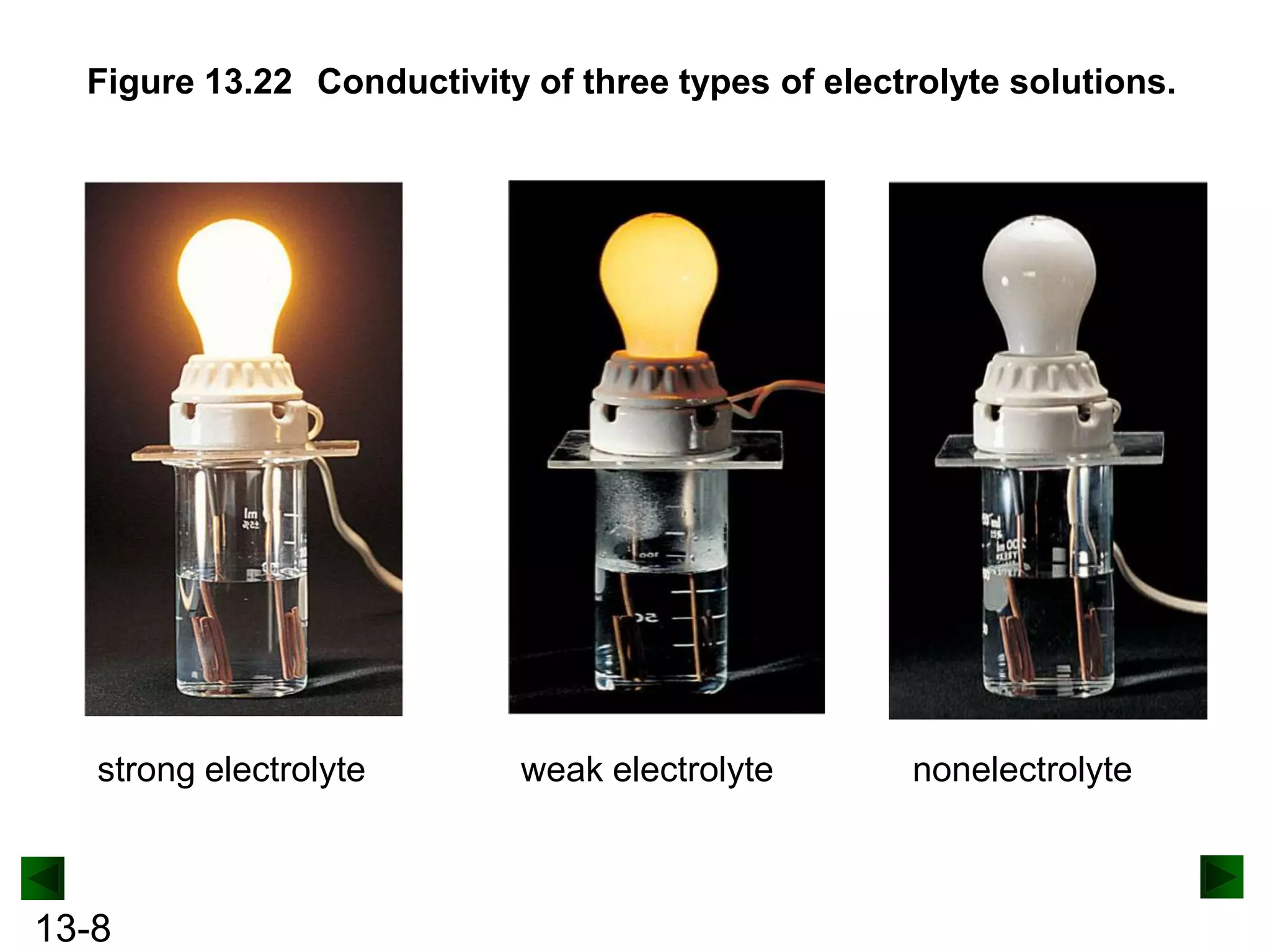
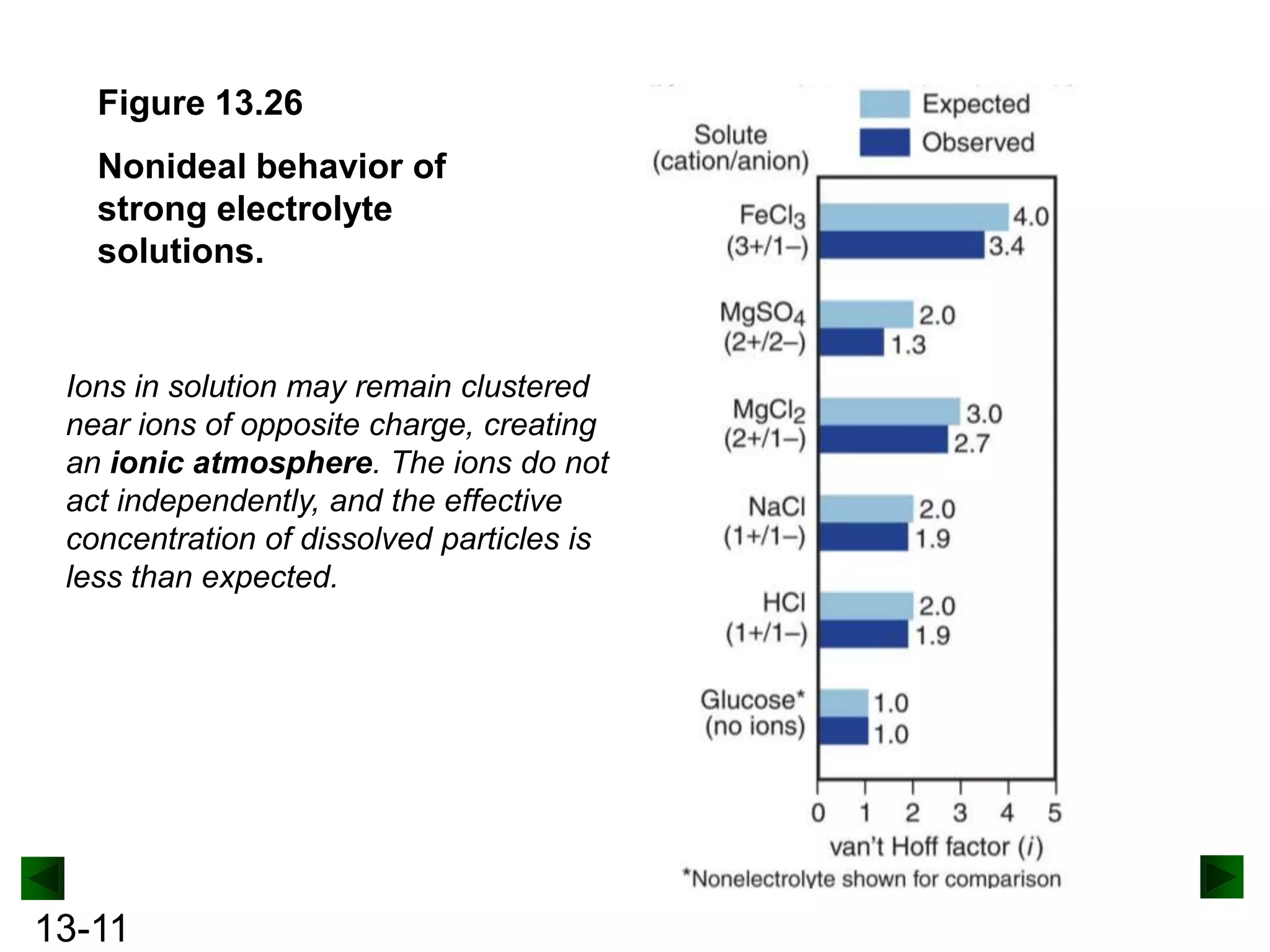
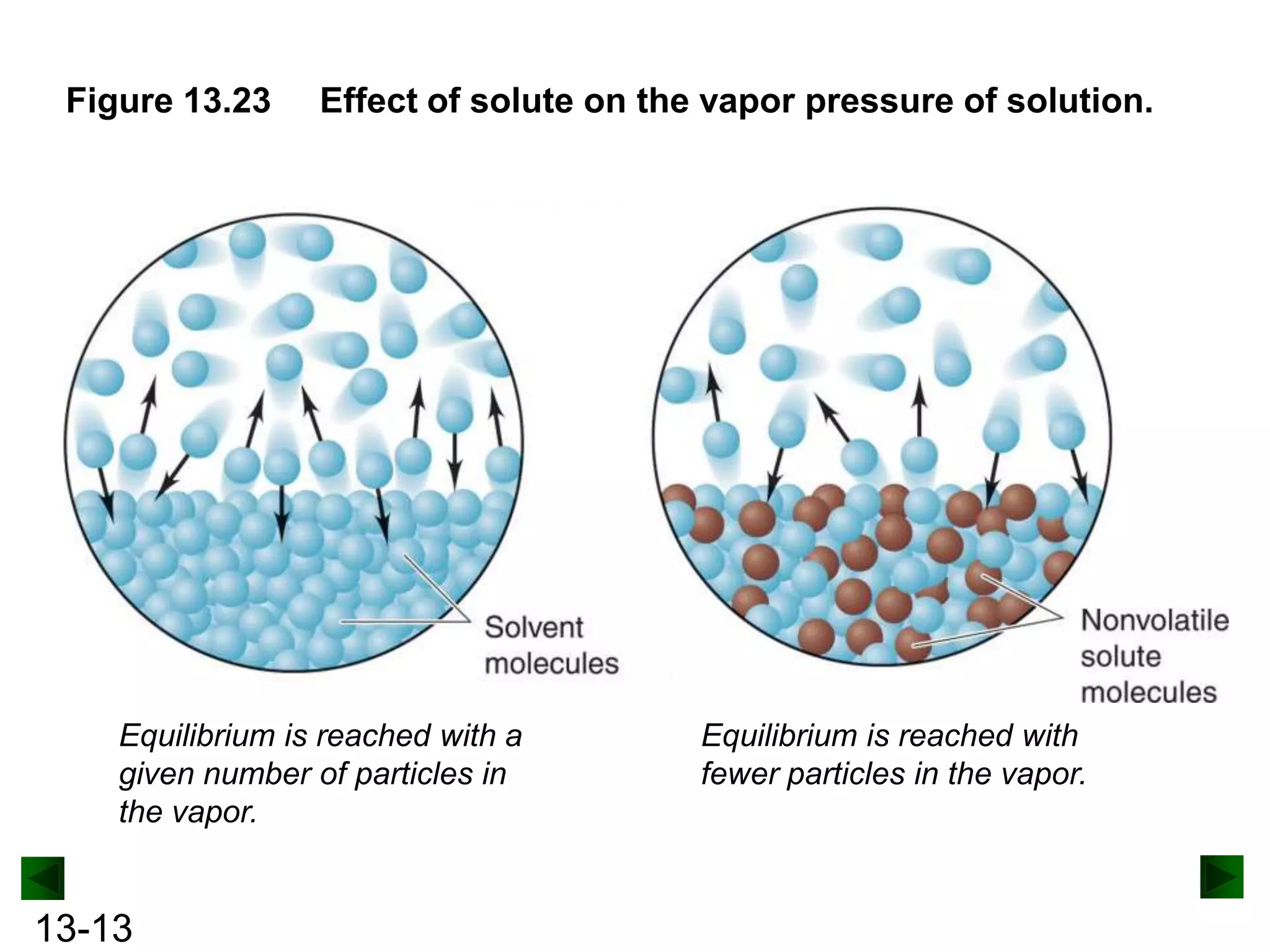
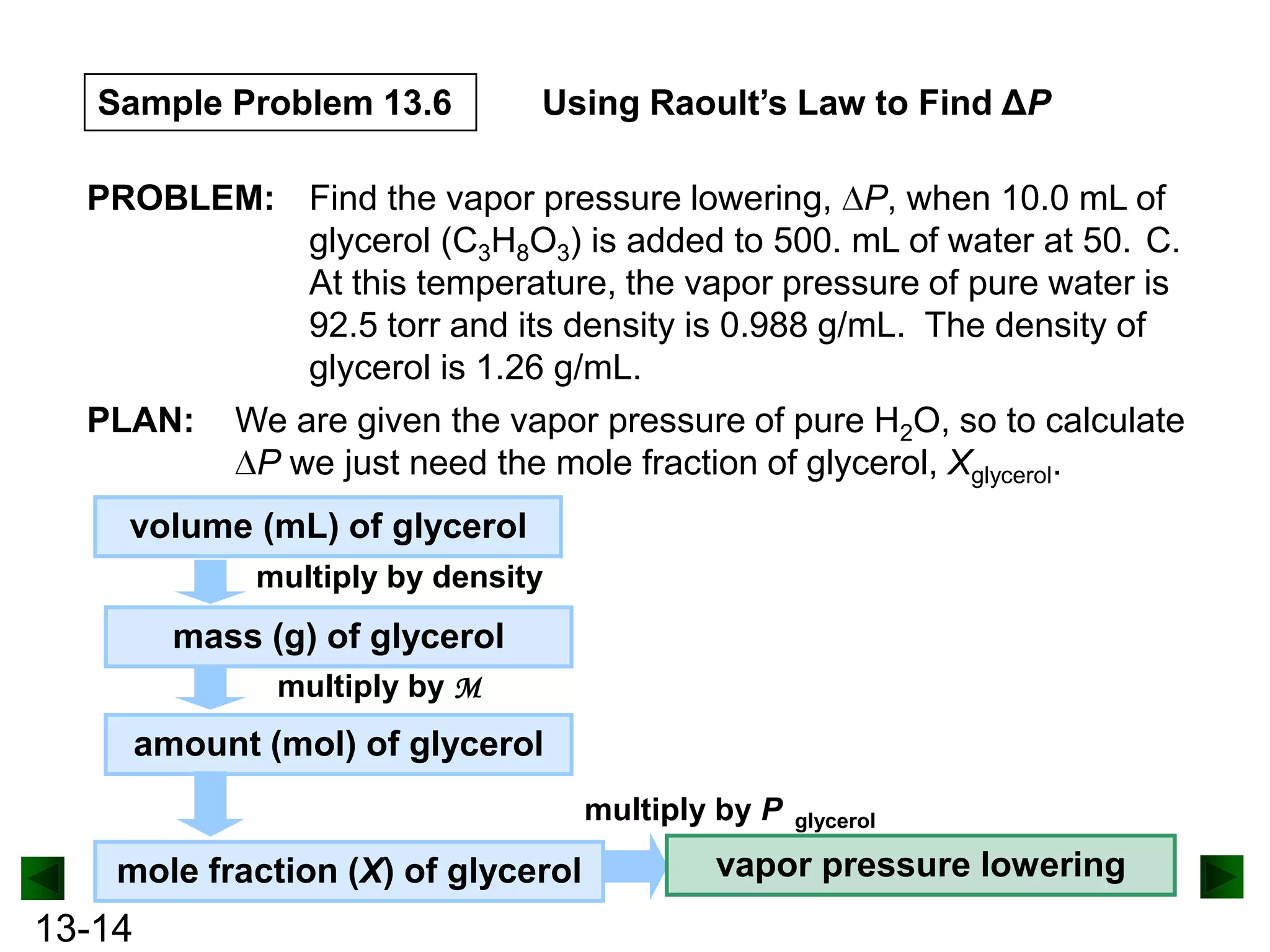
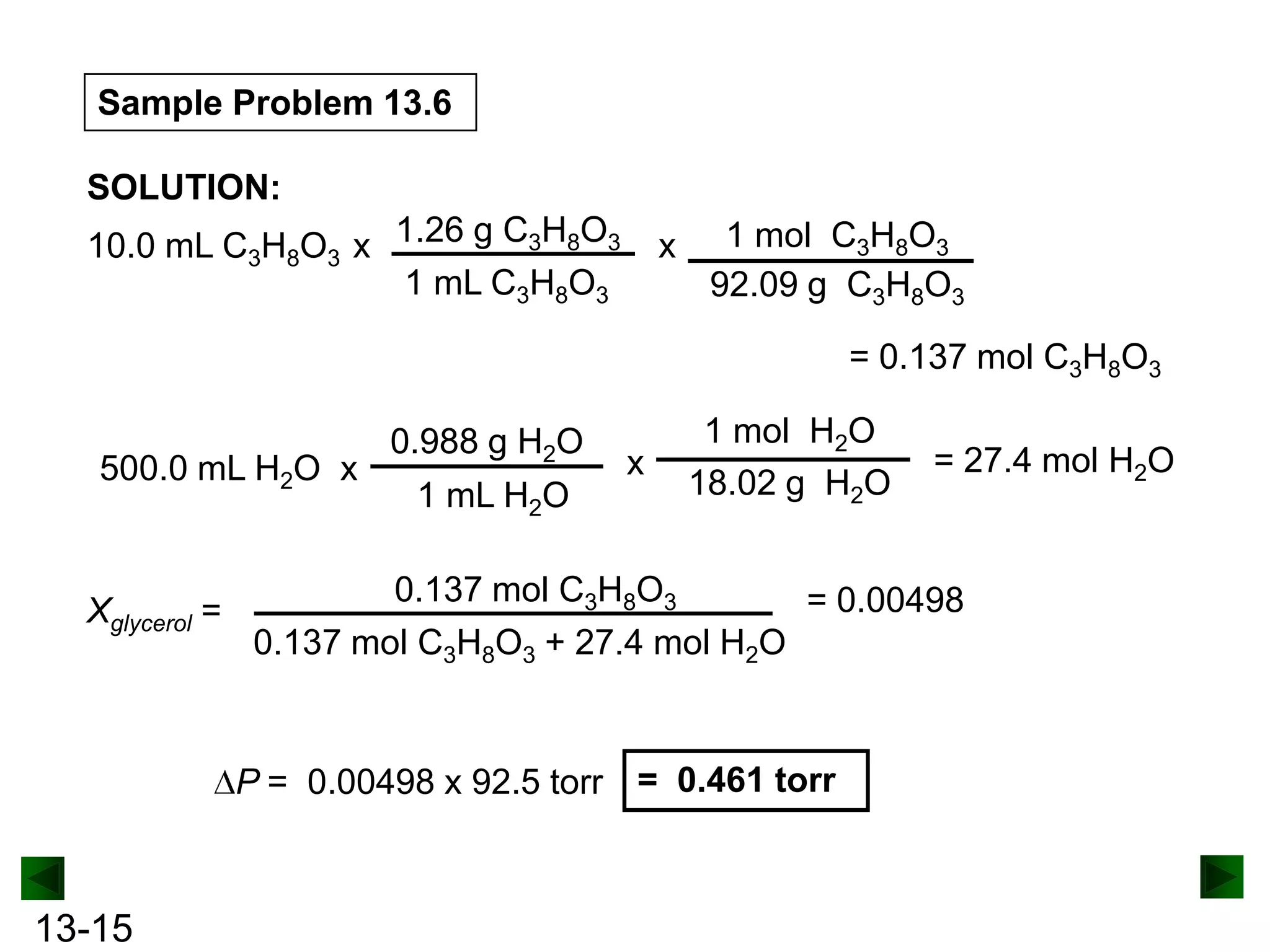
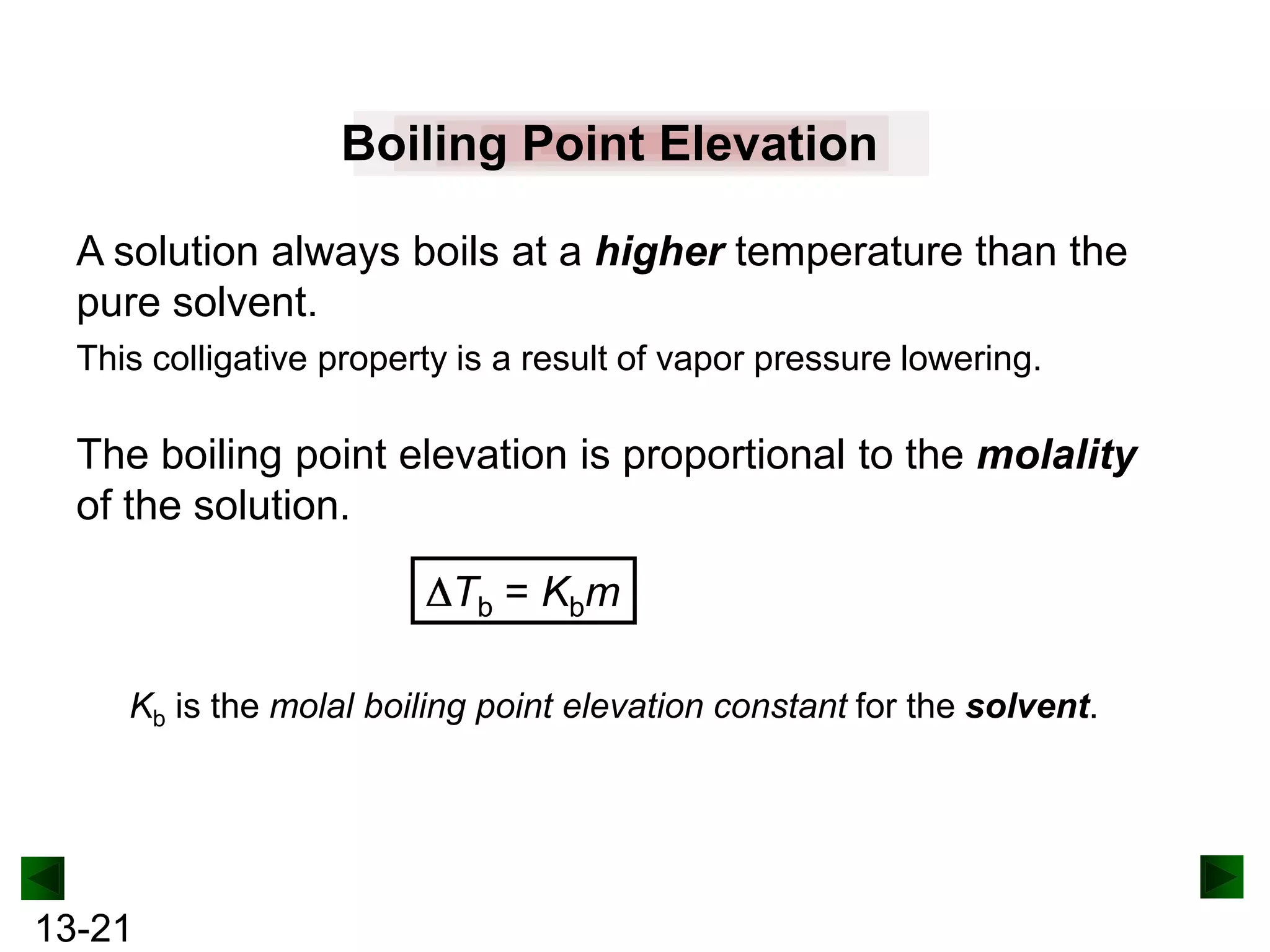
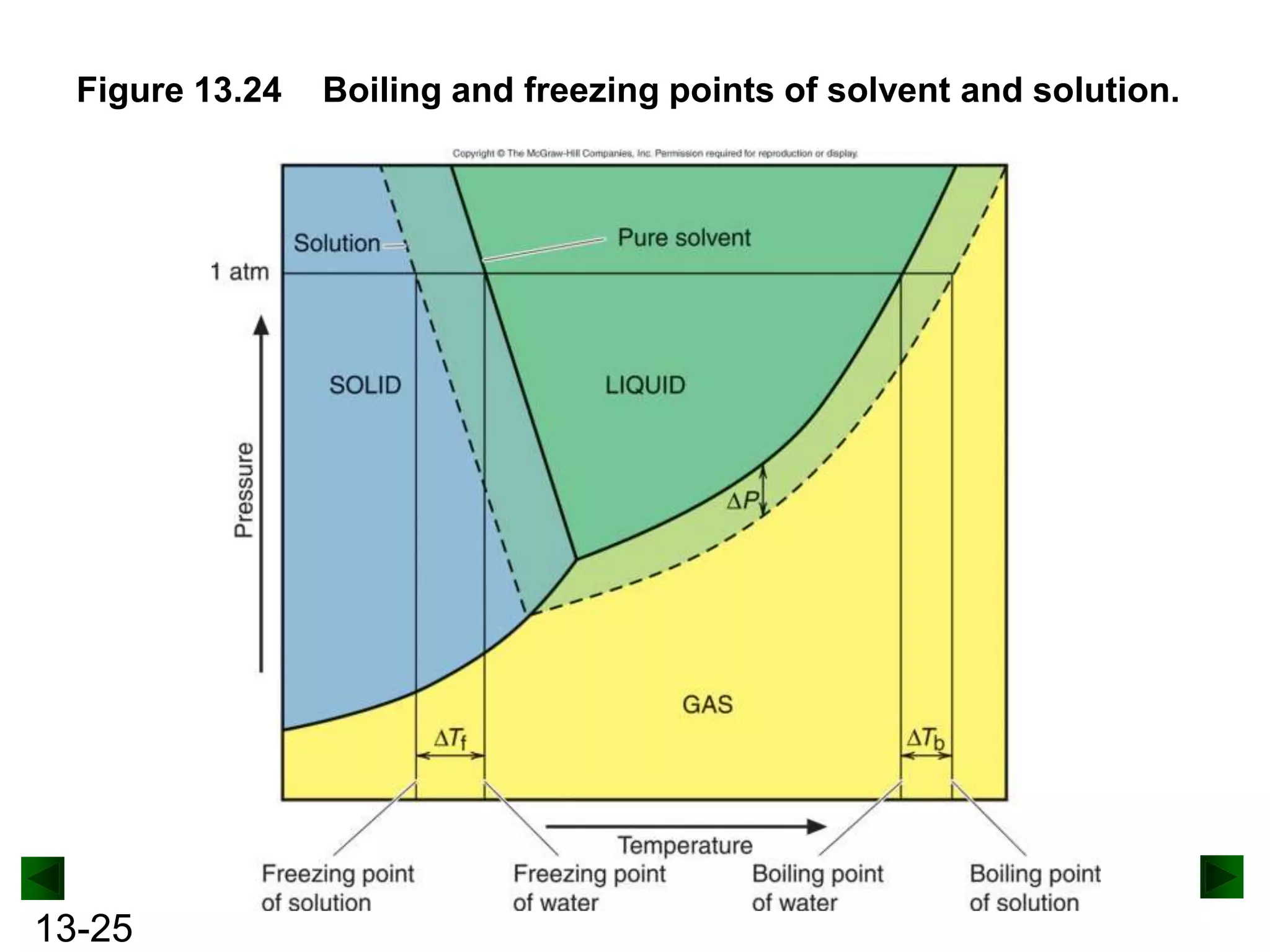
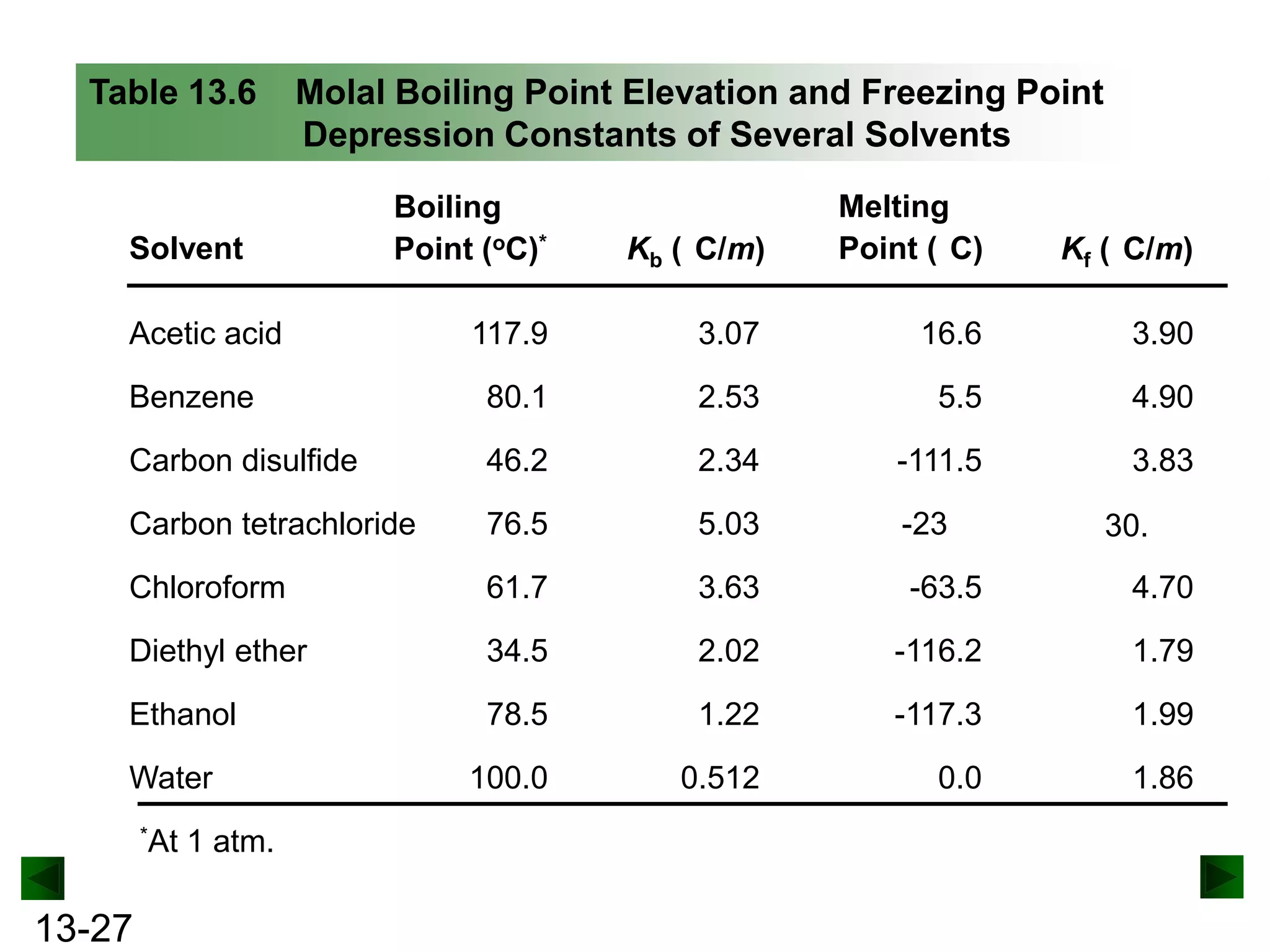
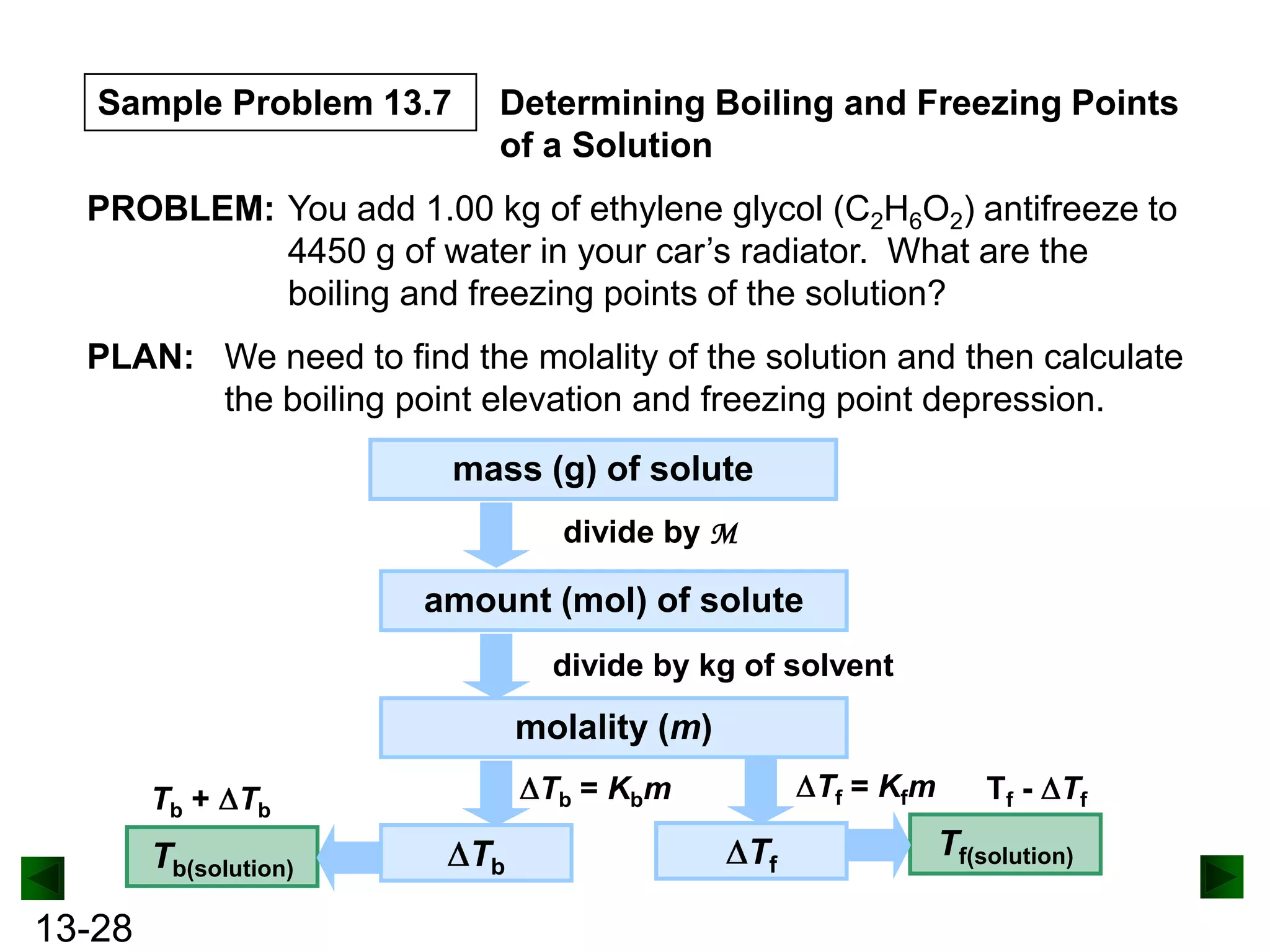
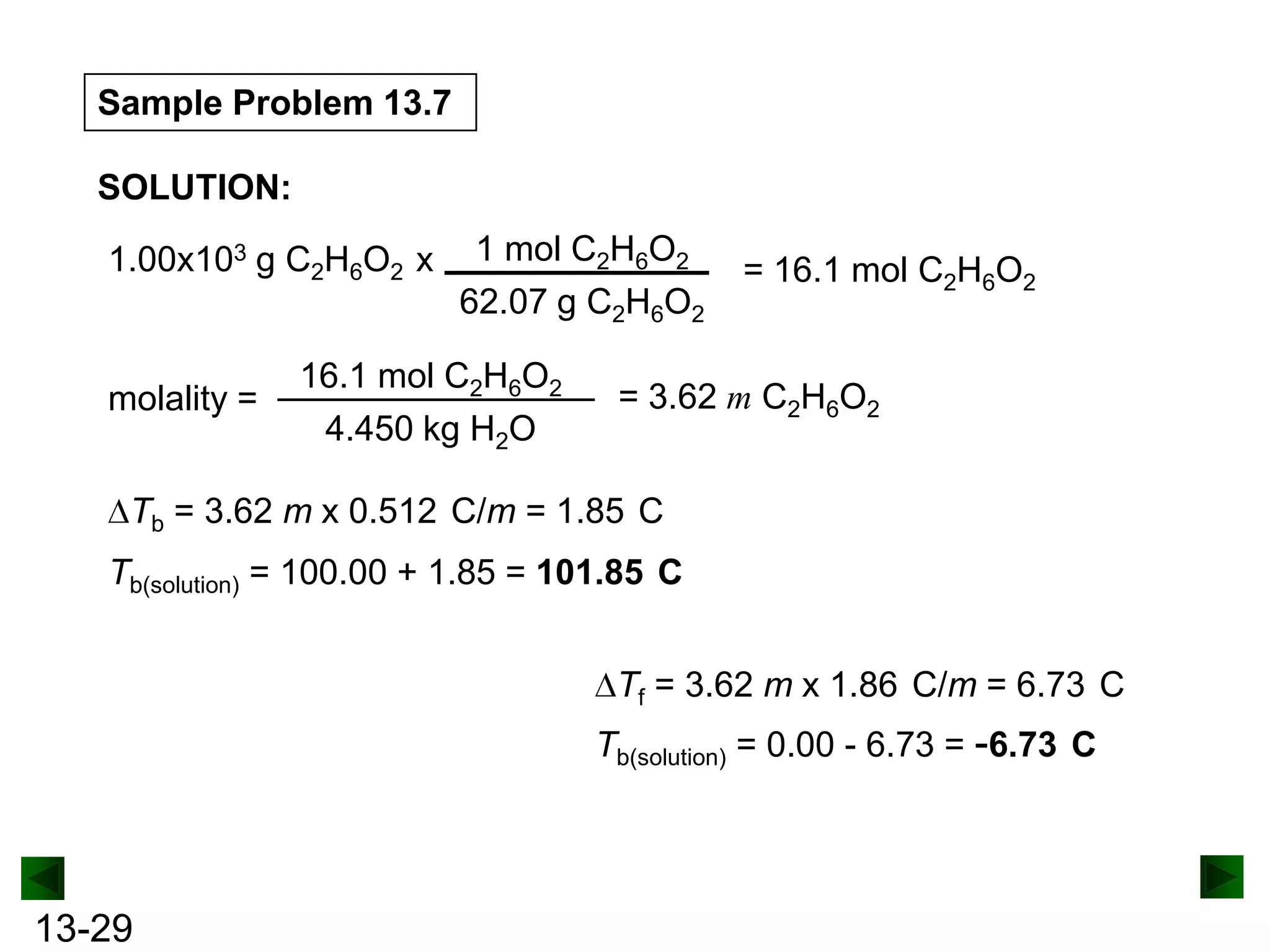
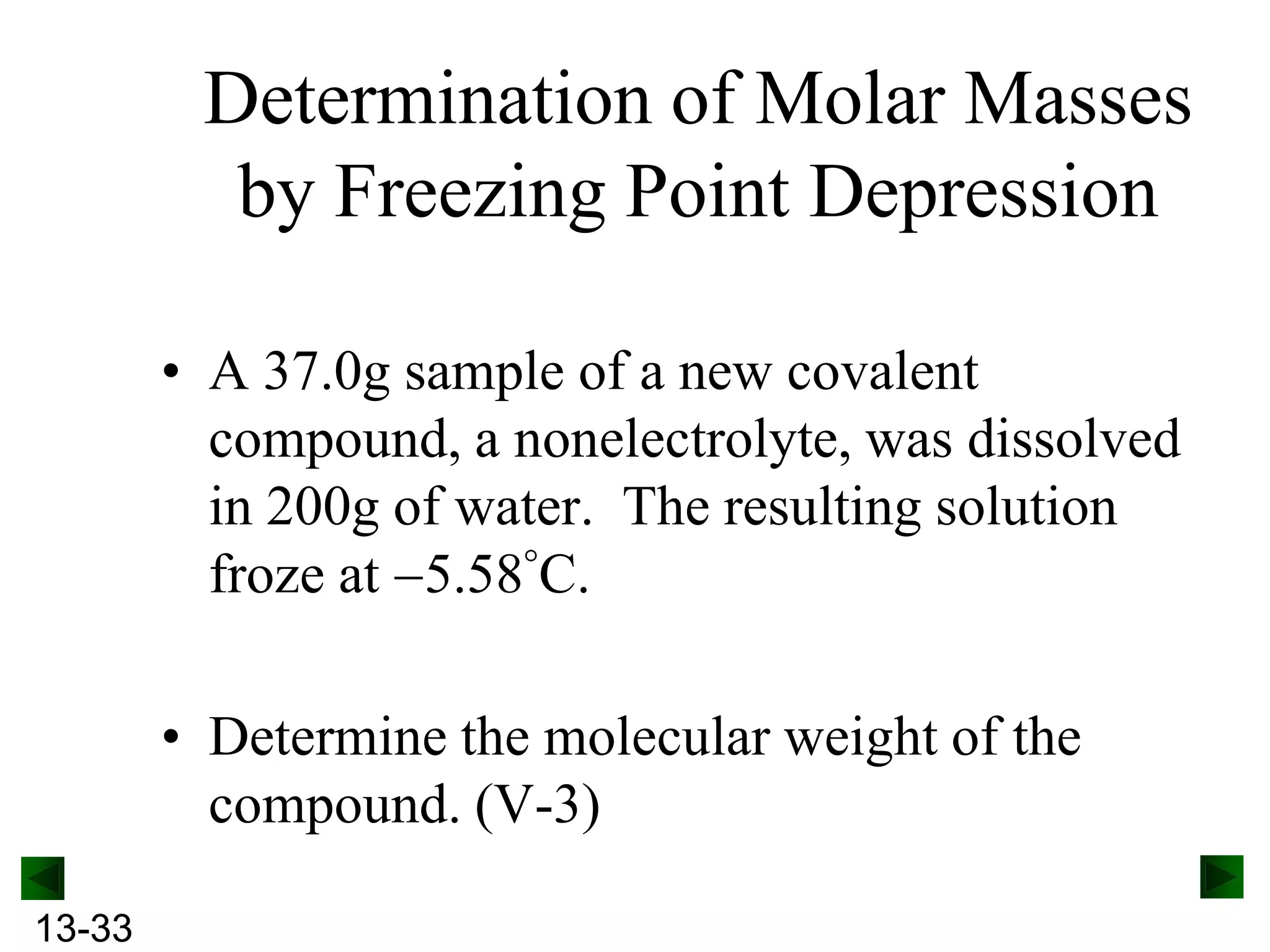
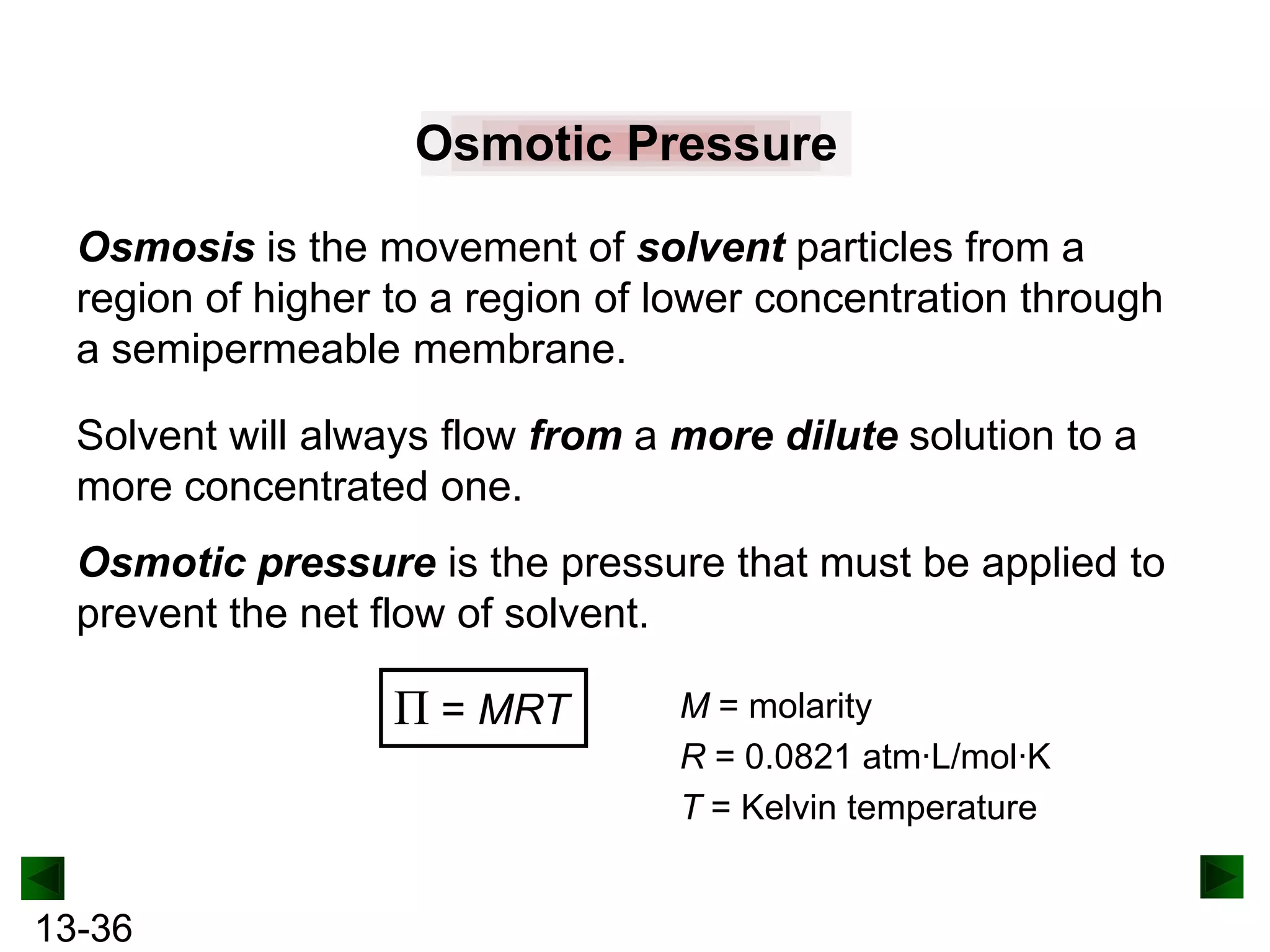
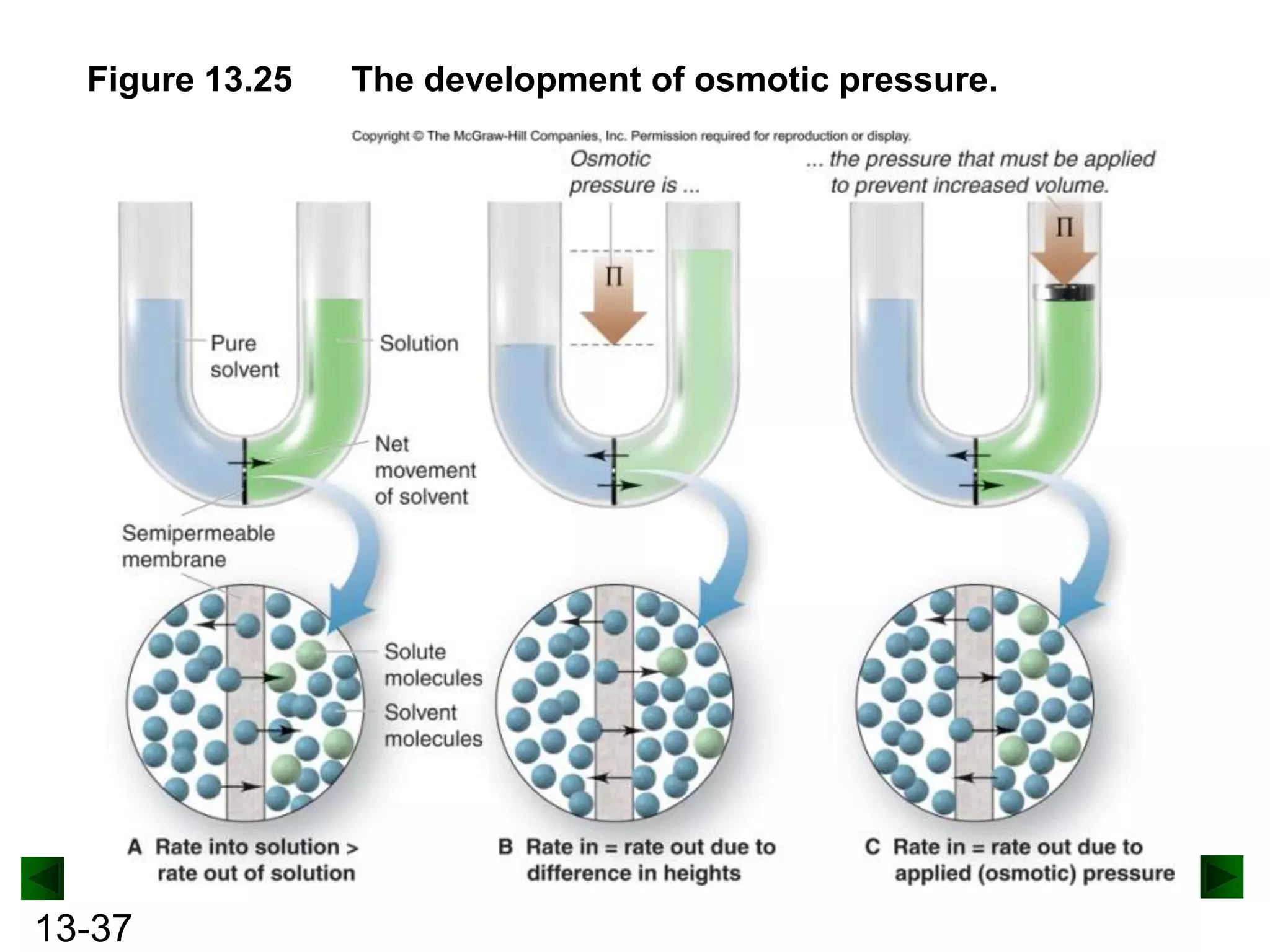
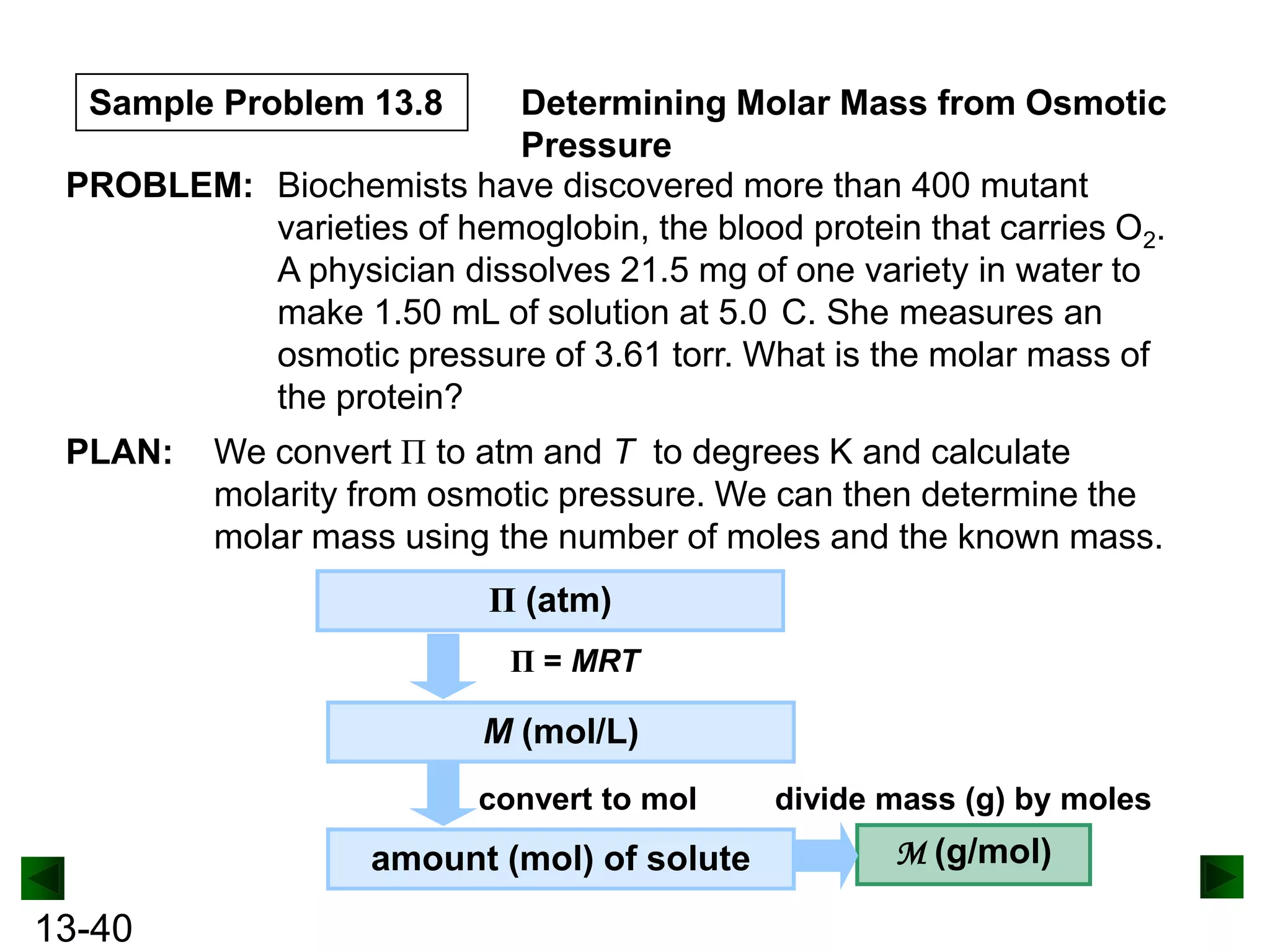
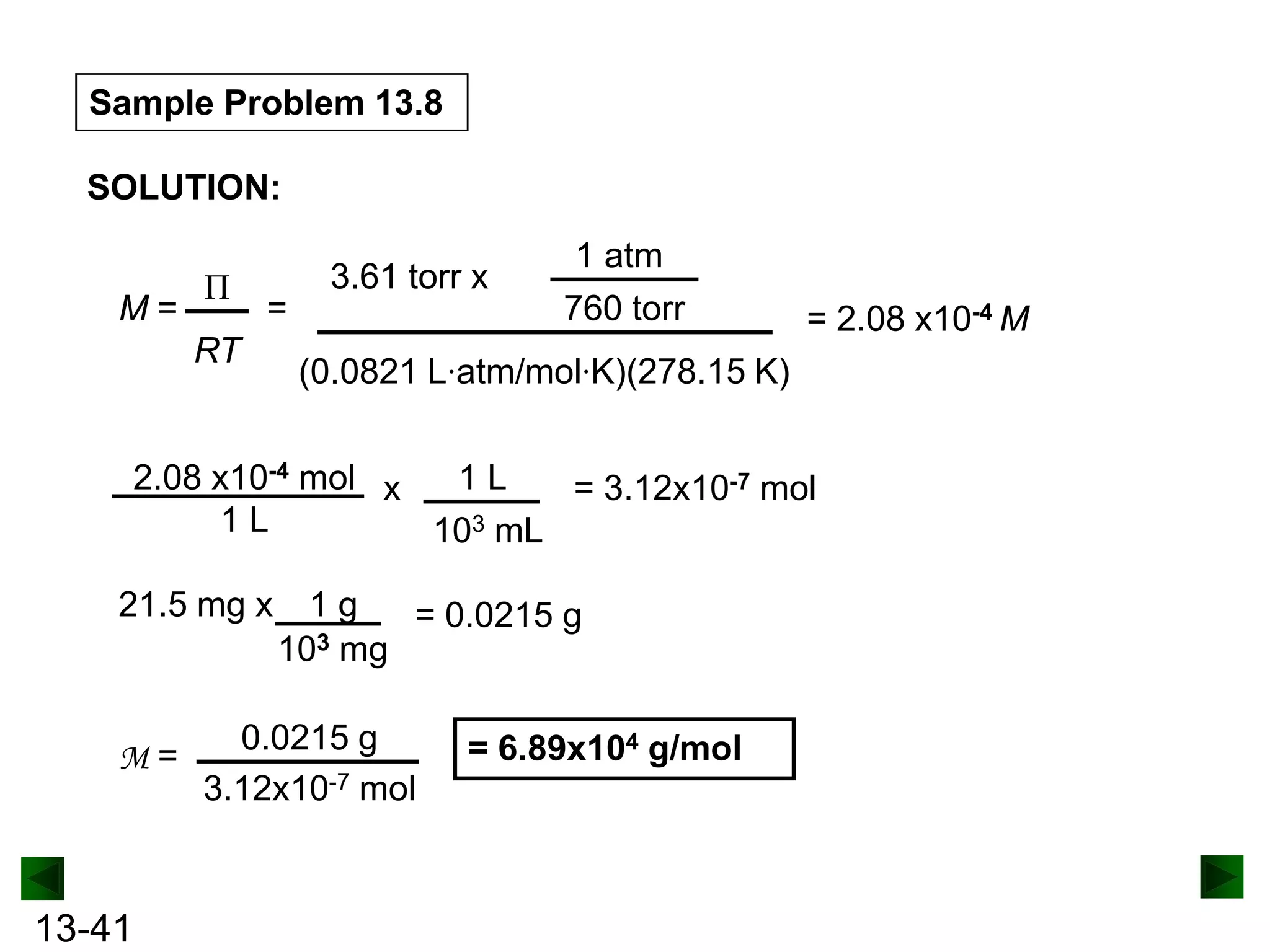
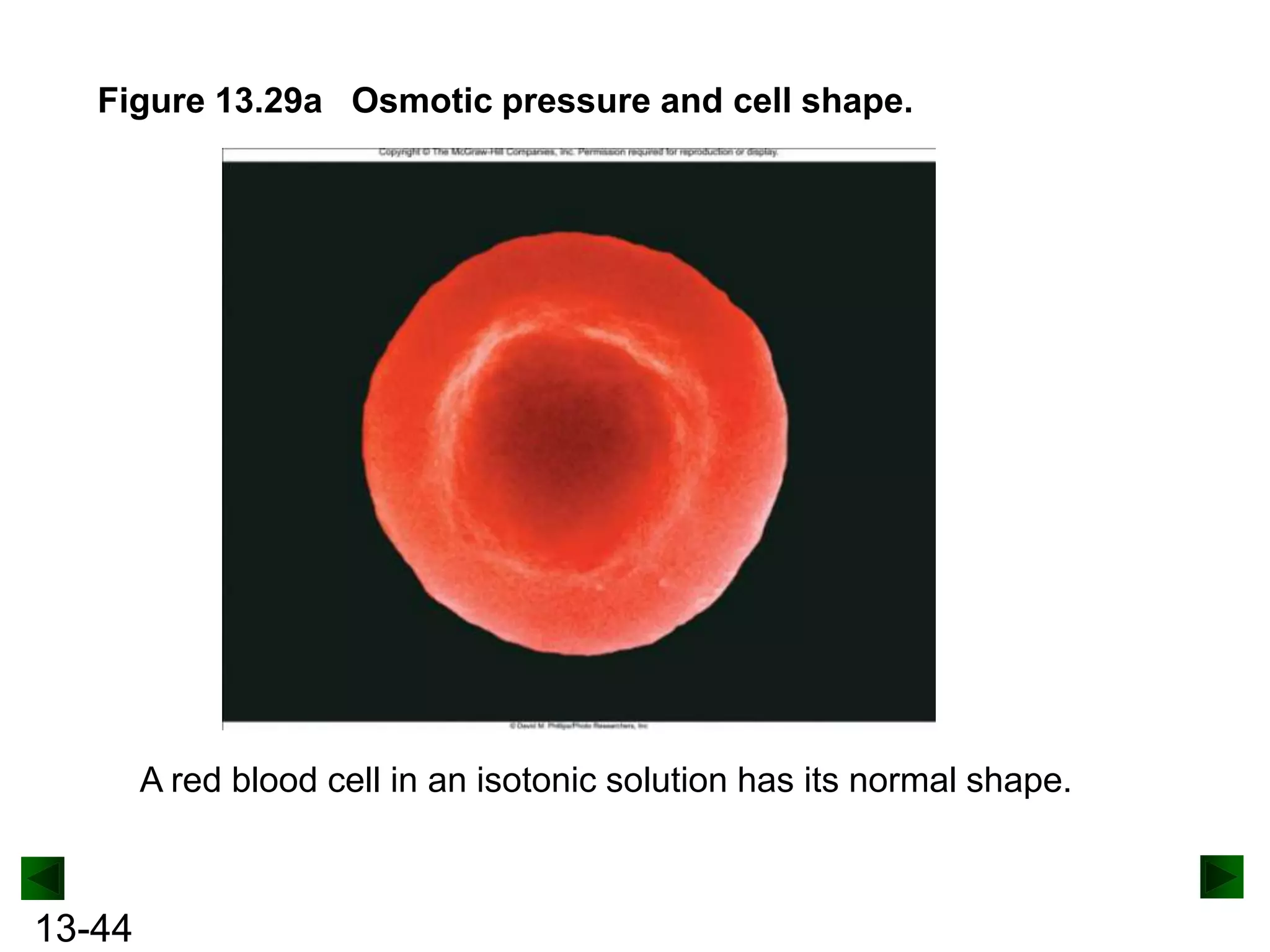
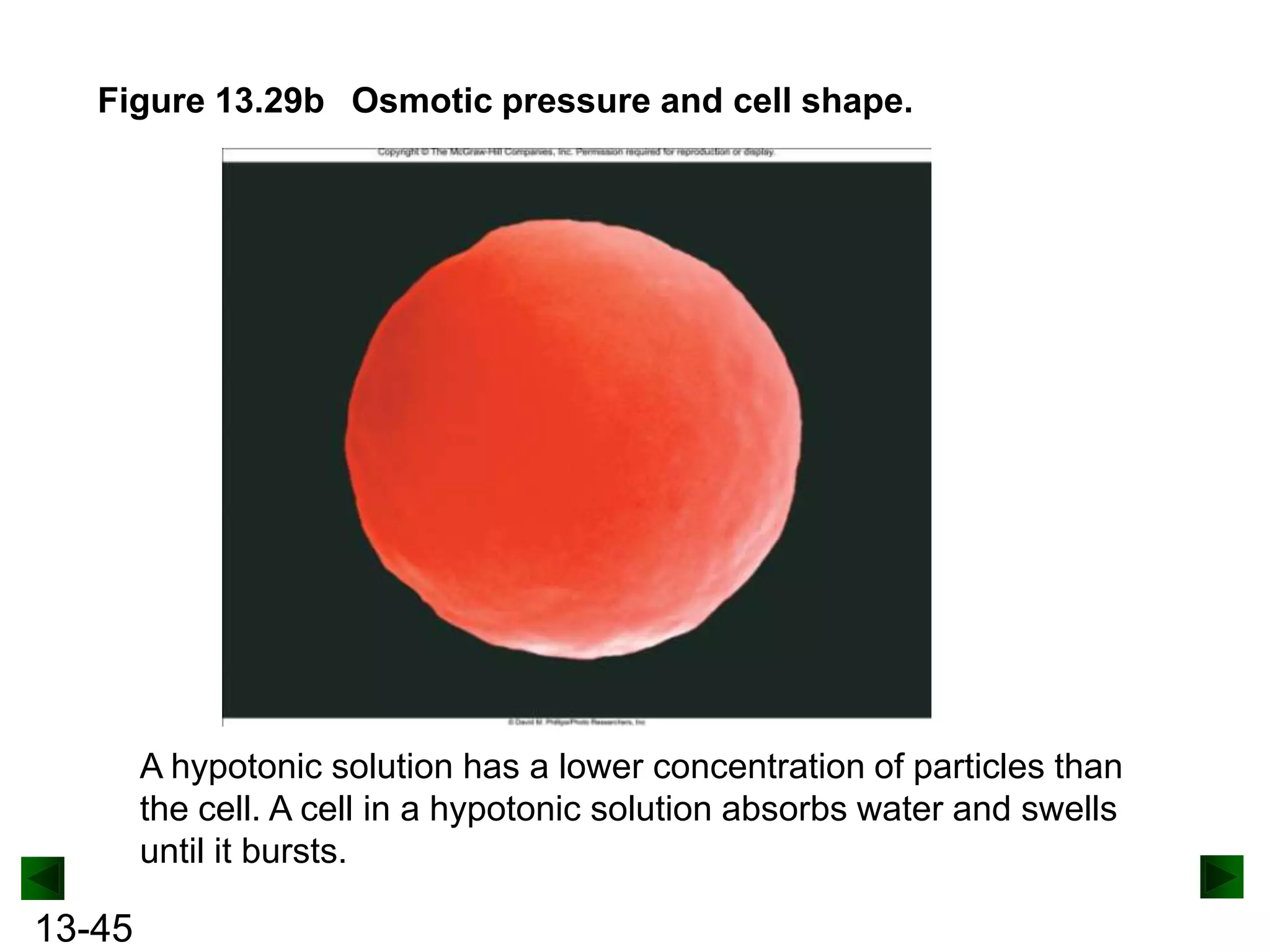
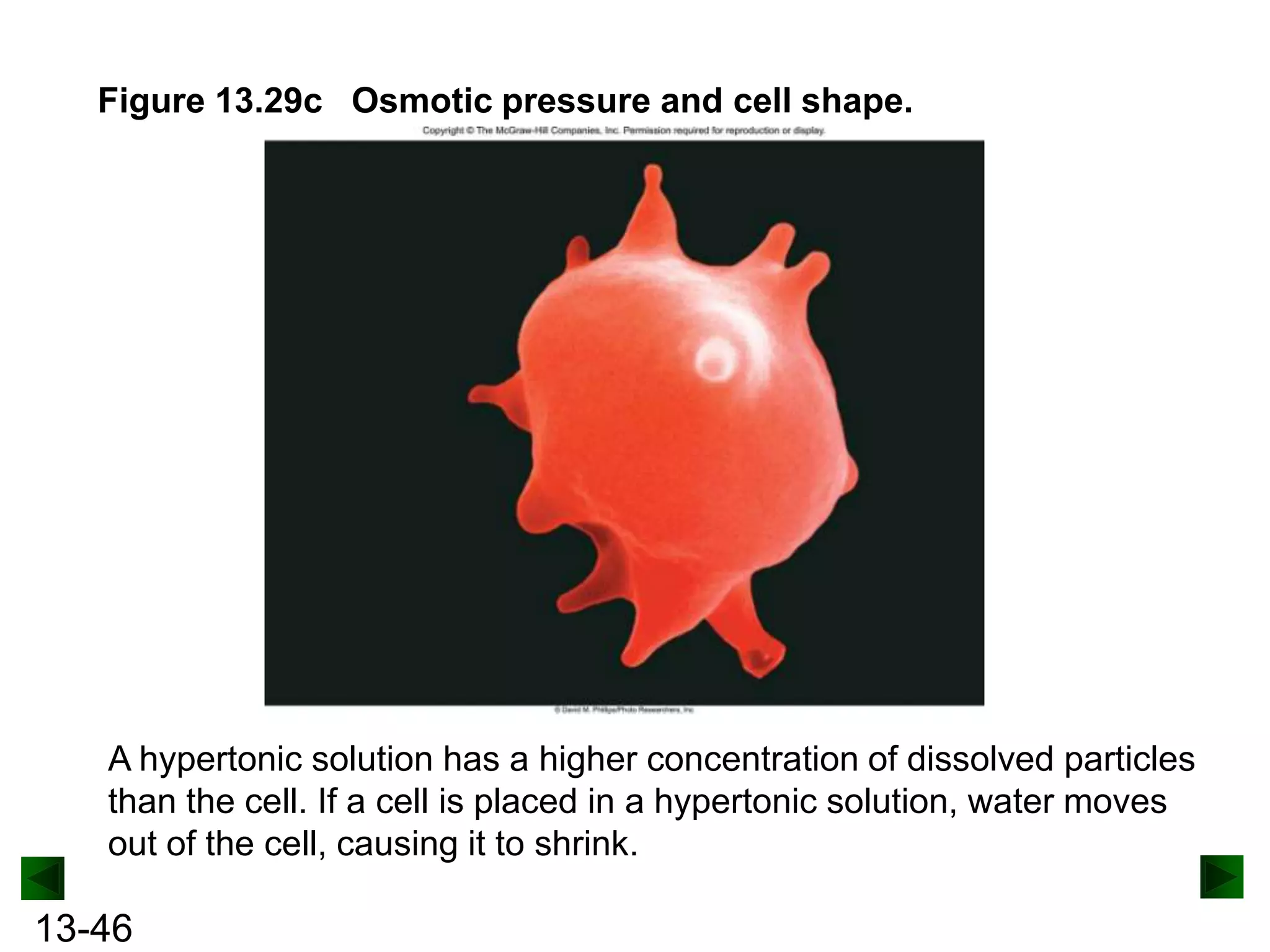
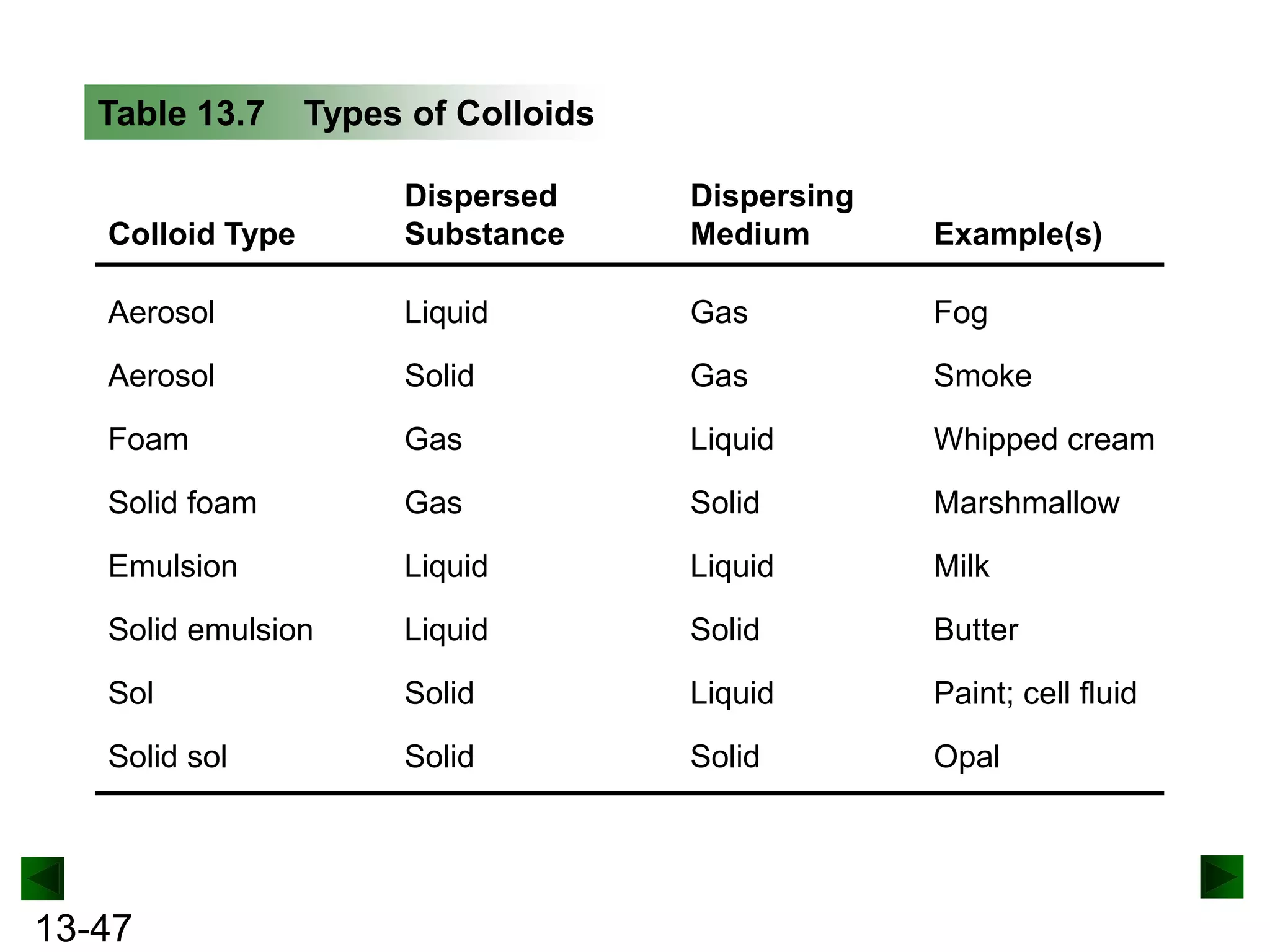
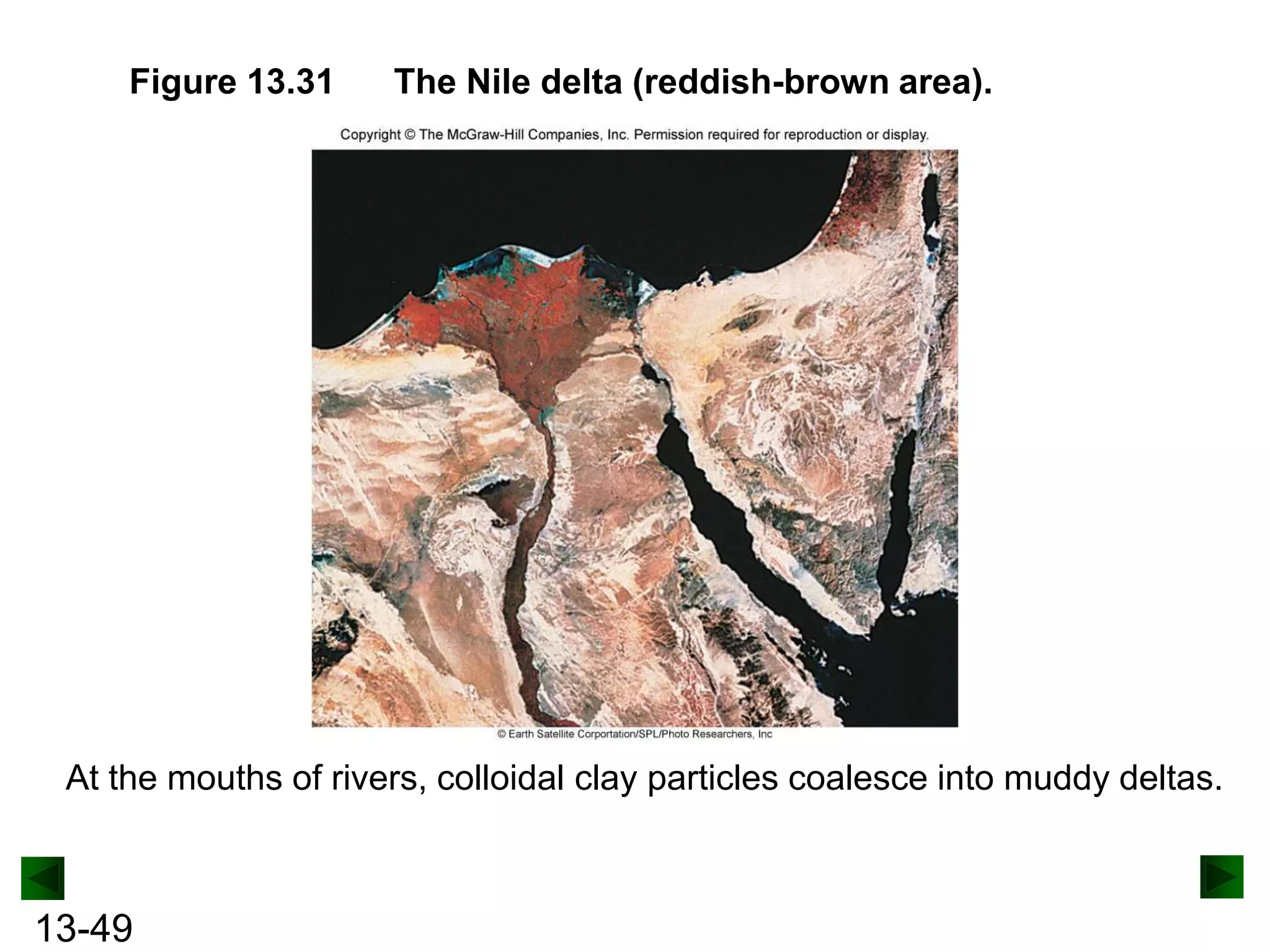
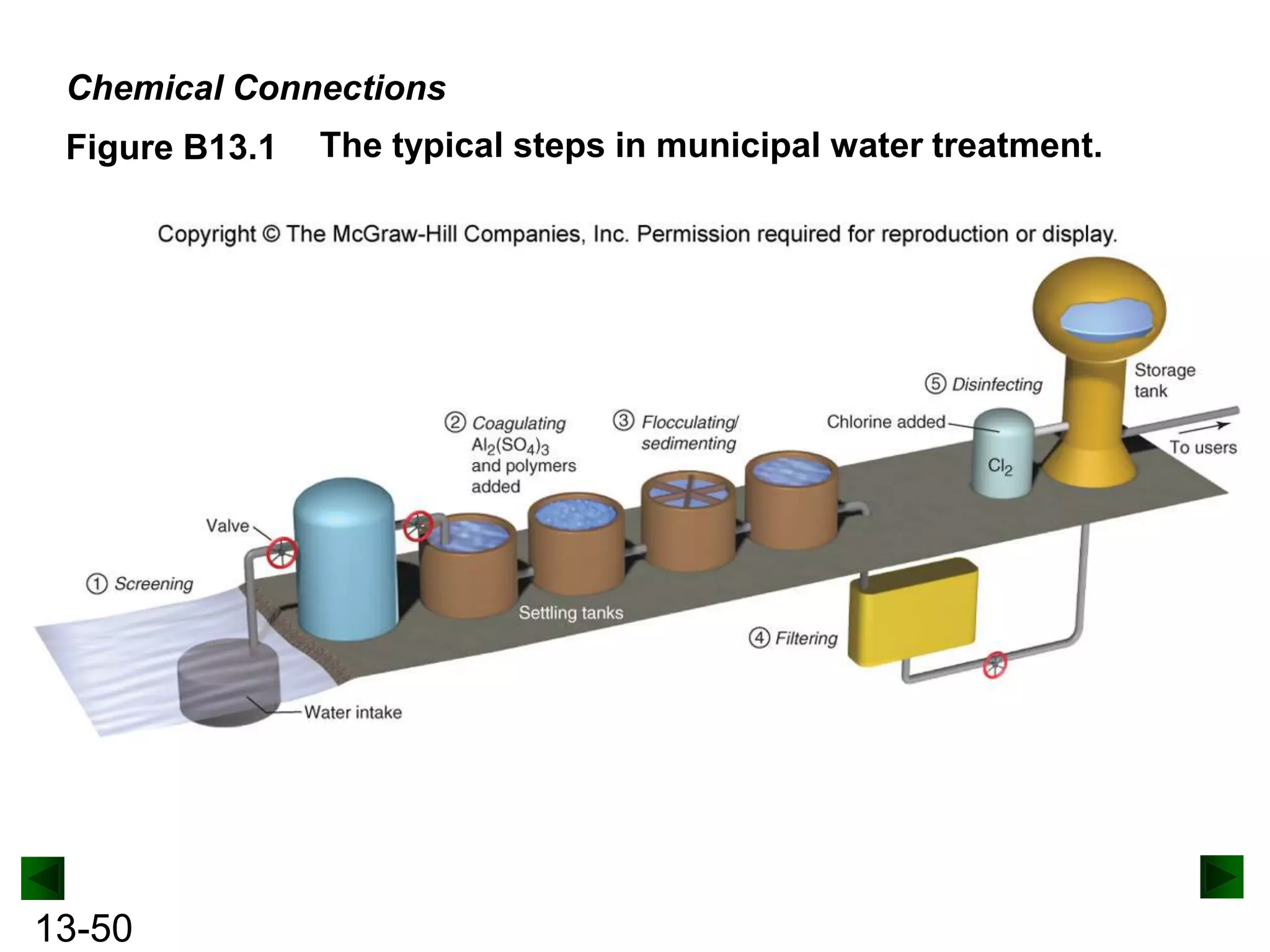
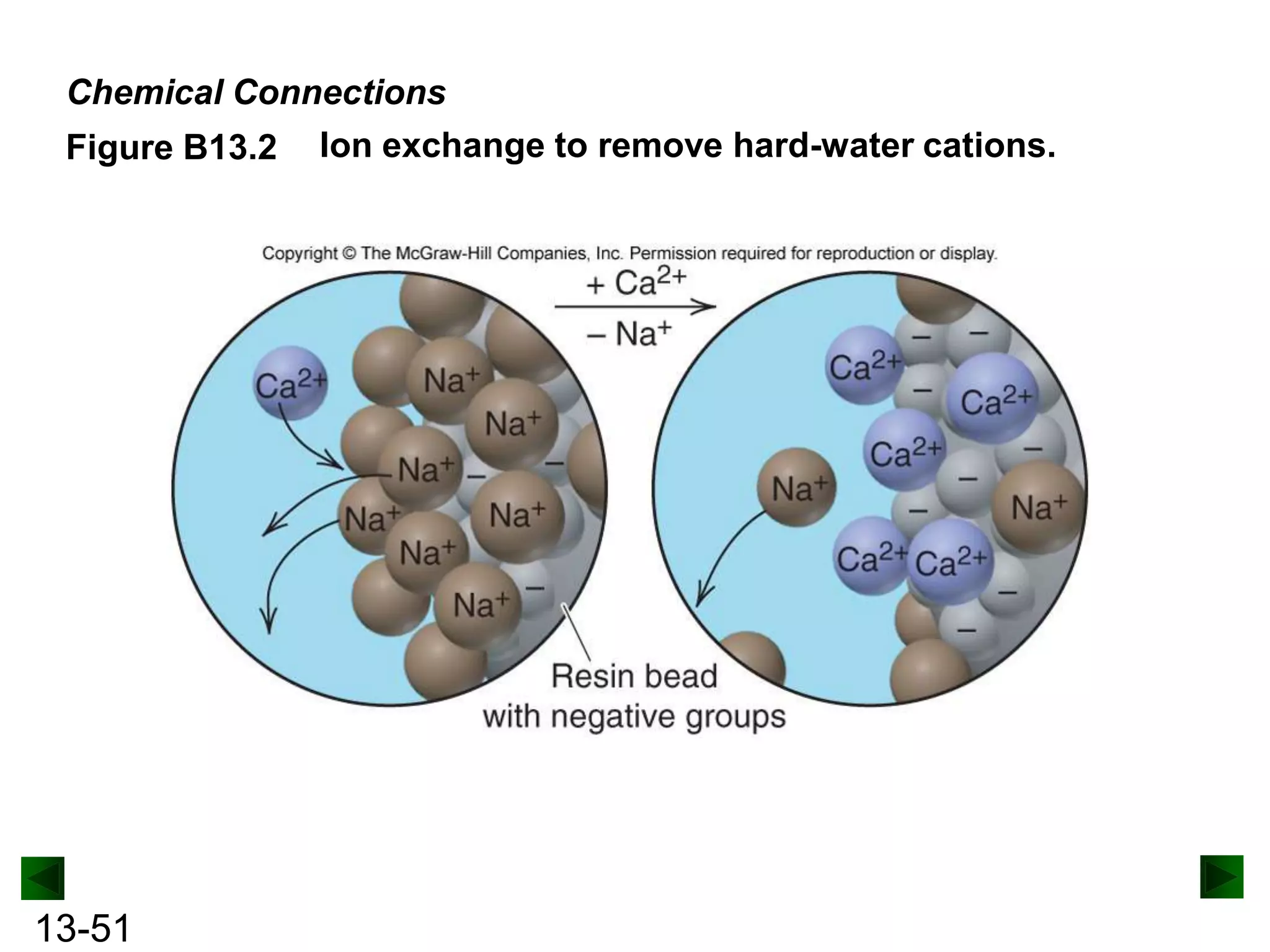
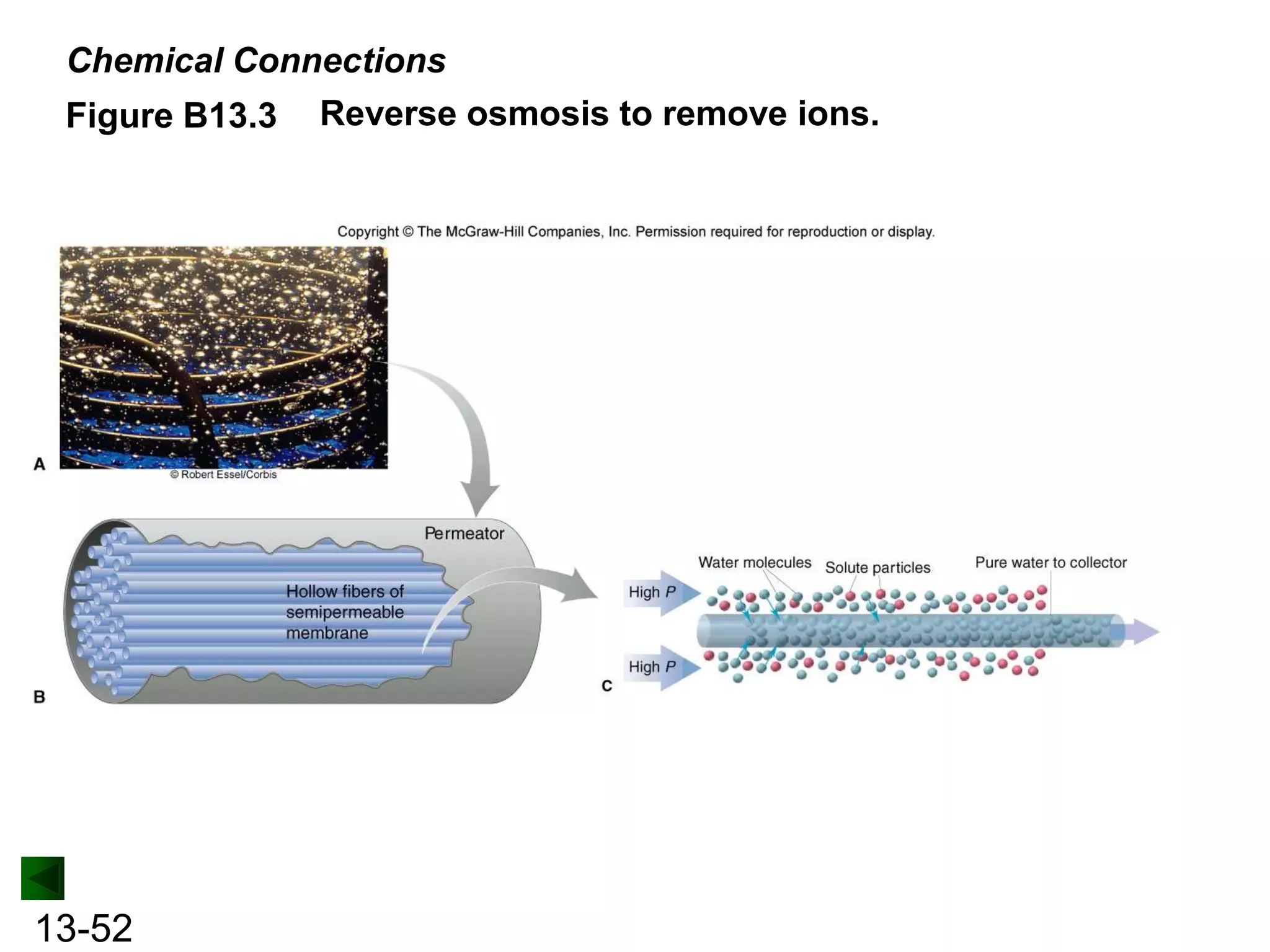
The document provides an overview of colligative properties of solutions, which are physical properties that depend on the number of solute particles in solution rather than the chemical identity of the solute. Examples of colligative properties discussed include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. Formulas are provided to calculate these colligative properties based on variables like molality, vapor pressure of the pure solvent, and temperature.