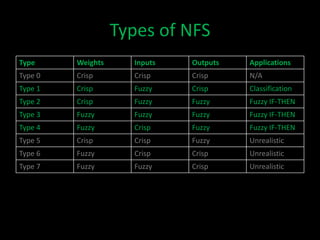
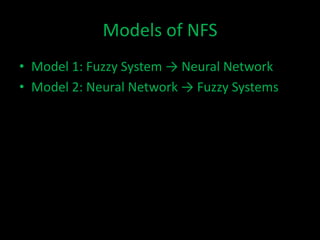
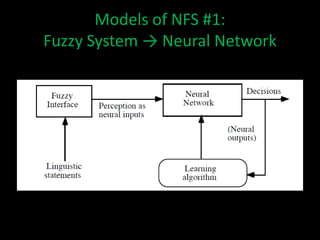
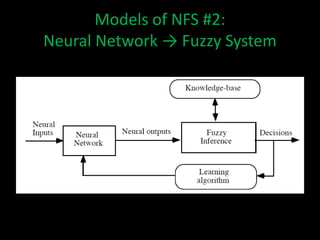
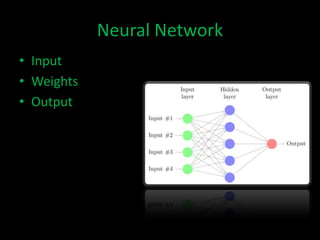
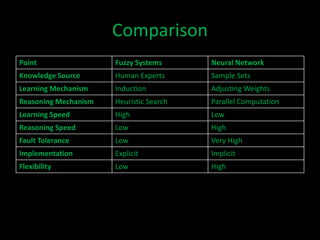
Neuro-fuzzy systems combine neural networks and fuzzy logic to overcome the limitations of each. They were created to achieve the mapping precision of neural networks and the interpretability of fuzzy systems. There are different types of neuro-fuzzy systems depending on whether the inputs, outputs, and weights are crisp or fuzzy. Two common models are fuzzy systems providing input to neural networks, and neural networks providing input to fuzzy systems. Neuro-fuzzy systems have applications in domains like measuring water opacity, improving financial ratings, and automatically adjusting devices.





![Steps in Development of NFS
• Development of Fuzzy Neural Models
[Neurons]
• Development of synaptic connection models
which incorporate fuzziness into Neural
Network [Weights]
• Development of Learning Algorithms [Method
of adjusting weights]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuro-fuzzysystems-121005075858-phpapp02/85/Neuro-fuzzy-systems-9-320.jpg)