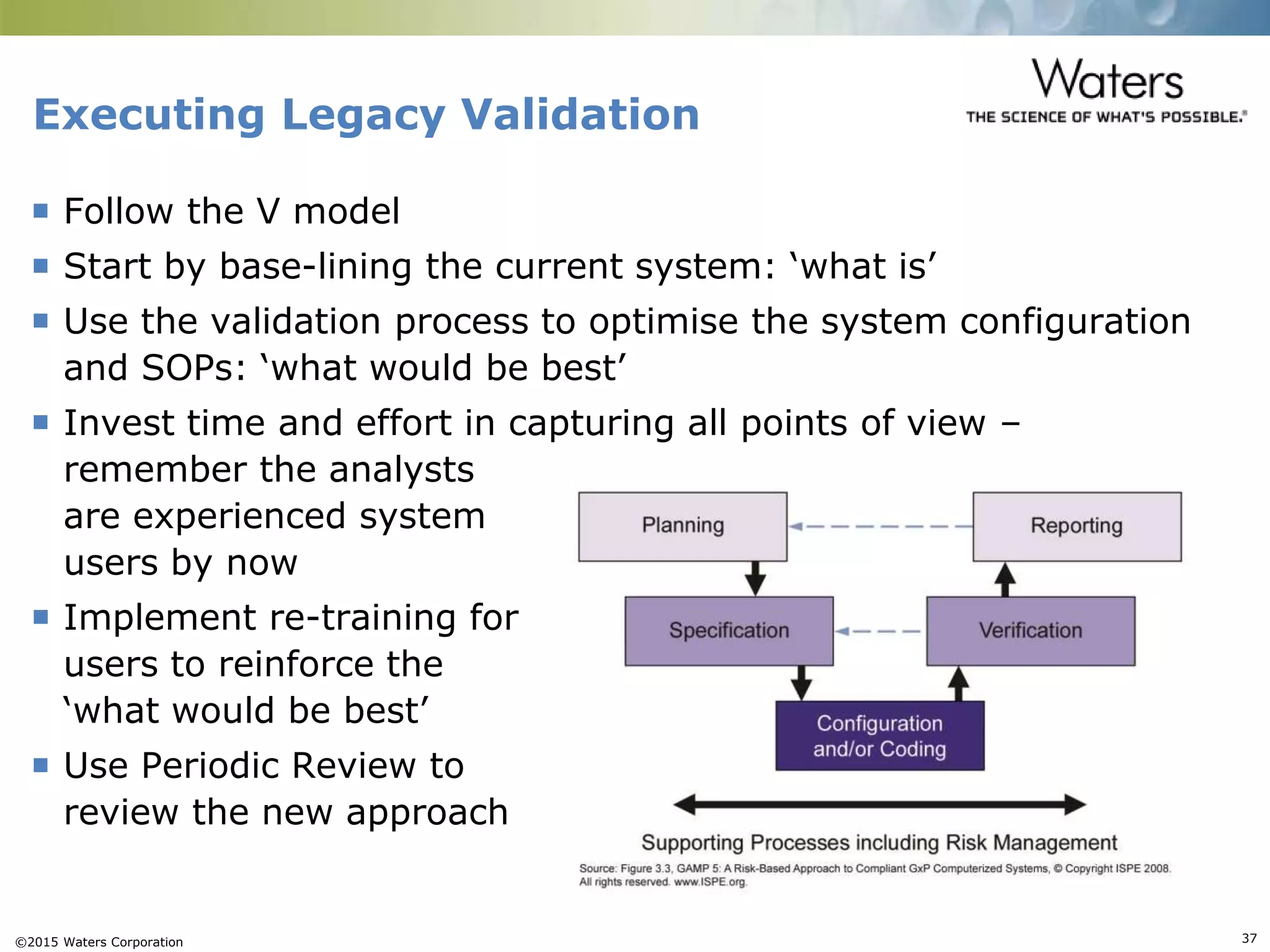
This document provides an introduction to computerized system validation. It discusses the importance of validating computerized systems used in quality and testing laboratories to ensure accurate and reliable results. The document outlines some of the key regulatory requirements for computerized system validation from international regulations like EU GMP and US CFR Part 11. It also discusses the difference between qualification and validation activities and explains the various stages of the computerized system validation life cycle from creating specifications and risk assessments to testing, documenting results and ensuring ongoing compliance.