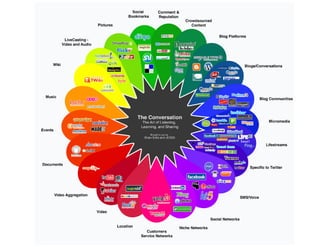
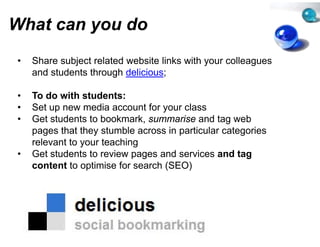
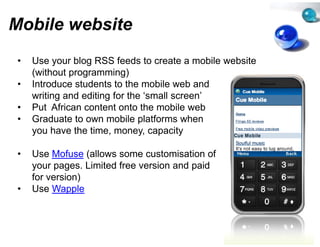
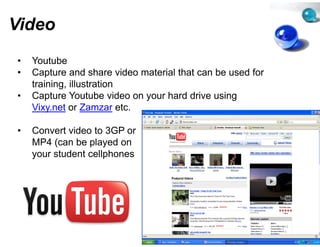
This document provides suggestions for overcoming challenges in teaching online journalism and mainstreaming new media in environments with limited resources. It proposes hardware solutions like refurbished computers and utilizing students' mobile phones. It recommends free or low-cost software alternatives and online tools that can be used for classes, research, publishing, and production. The document emphasizes that principles of journalism are more important than specific technologies and encourages sharing resources through open communities.



![Hardware solutions?
• Students purchase netbo computers (Linux or
ook
Windows OS) as a prerequisite for enrolment (most
books, documents and te eaching materials could be
provided electronically an cut down on printing
nd
costs [although copyright remains an issue])
t
• Get Microsoft , Nokia Ap
Nokia, pple
to subsidise costs based on bulk
sales
• Keep a lab of high end computers
for more advanced prod
p duction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmediatechnologiesforteachingandlearningdigitaljournalismcompatibilitymode-091011051600-phpapp01/85/New-Media-Technologies-For-Teaching-And-Learning-Digital-Journalism-4-320.jpg)