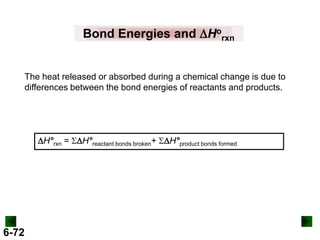
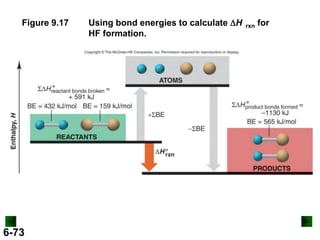
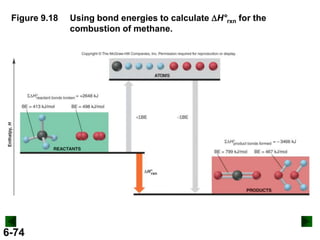
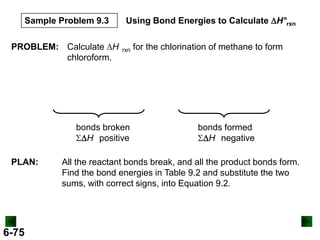
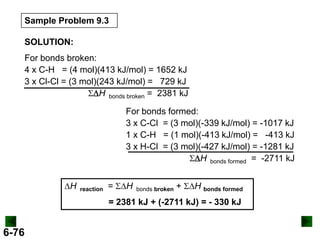
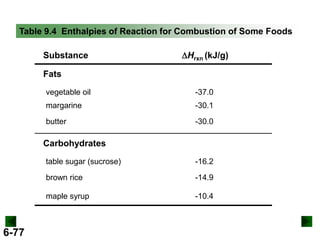
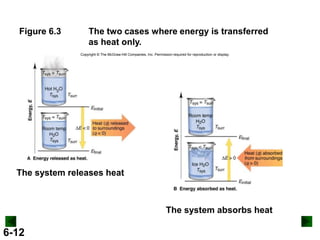
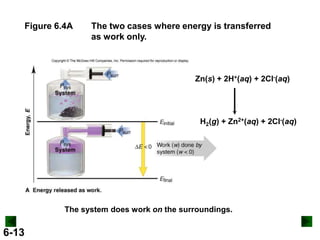
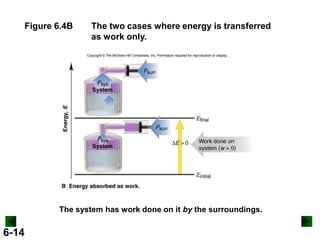
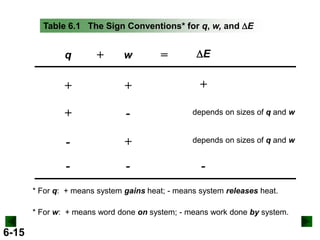
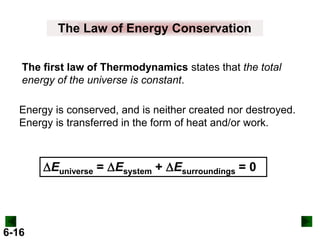
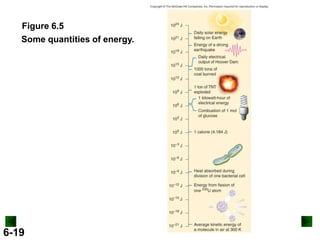
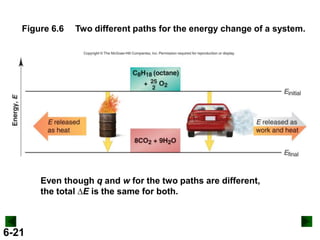
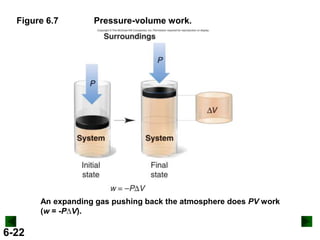
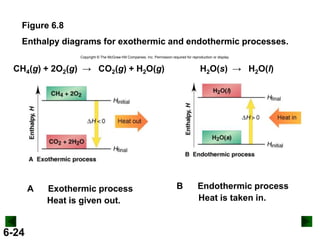
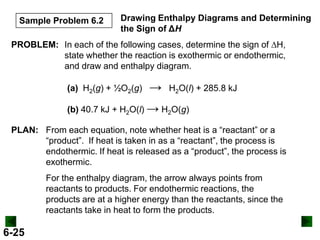
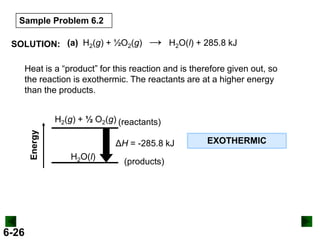
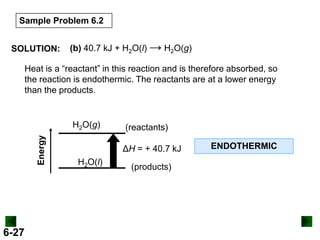
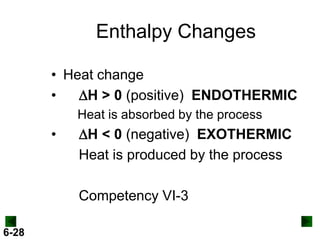
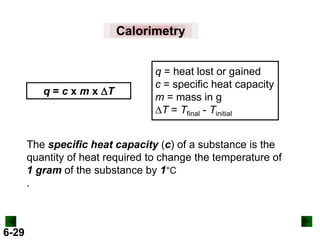
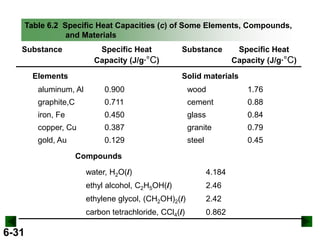
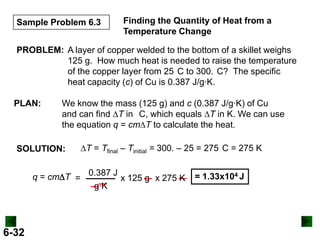
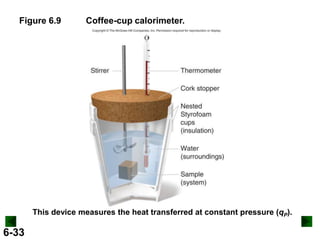
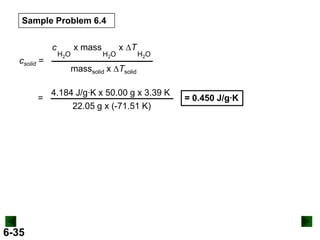
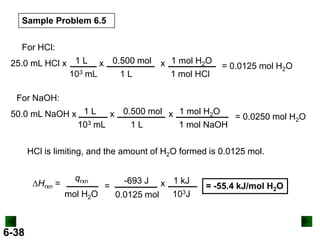
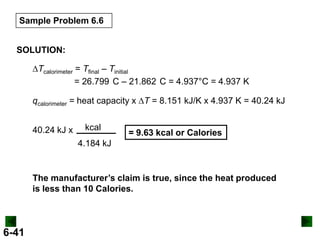
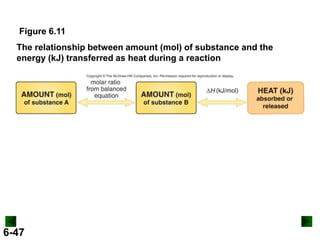
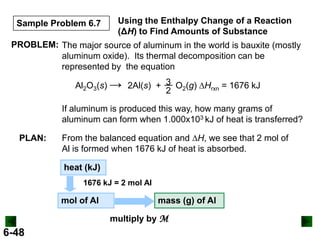
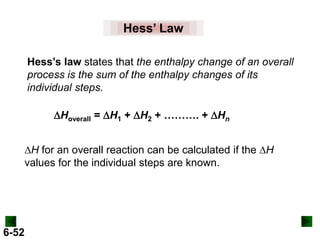
Thermochemistry deals with the heat involved in chemical and physical changes. It is a branch of thermodynamics that studies energy and its transformations. Enthalpy (H) is a measure of the total energy of a system at constant pressure and can be used to determine the heat of a reaction. Calorimetry experiments allow measurement of heat changes through determination of temperature changes of a system and surroundings using equations such as q = cmΔT. Bomb calorimetry and coffee cup calorimetry are two common techniques used to directly measure the heat of chemical reactions.






























![Sample Problem 6.10
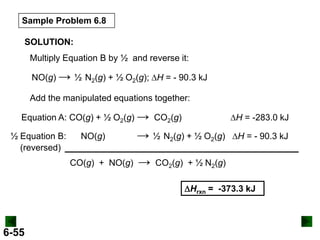
SOLUTION:
DHrxn = S mDH f (products) - S nDH f (reactants)
DHrxn = [4(DHof of NO(g) + 6(DHof of H2O(g)]
- [4(DH of NH3(g) + 5(DH of O2(g)]
= (4 mol)(90.3 kJ/mol) + (6 mol)(-241.8 kJ/mol) –
[(4 mol)(-45.9 kJ/mol) + (5 mol)(0 kJ/mol)]
= -906 kJ
DHrxn = -906 kJ
6-58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/new-chm-151-unit-9-power-points-140227172226-phpapp01/85/New-chm-151_unit_9_power_points-58-320.jpg)