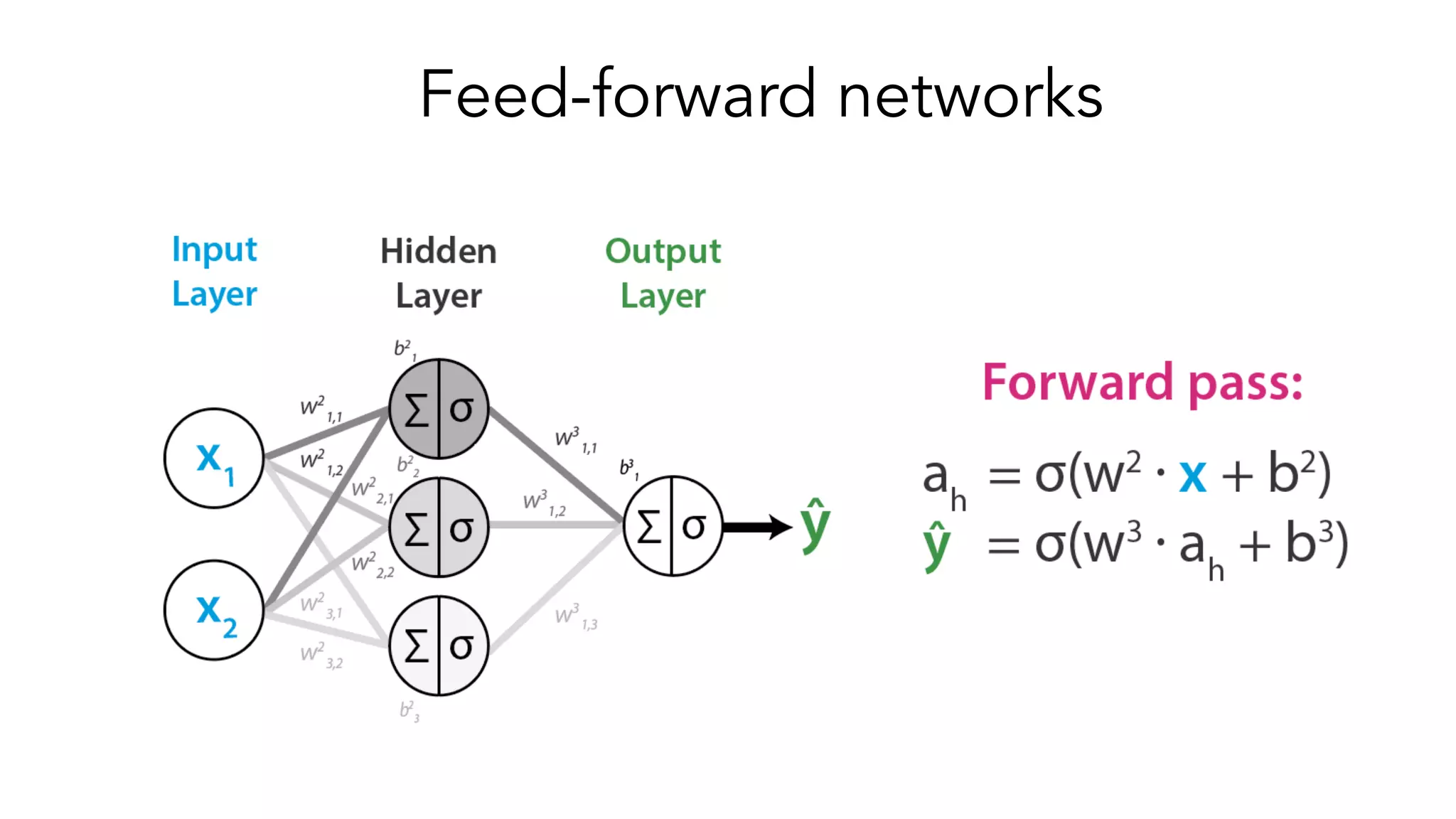
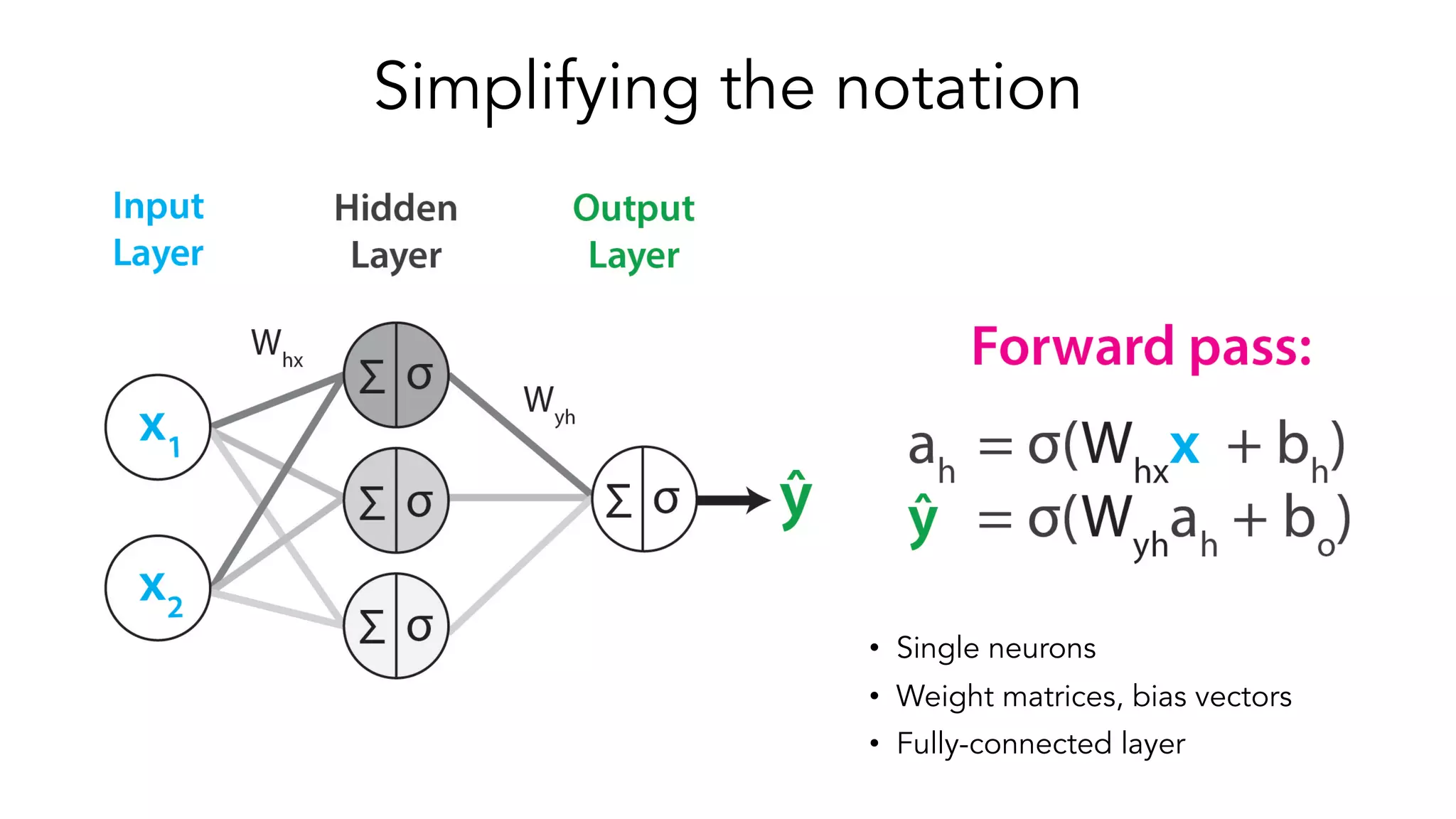
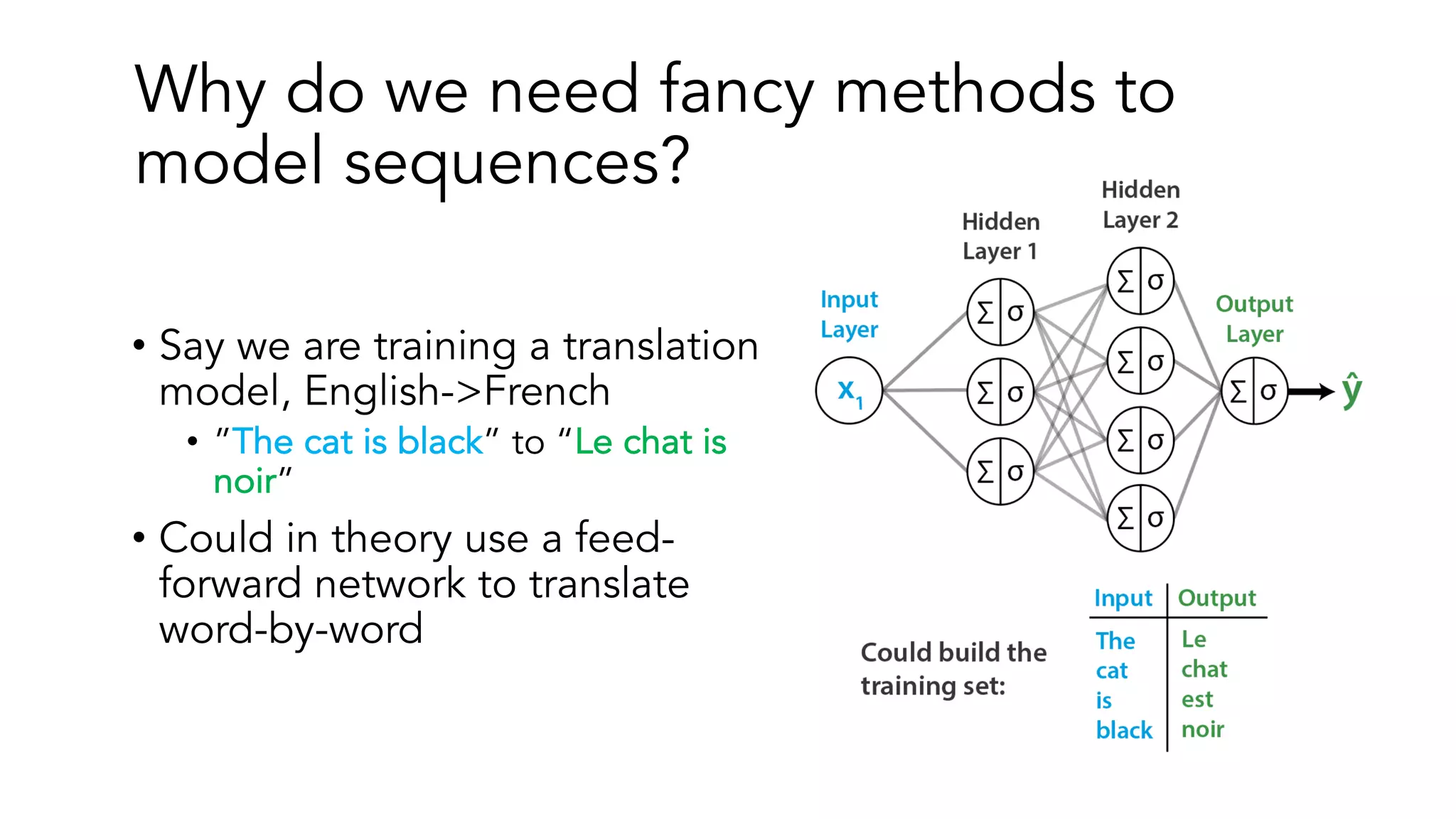
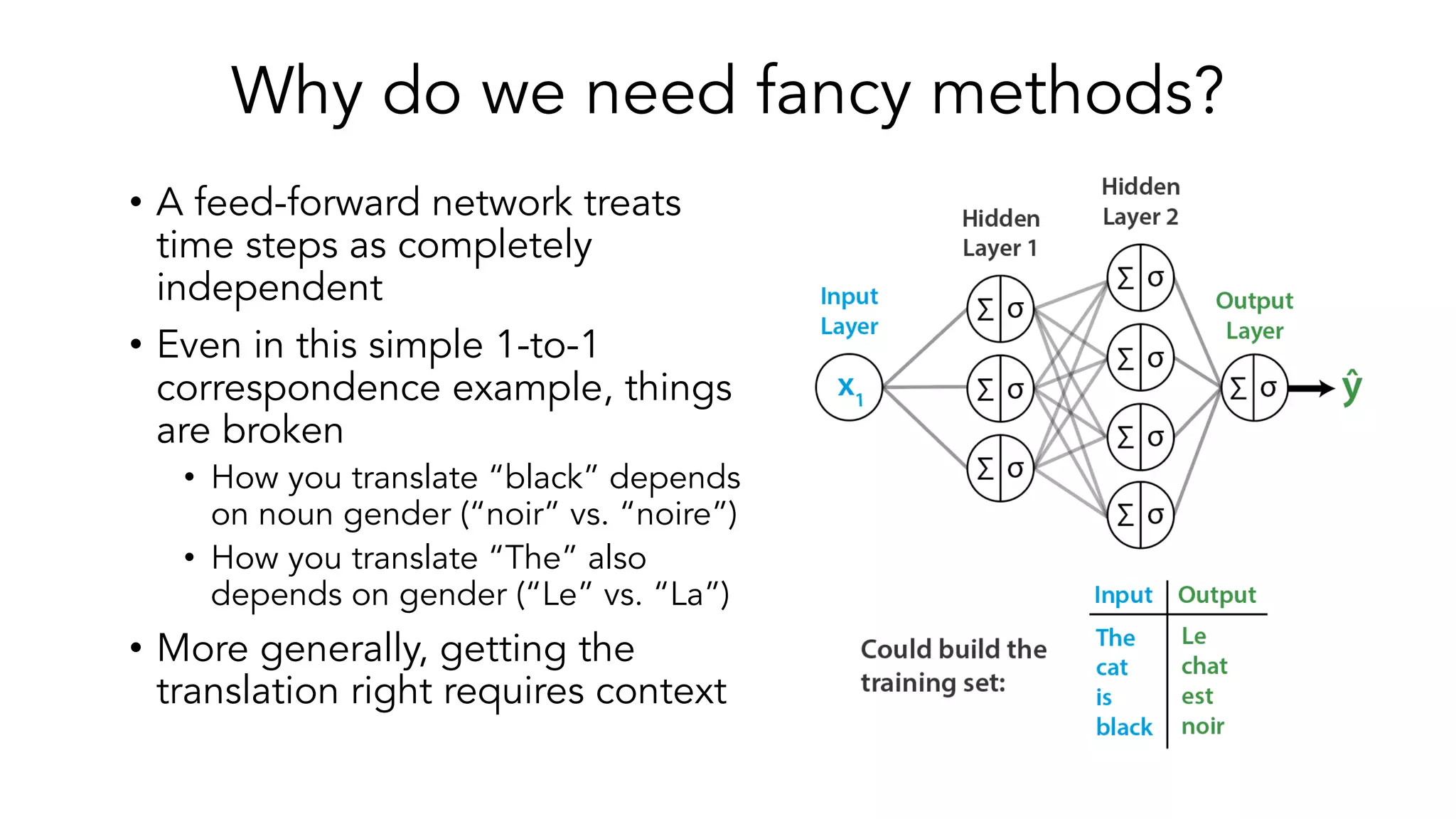
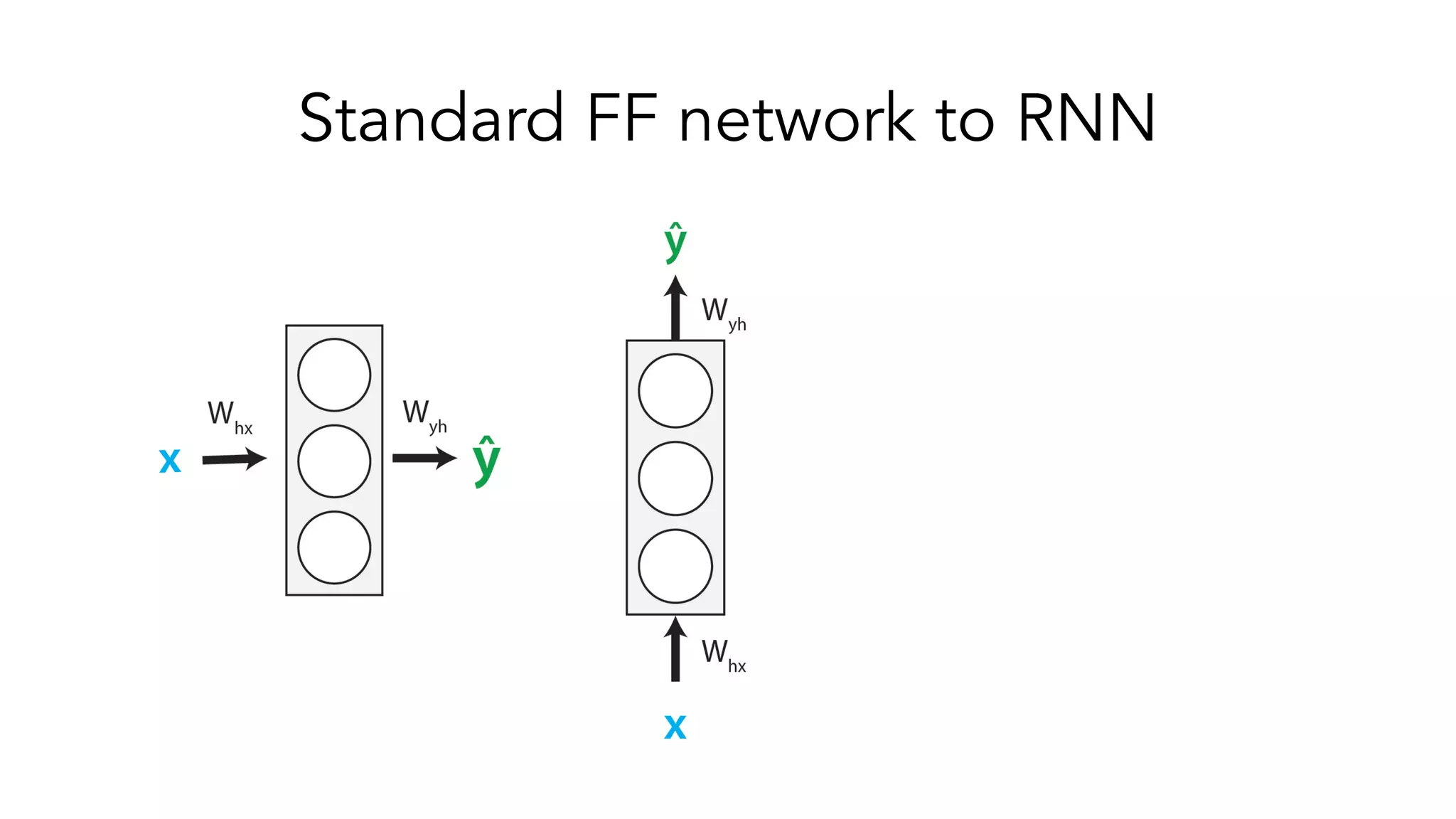
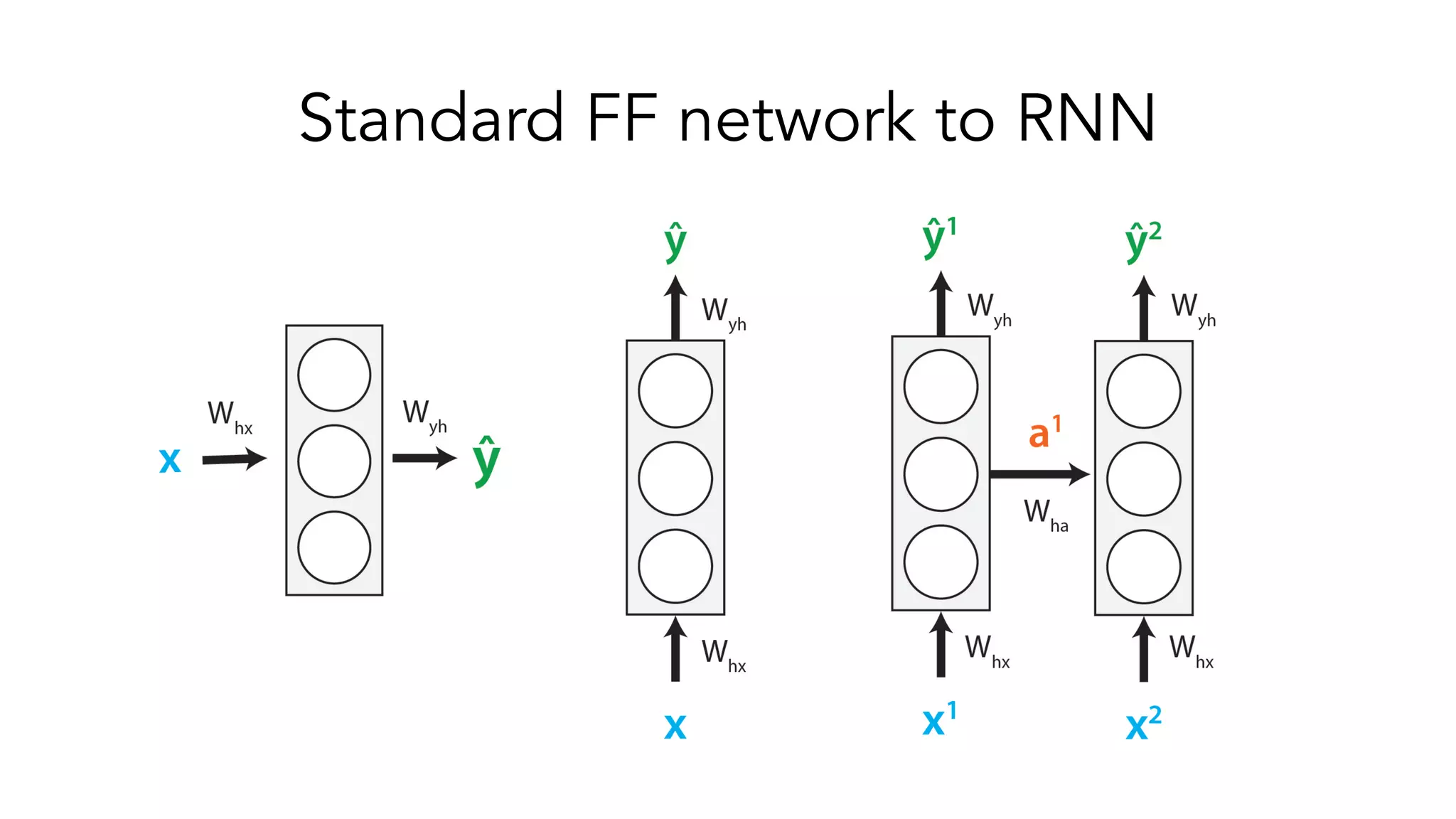
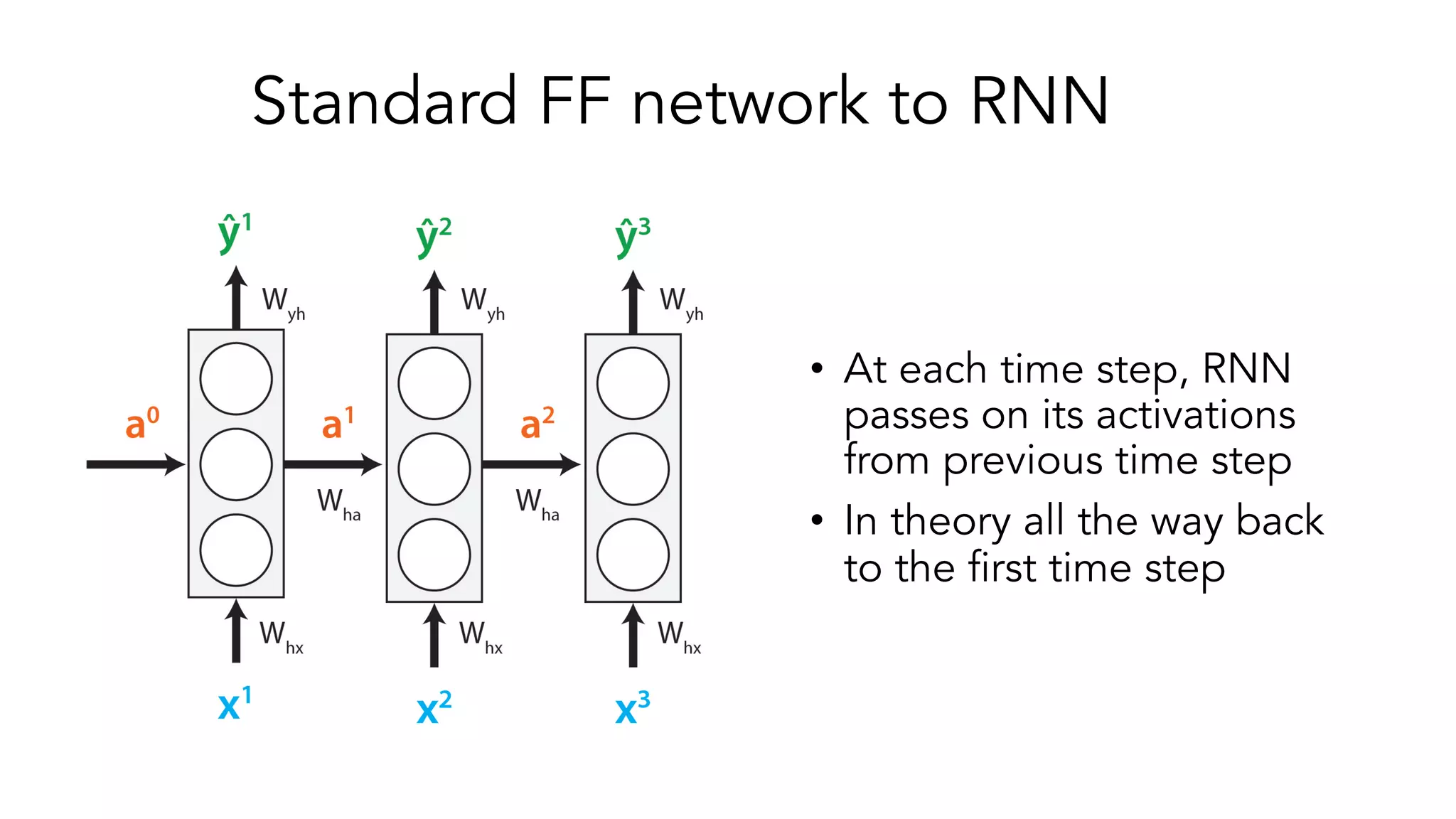
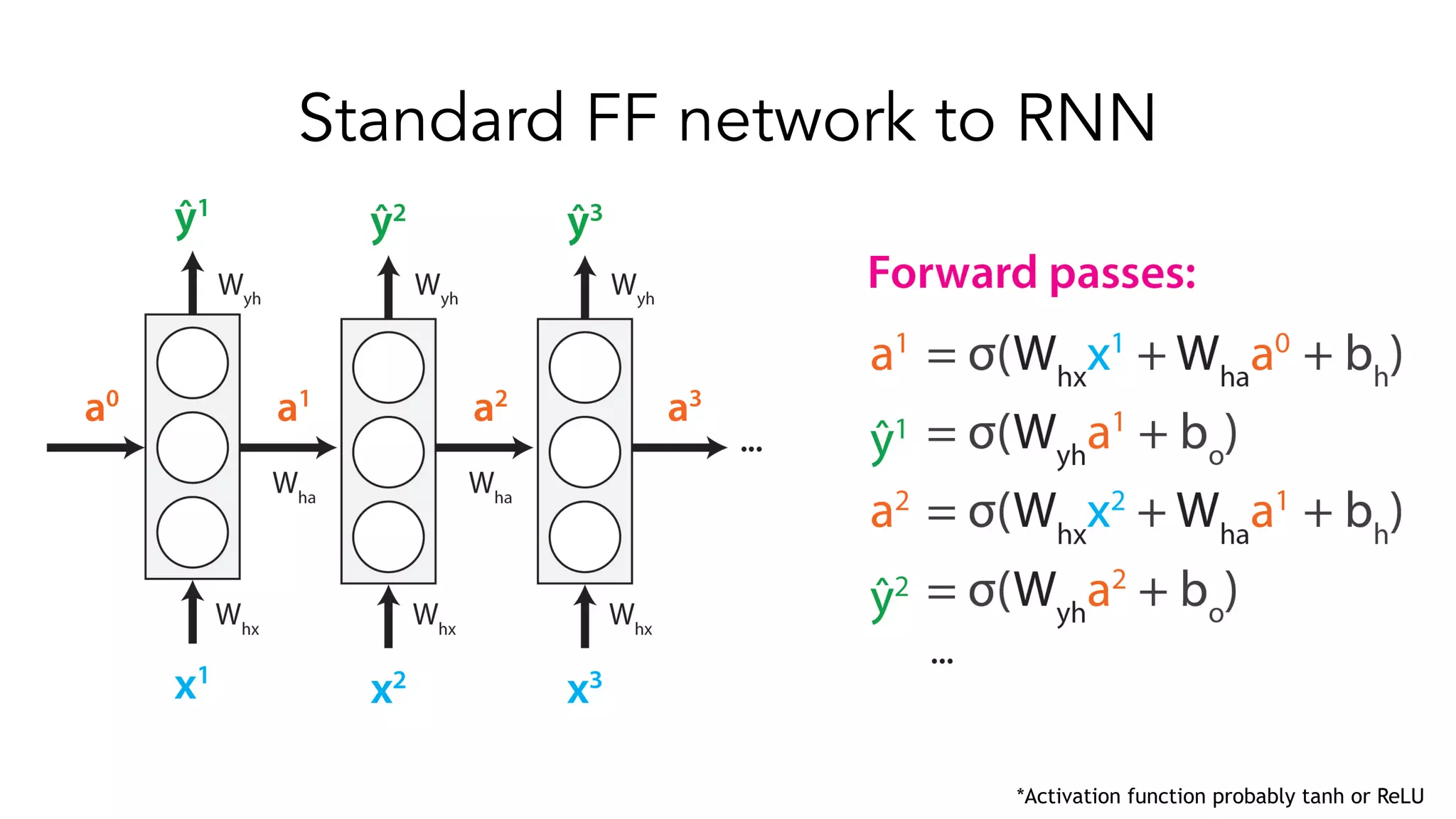
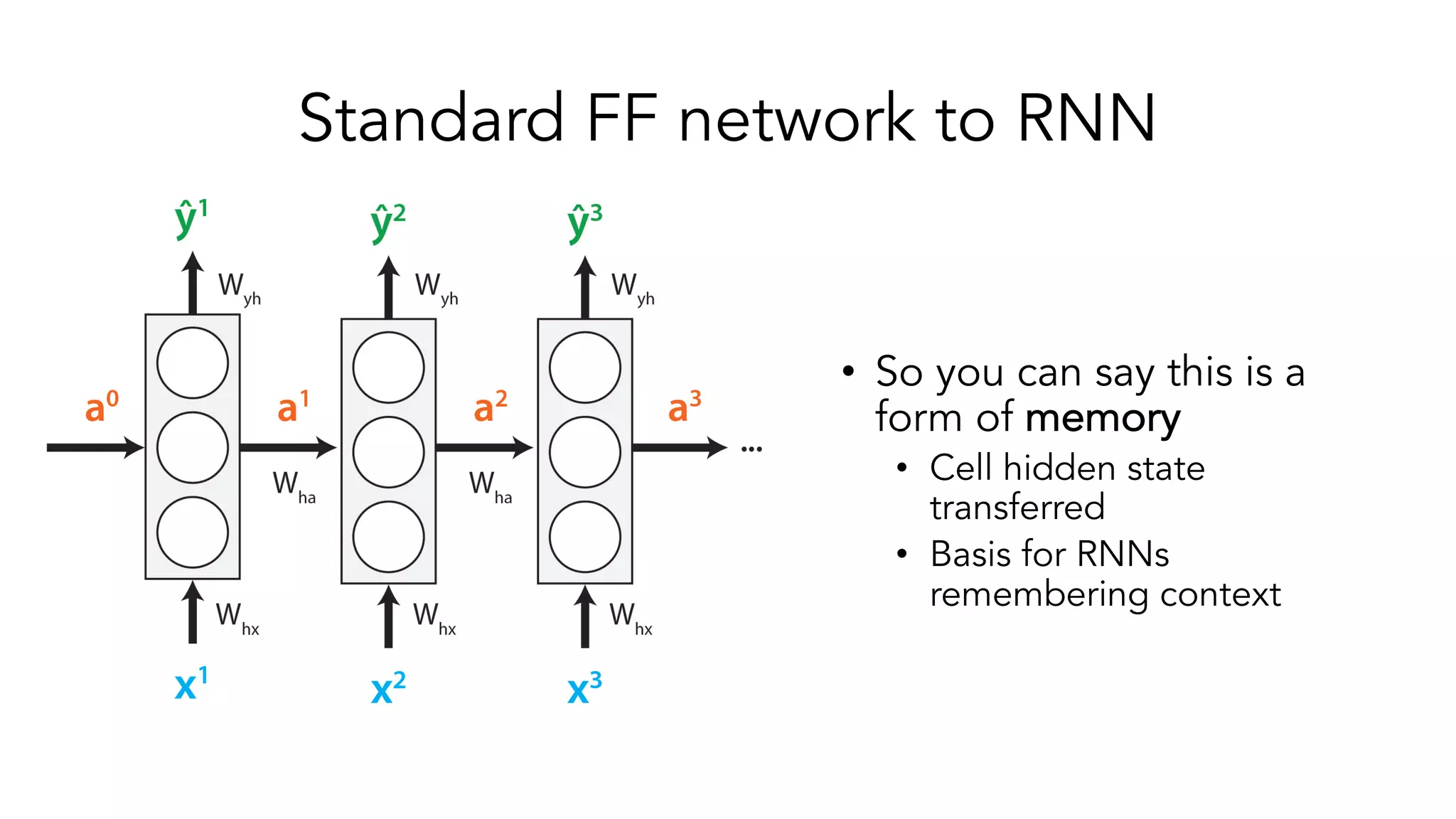
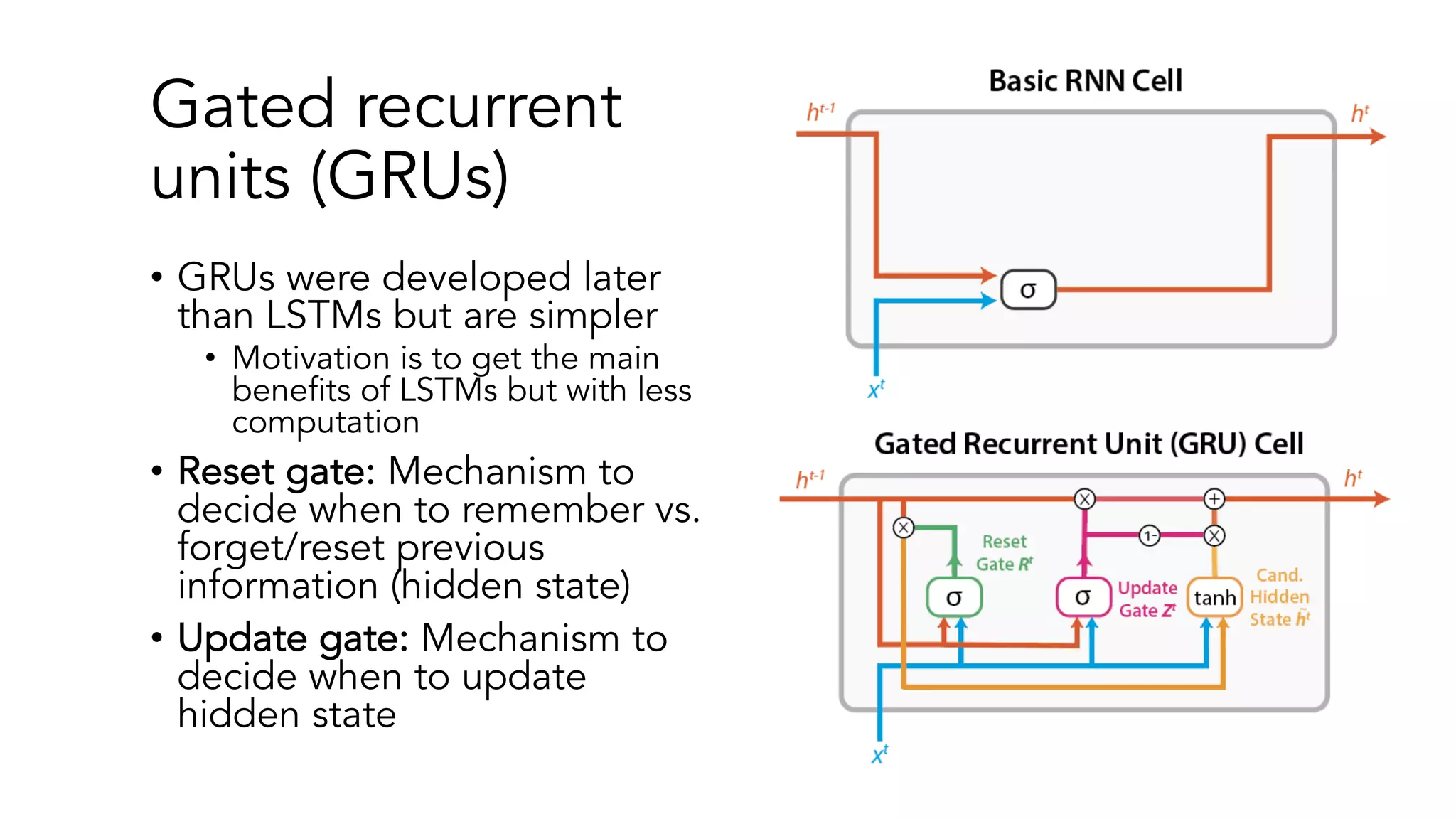
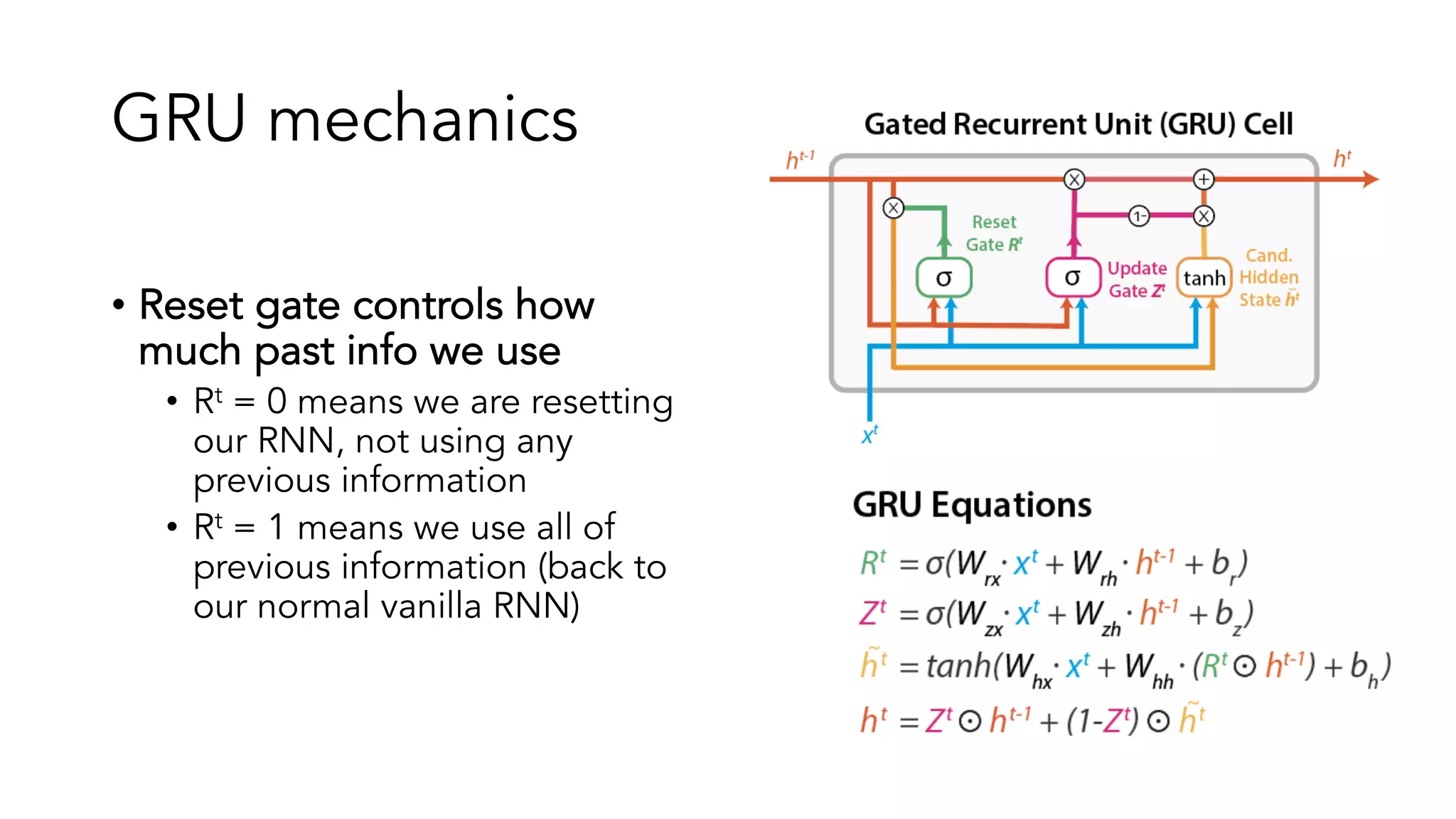
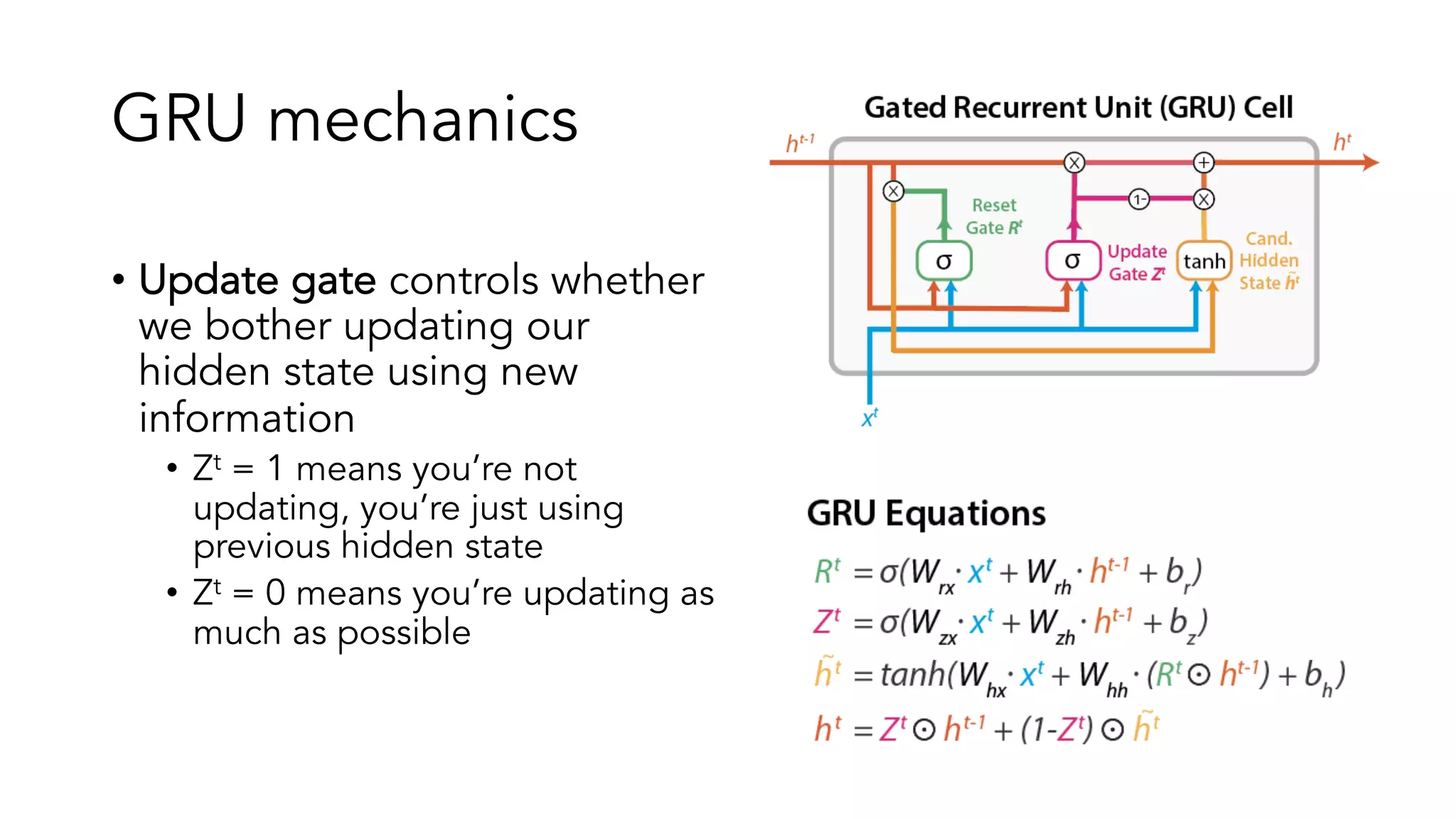
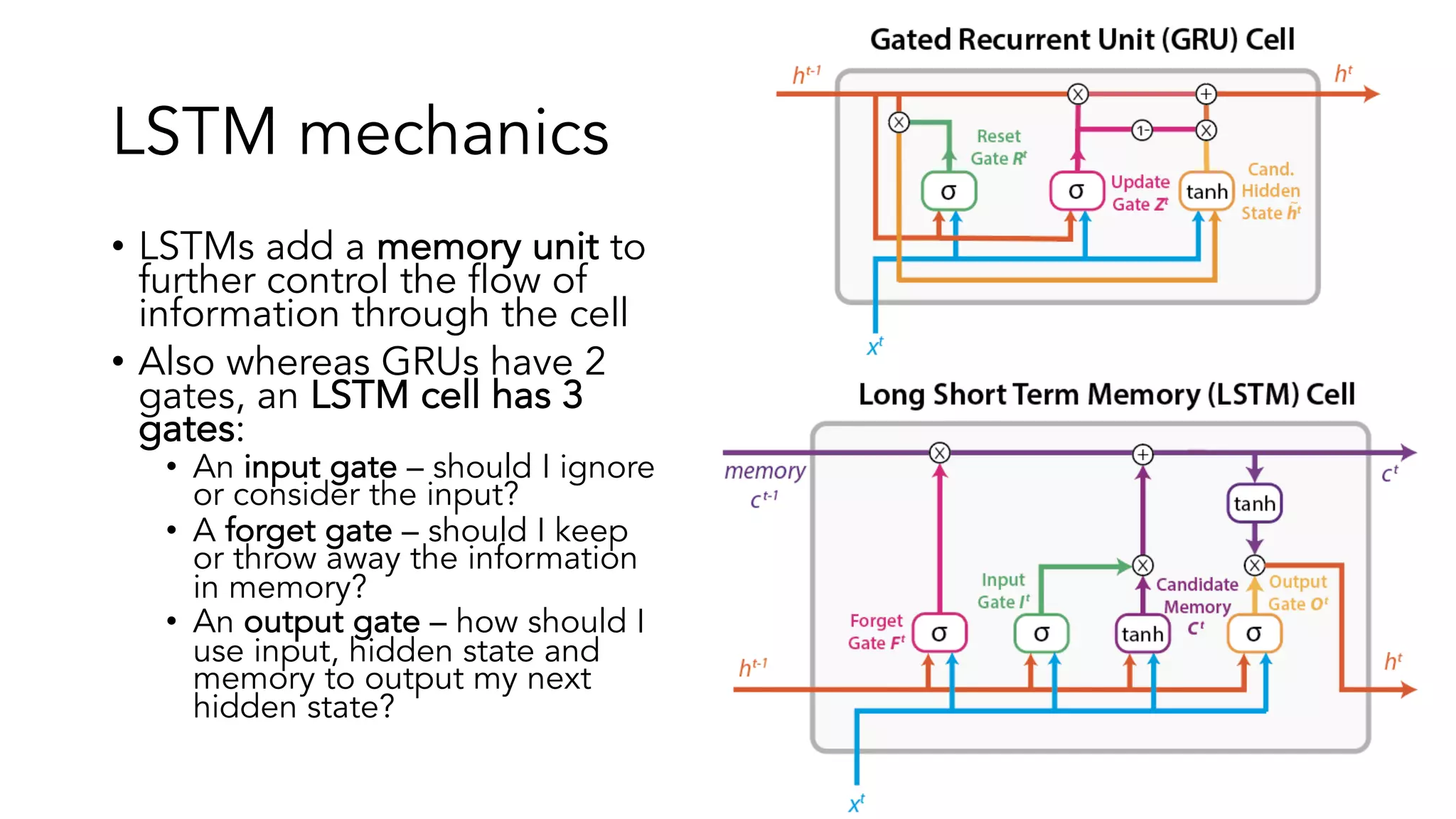
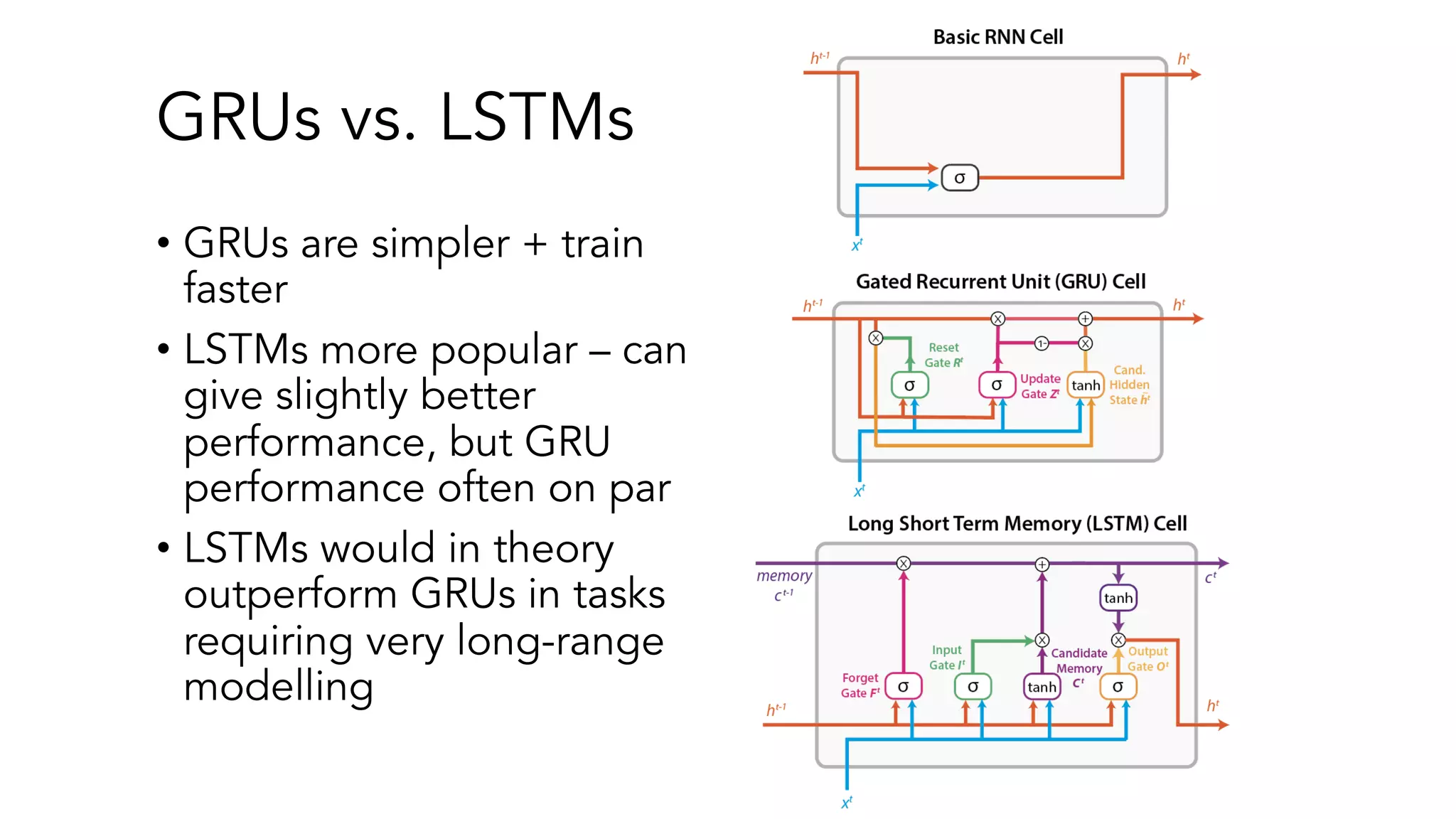
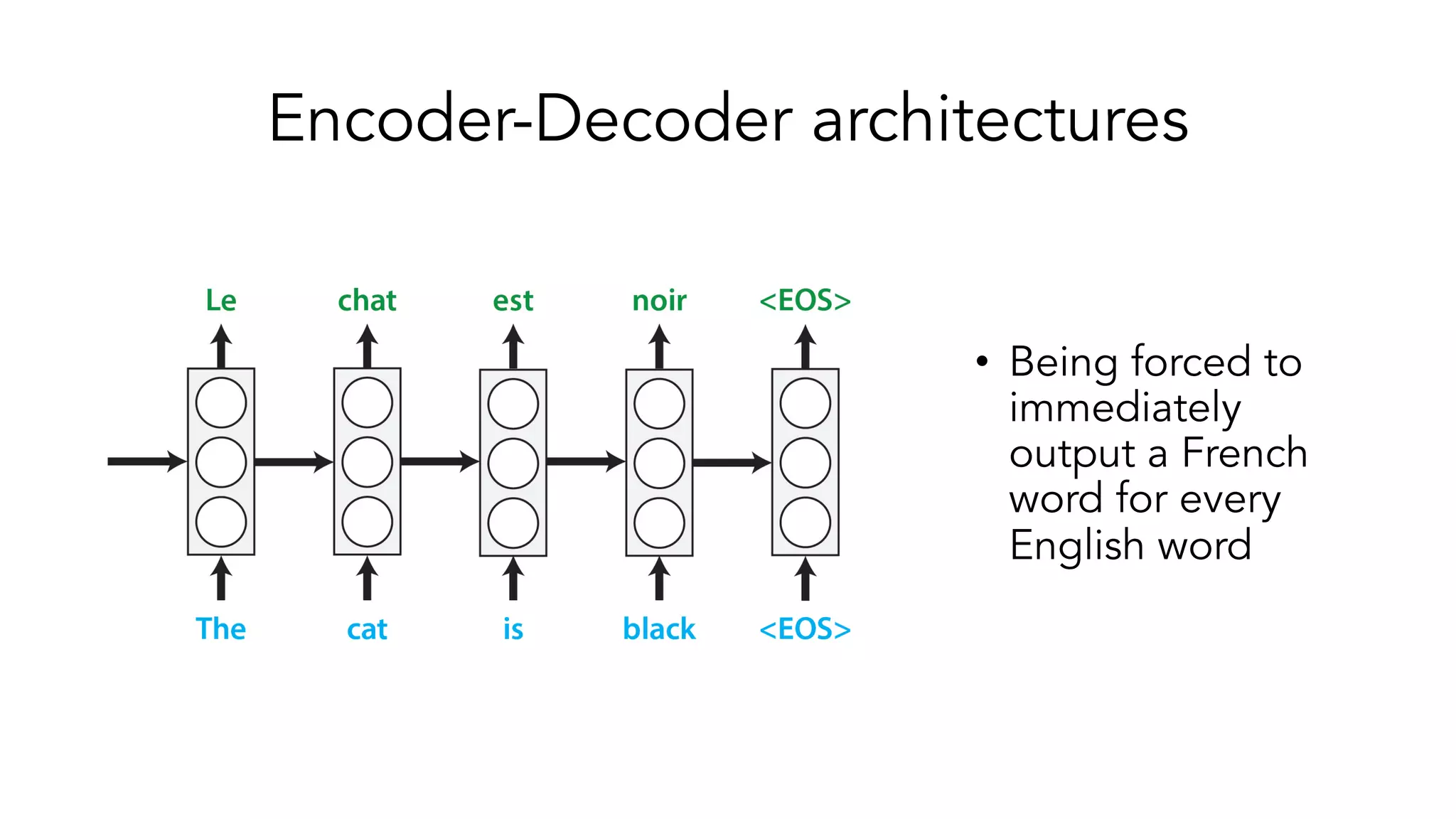
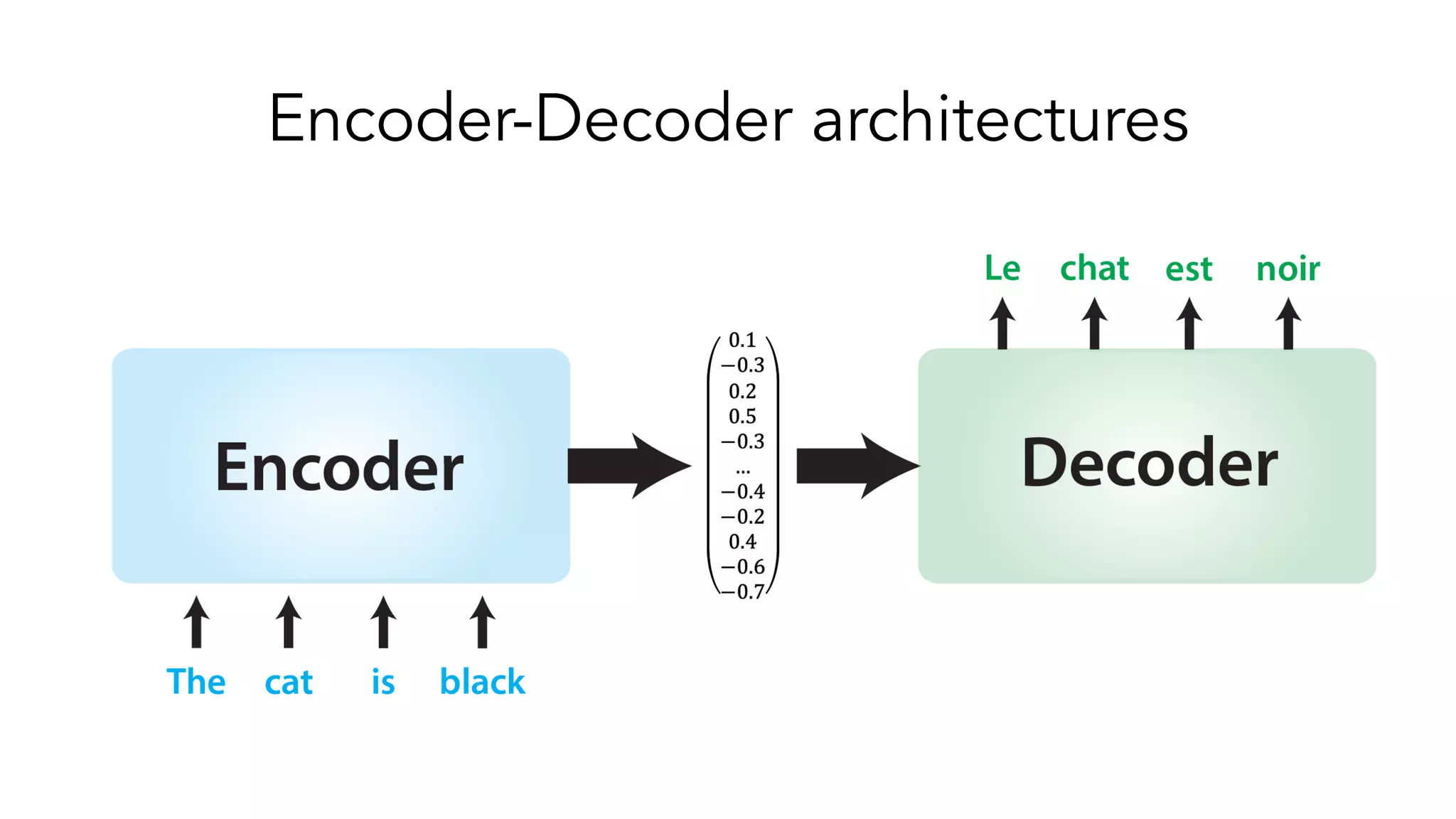
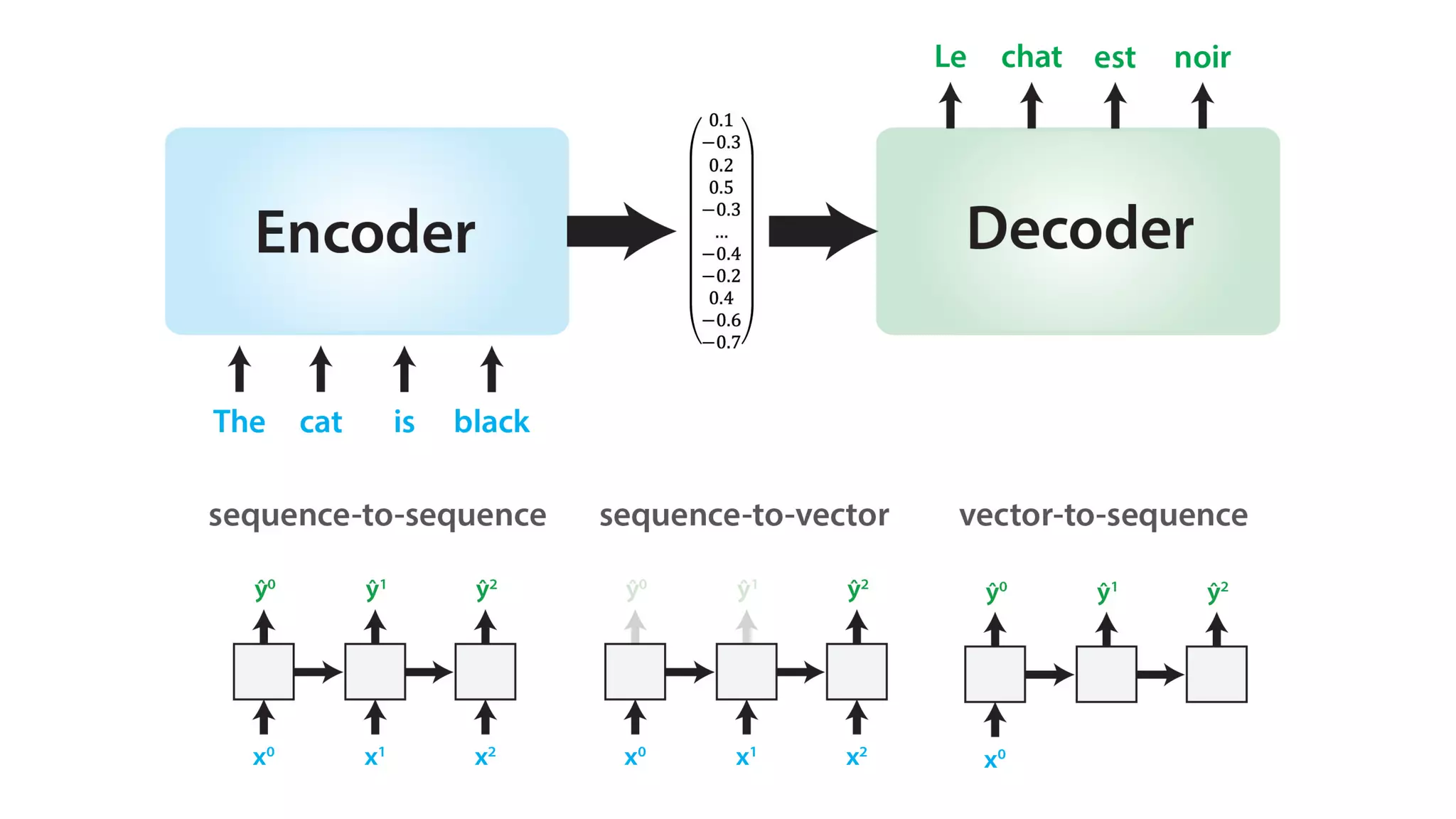
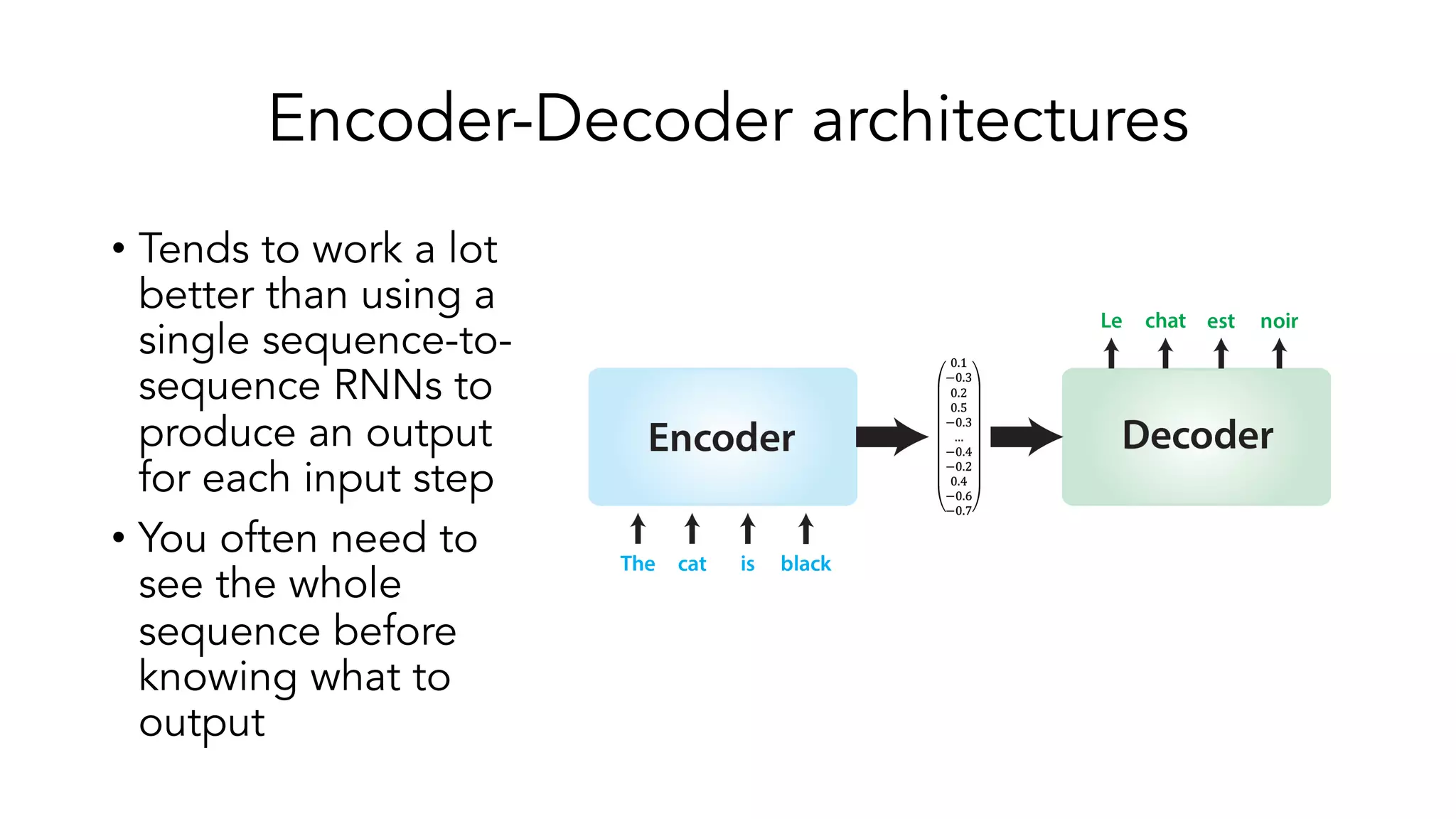
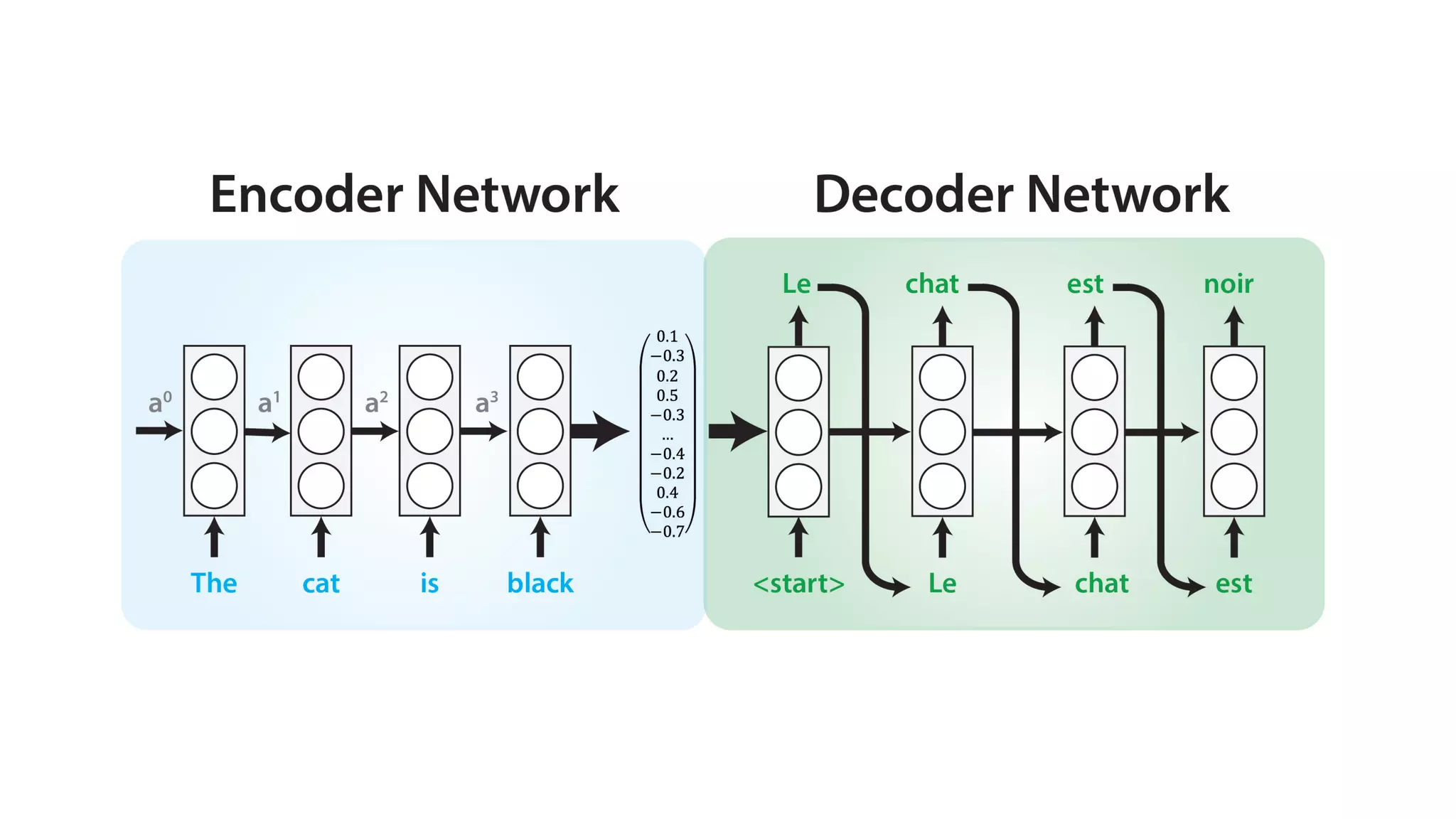
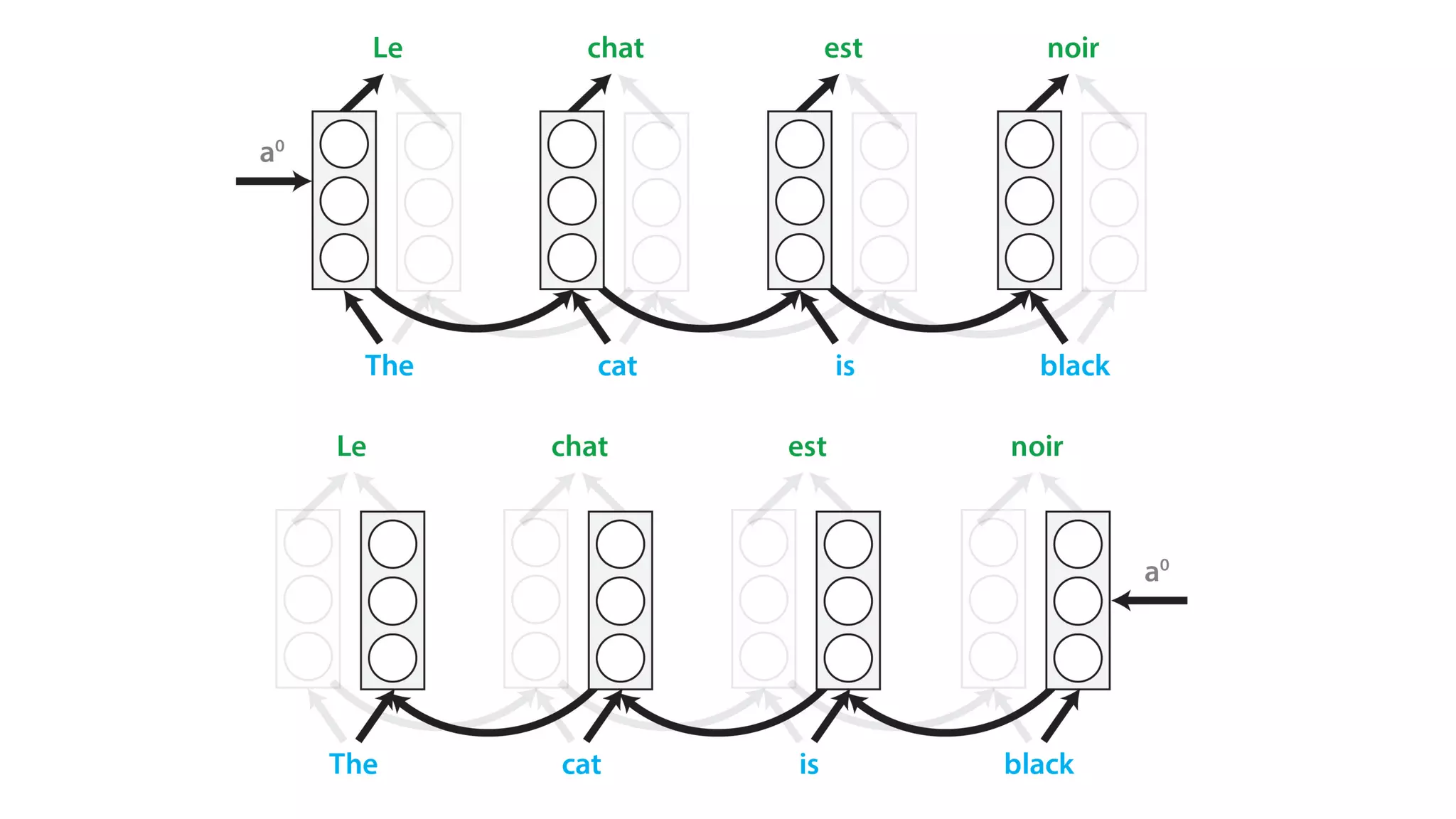
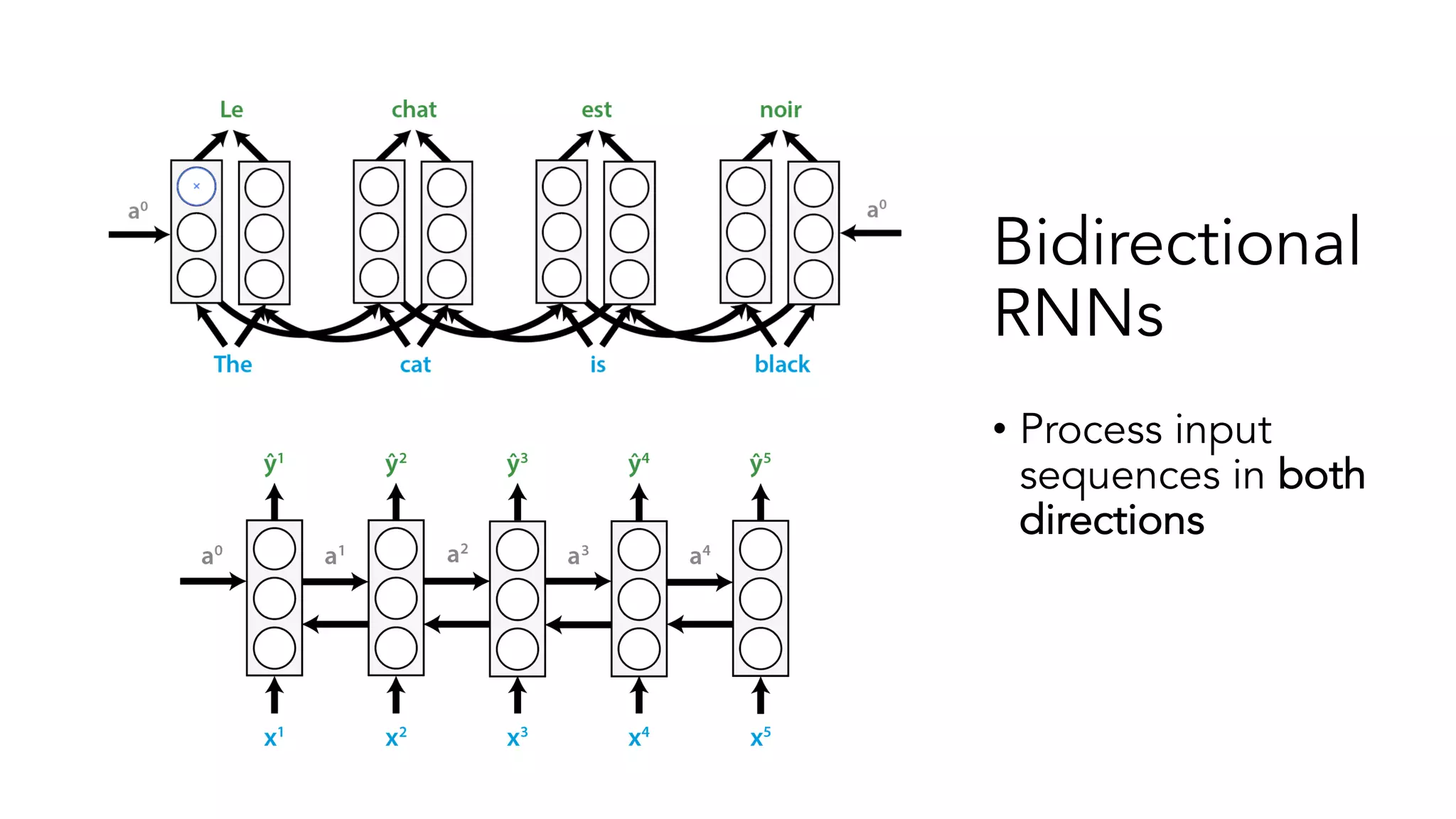
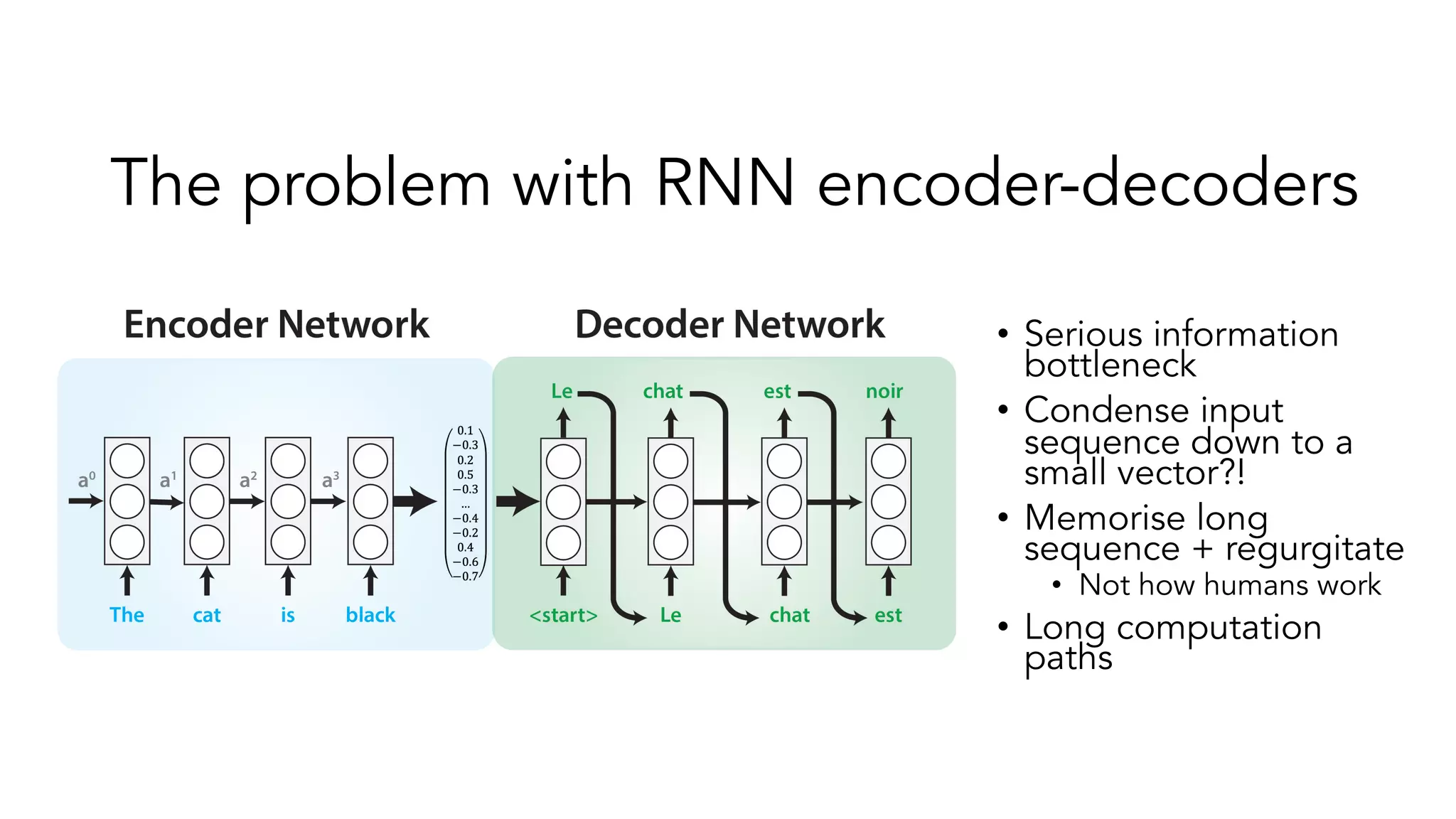
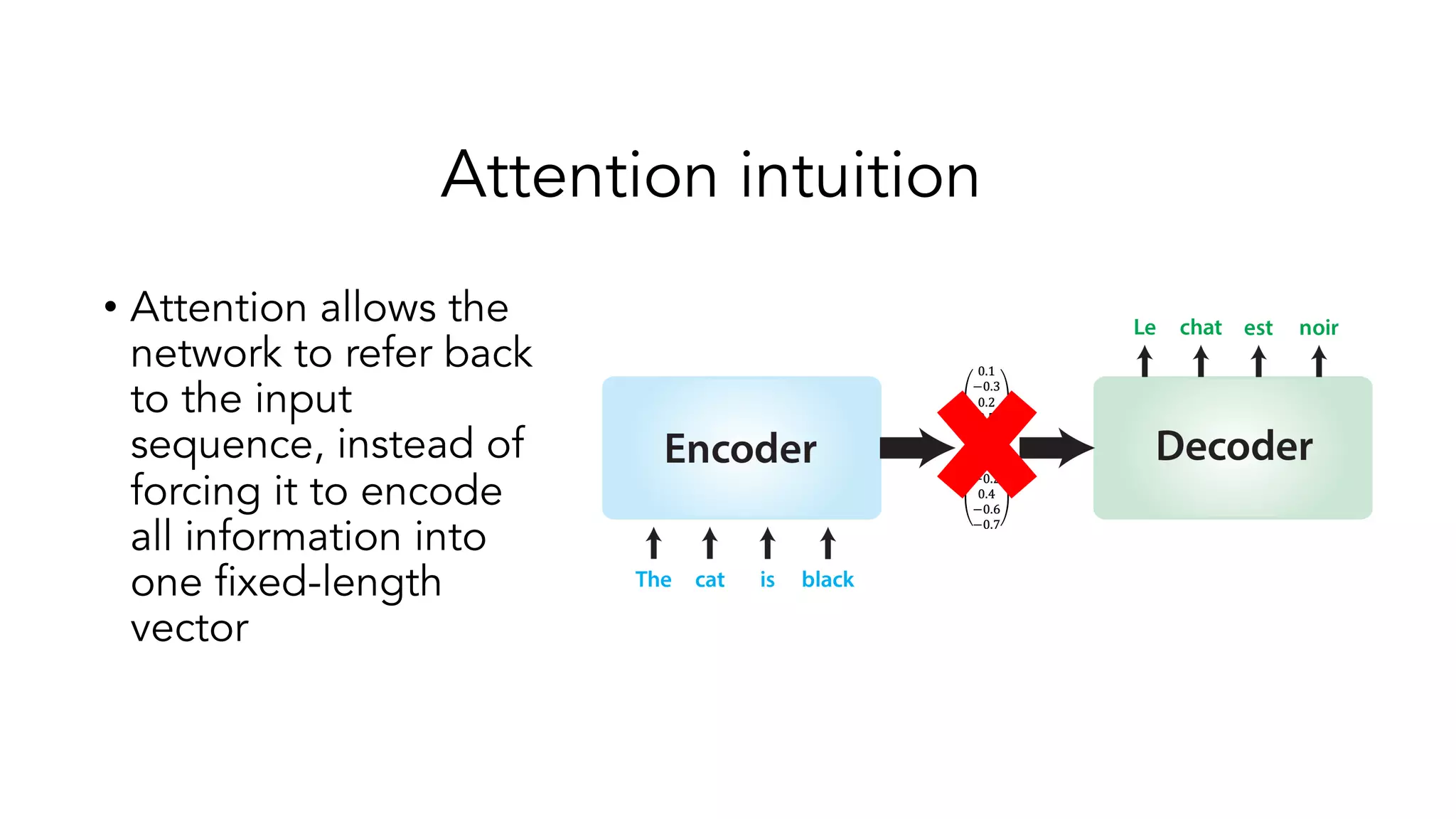
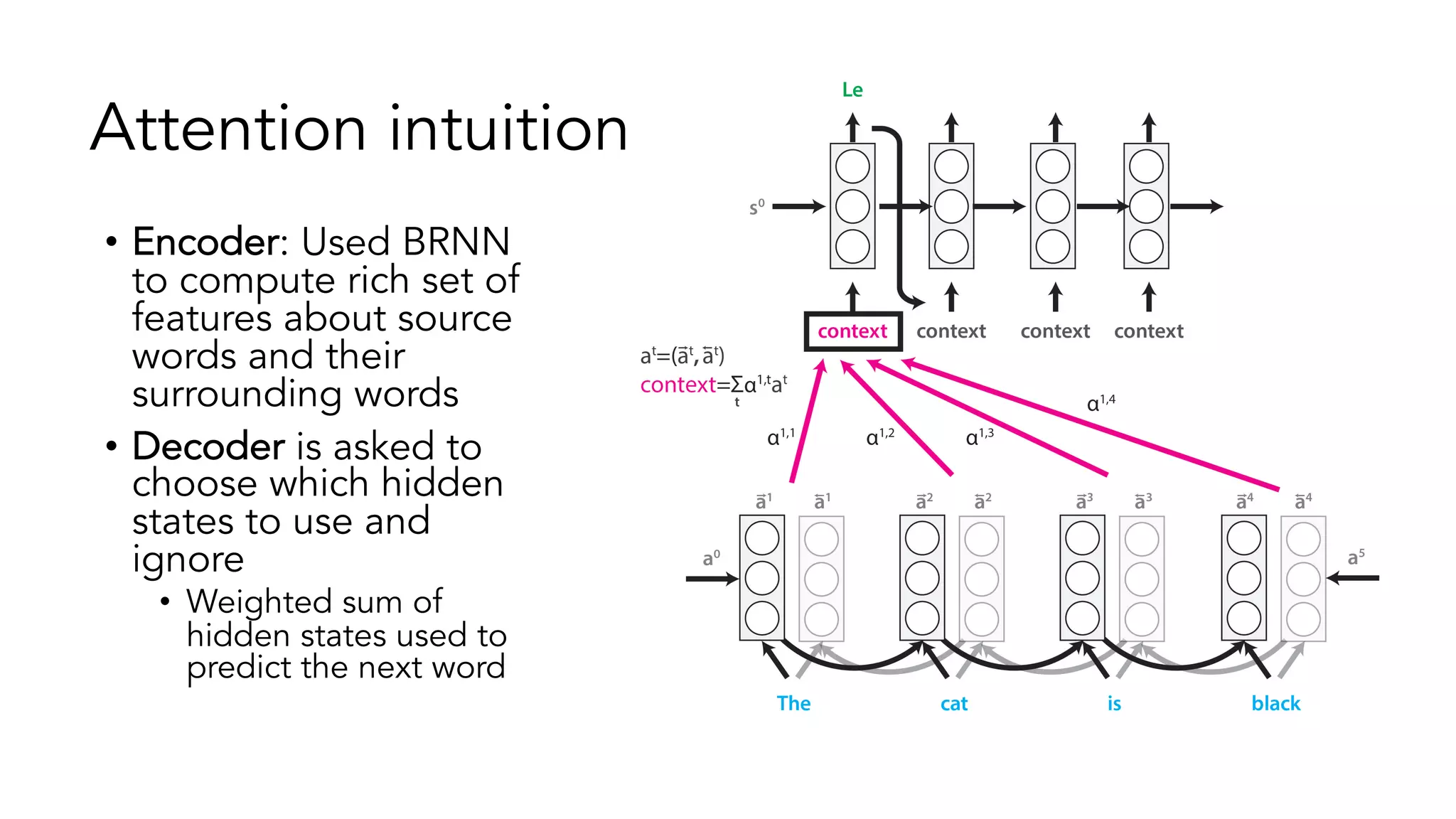
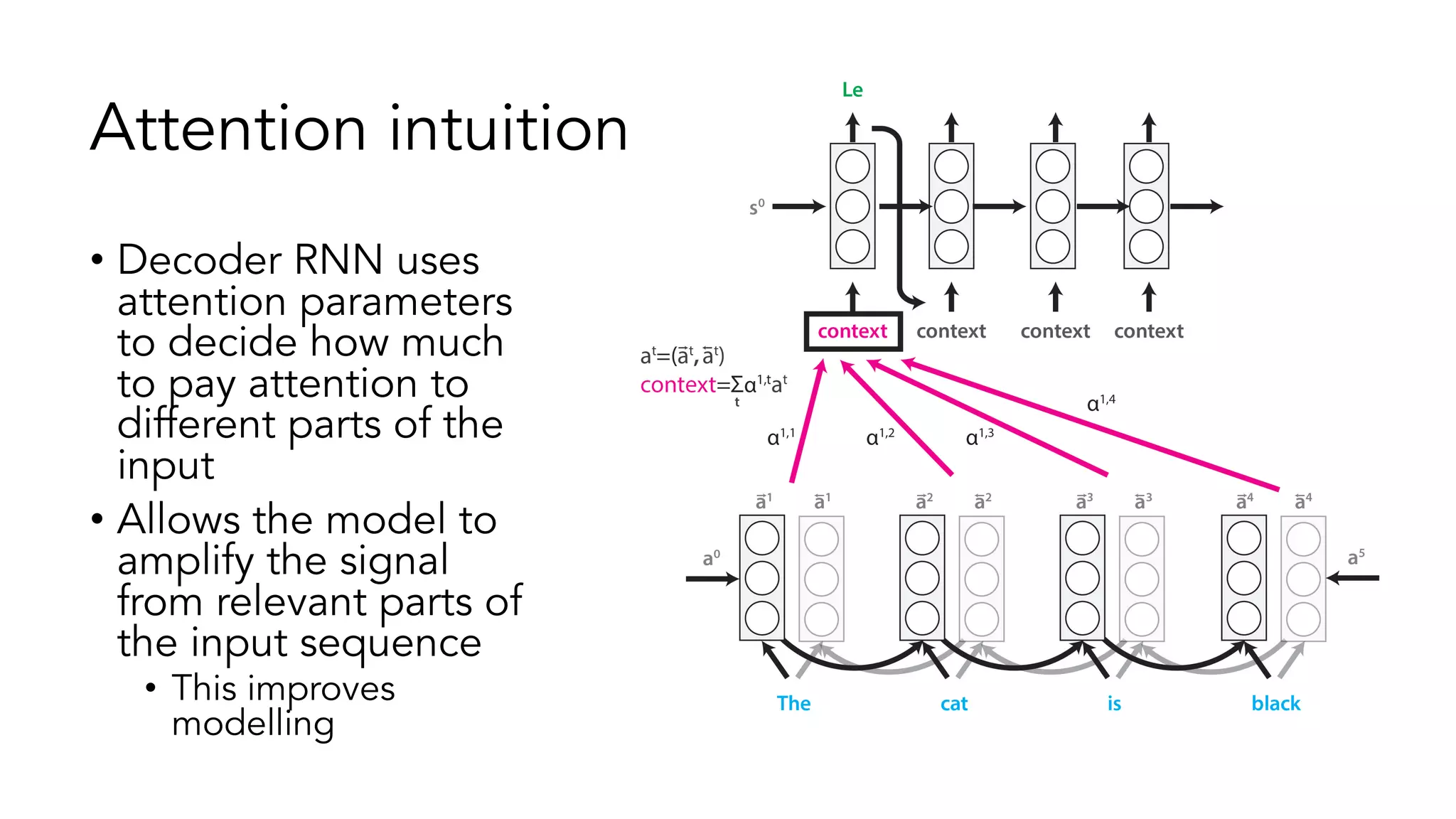
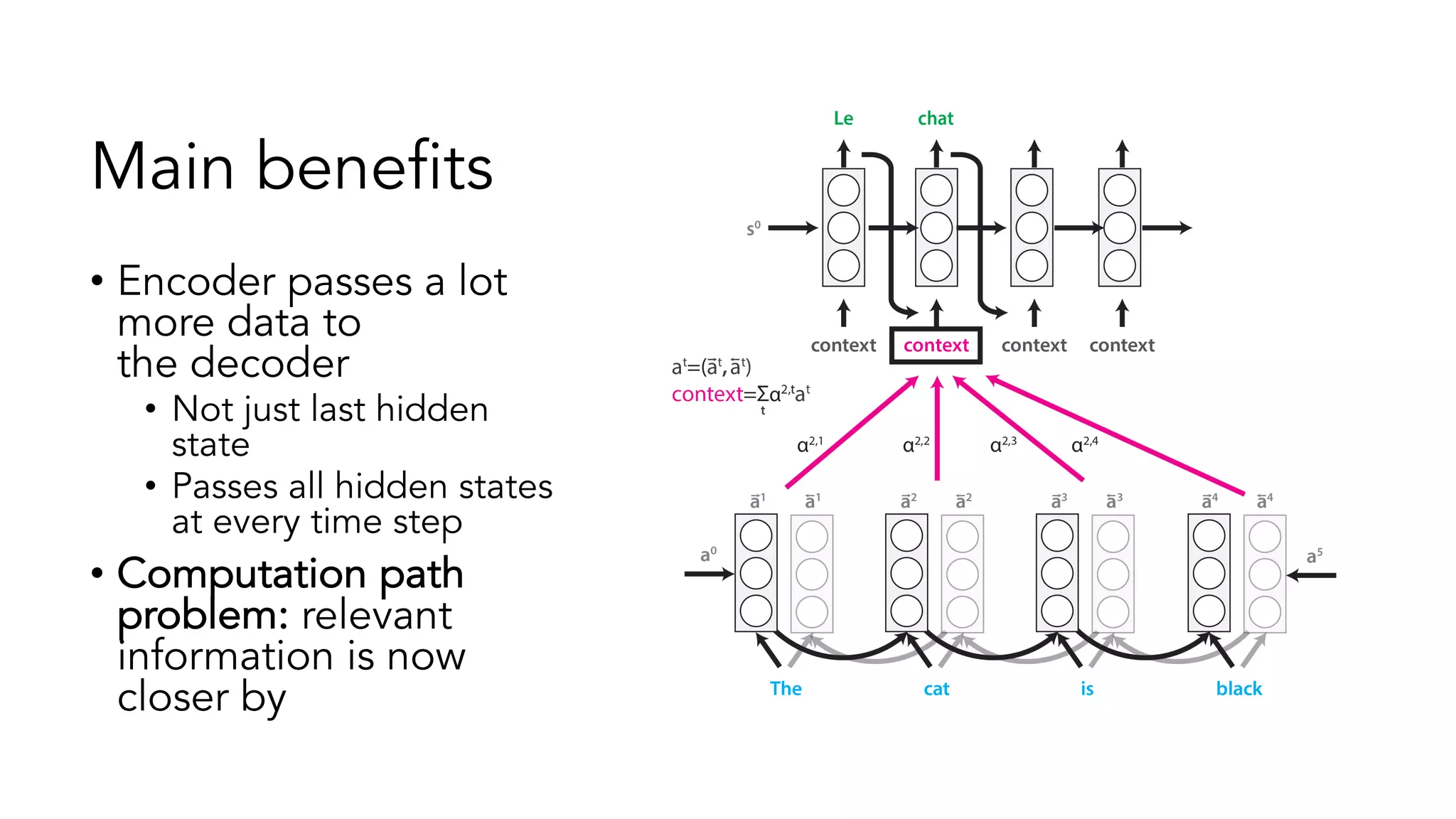
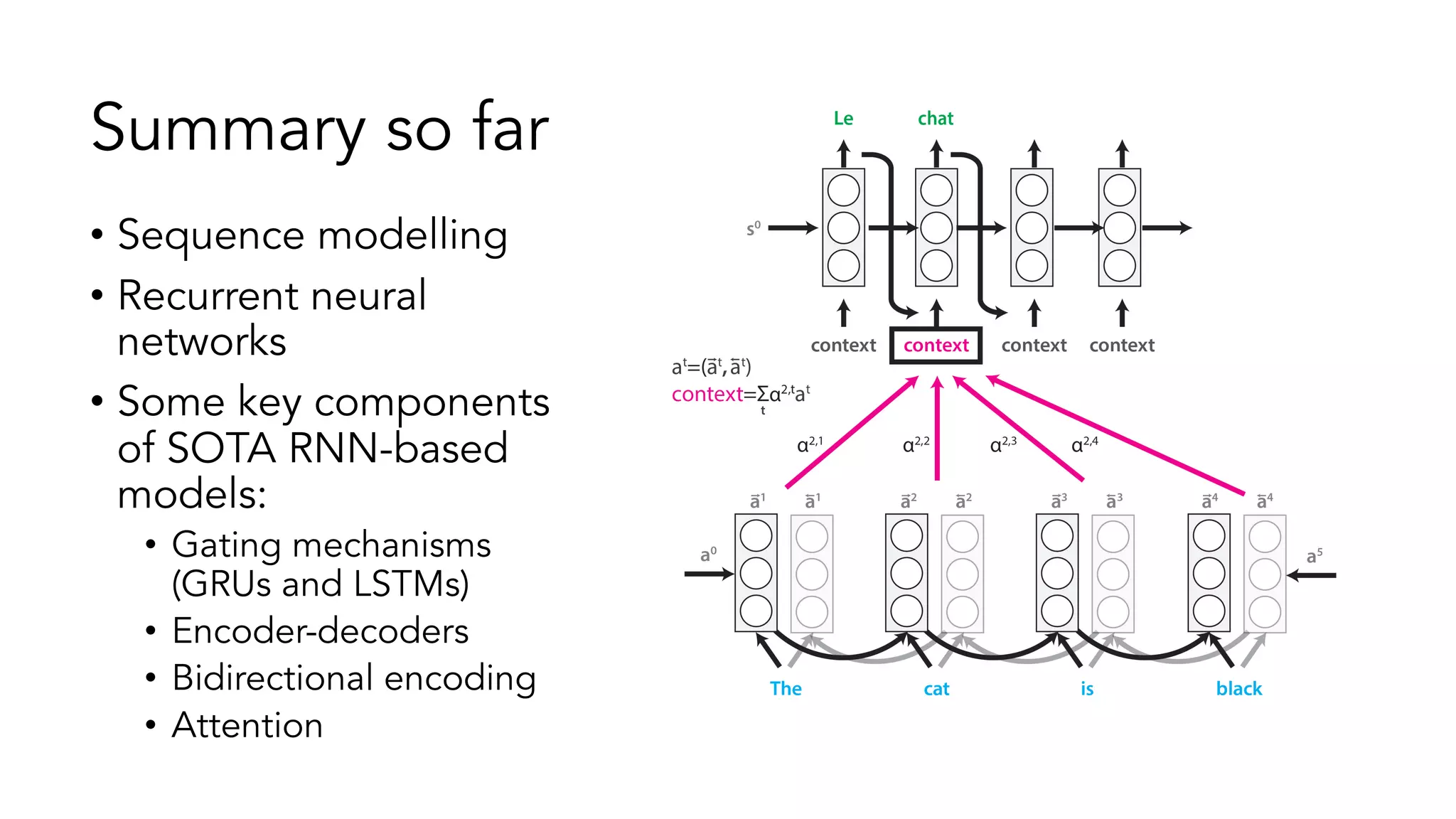
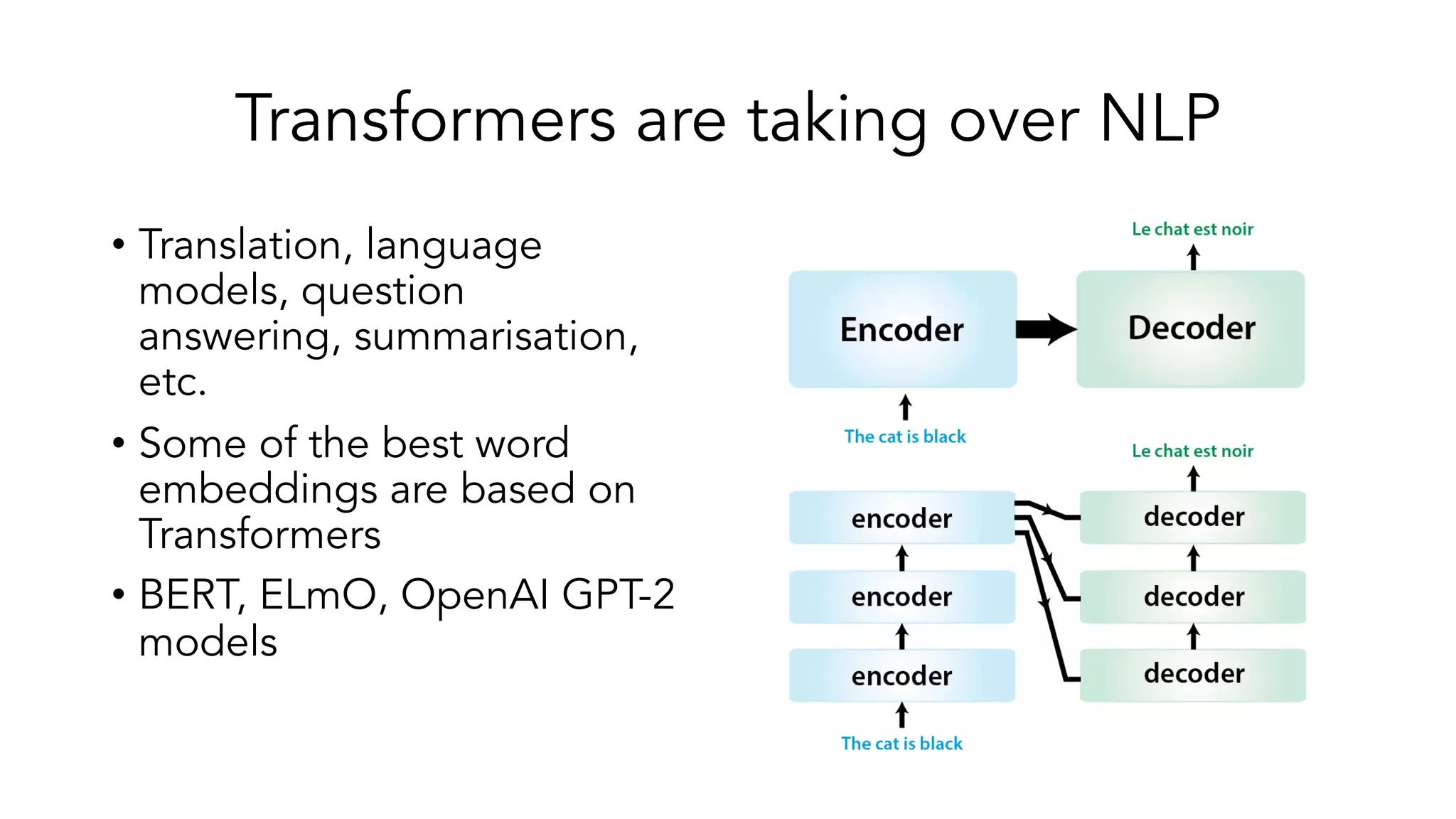
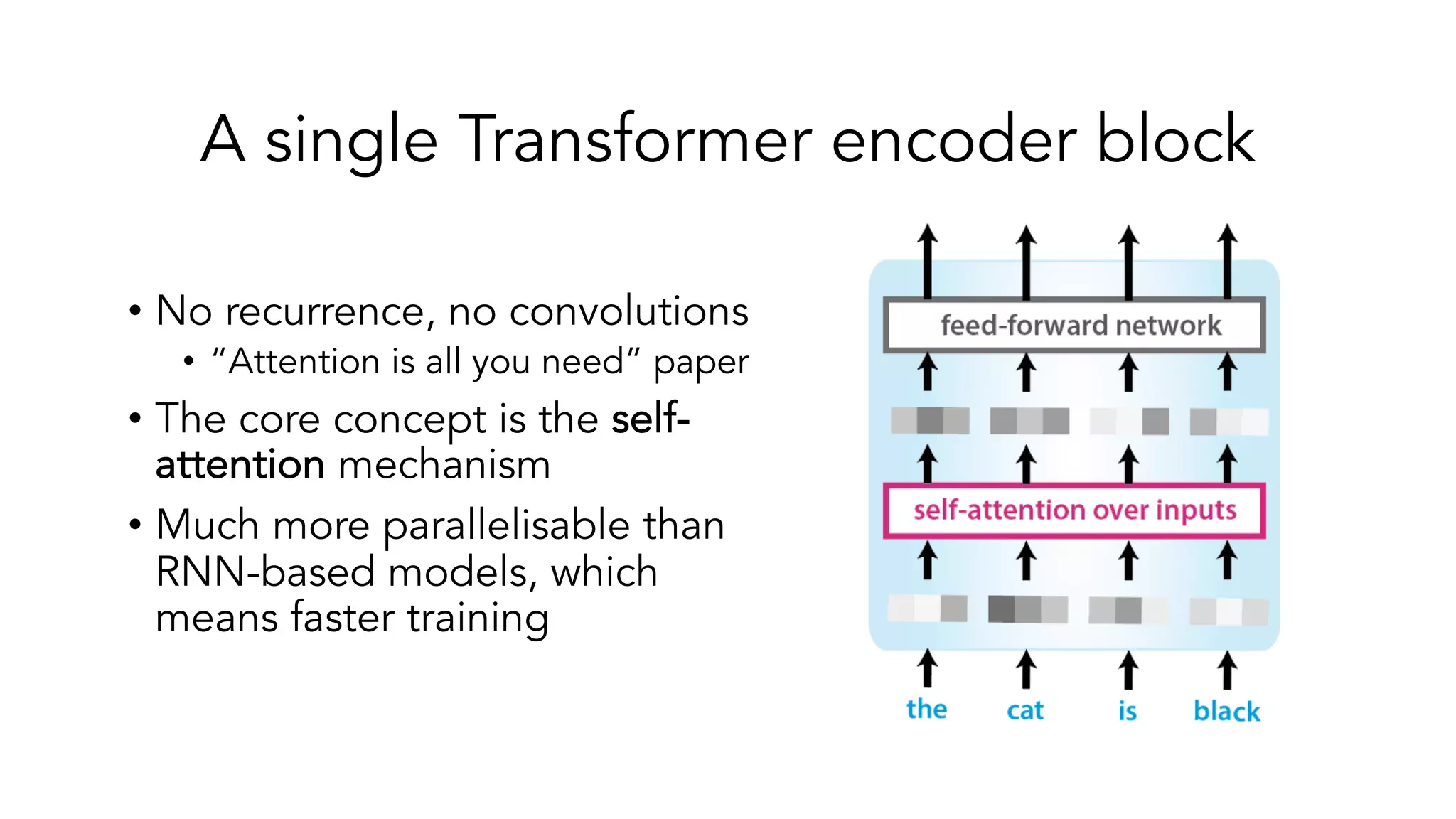
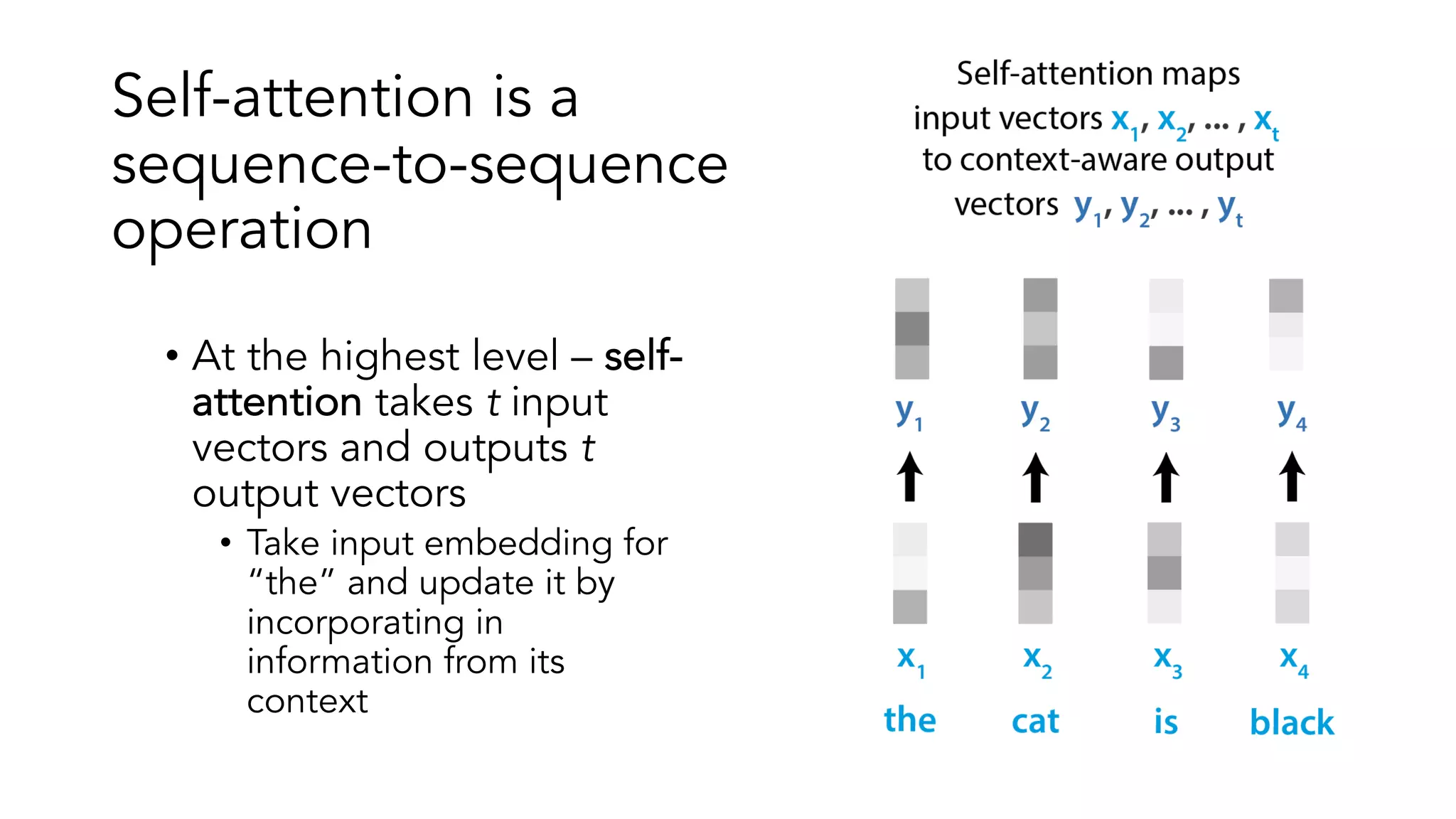
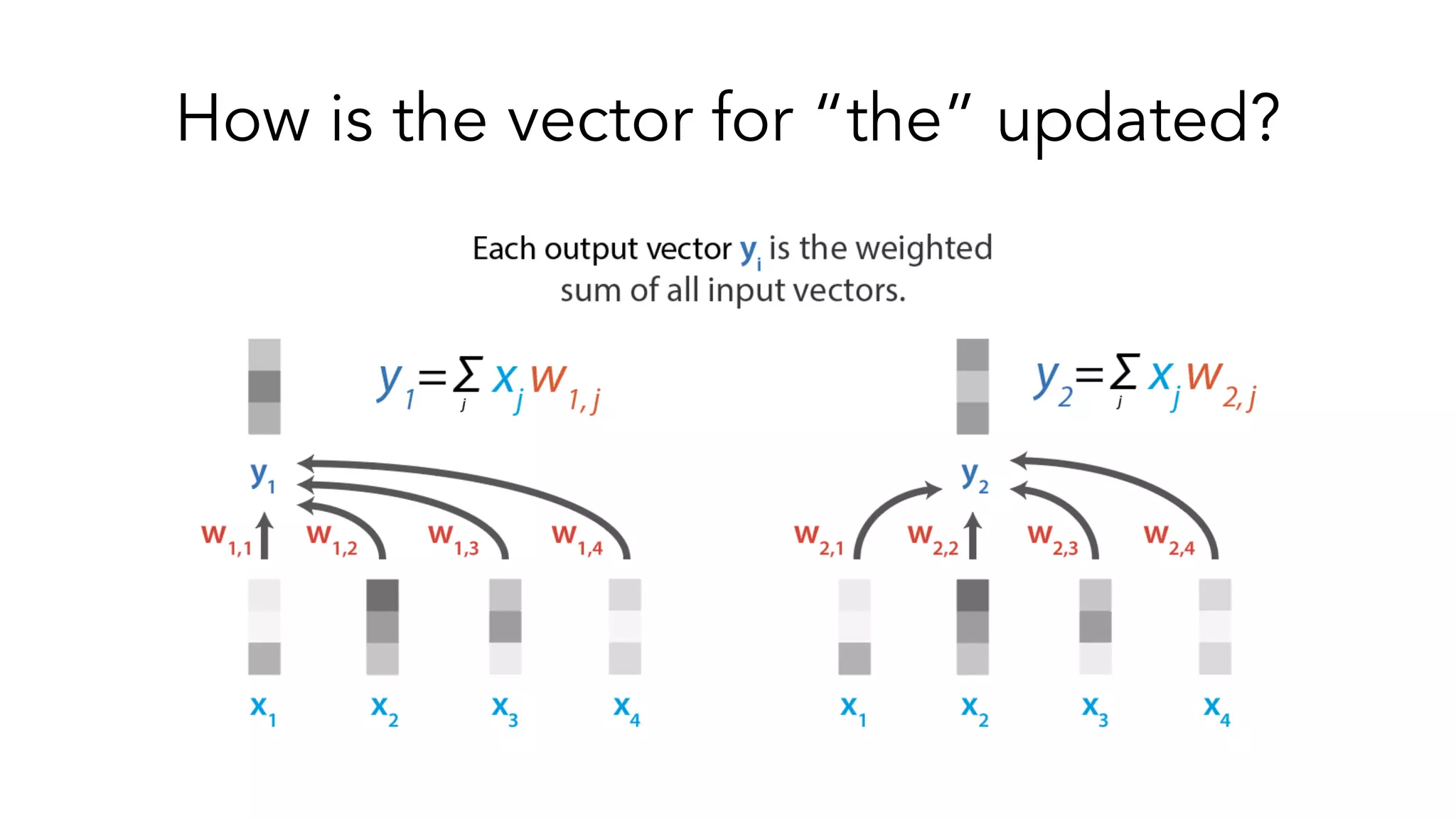
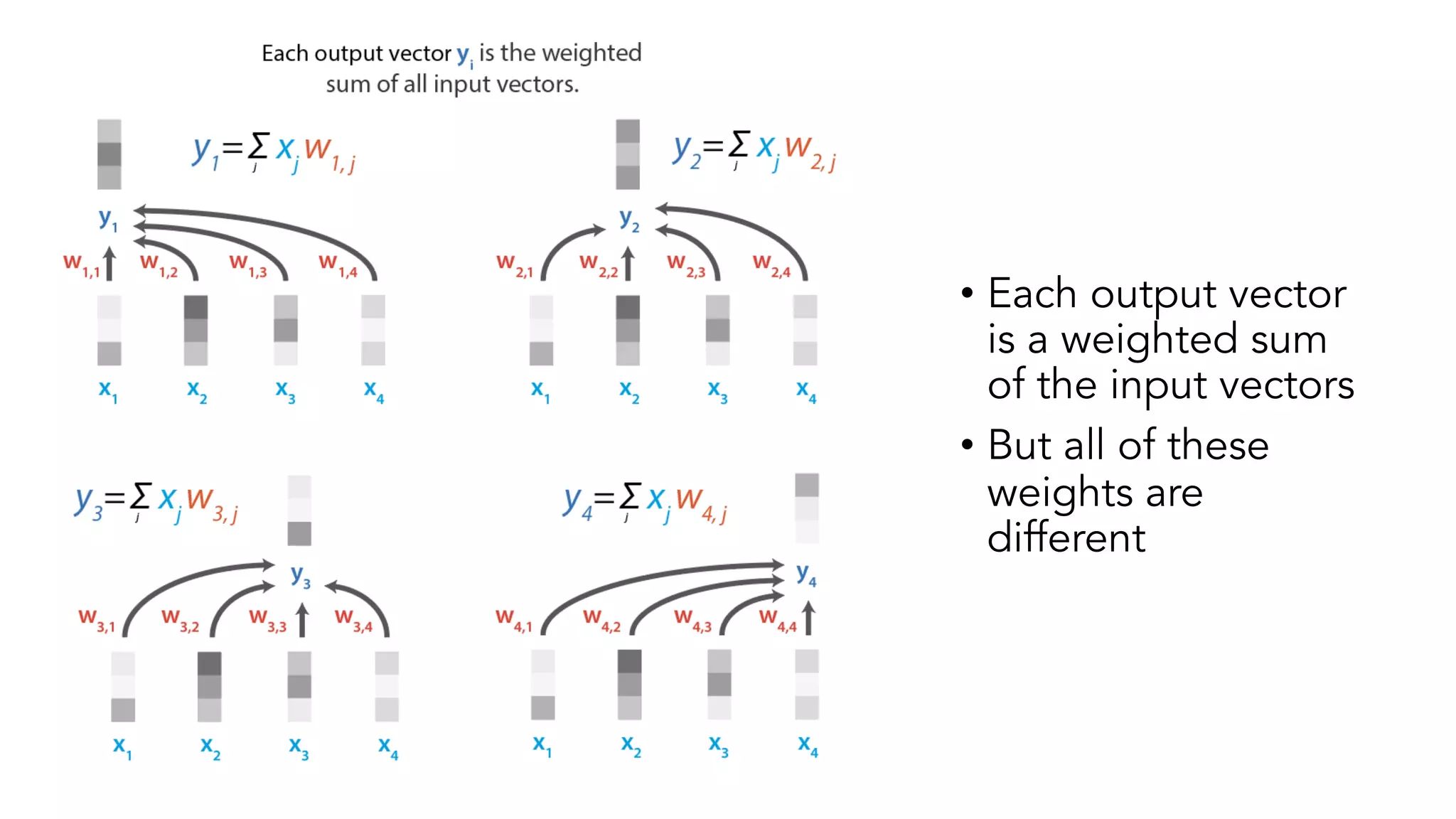
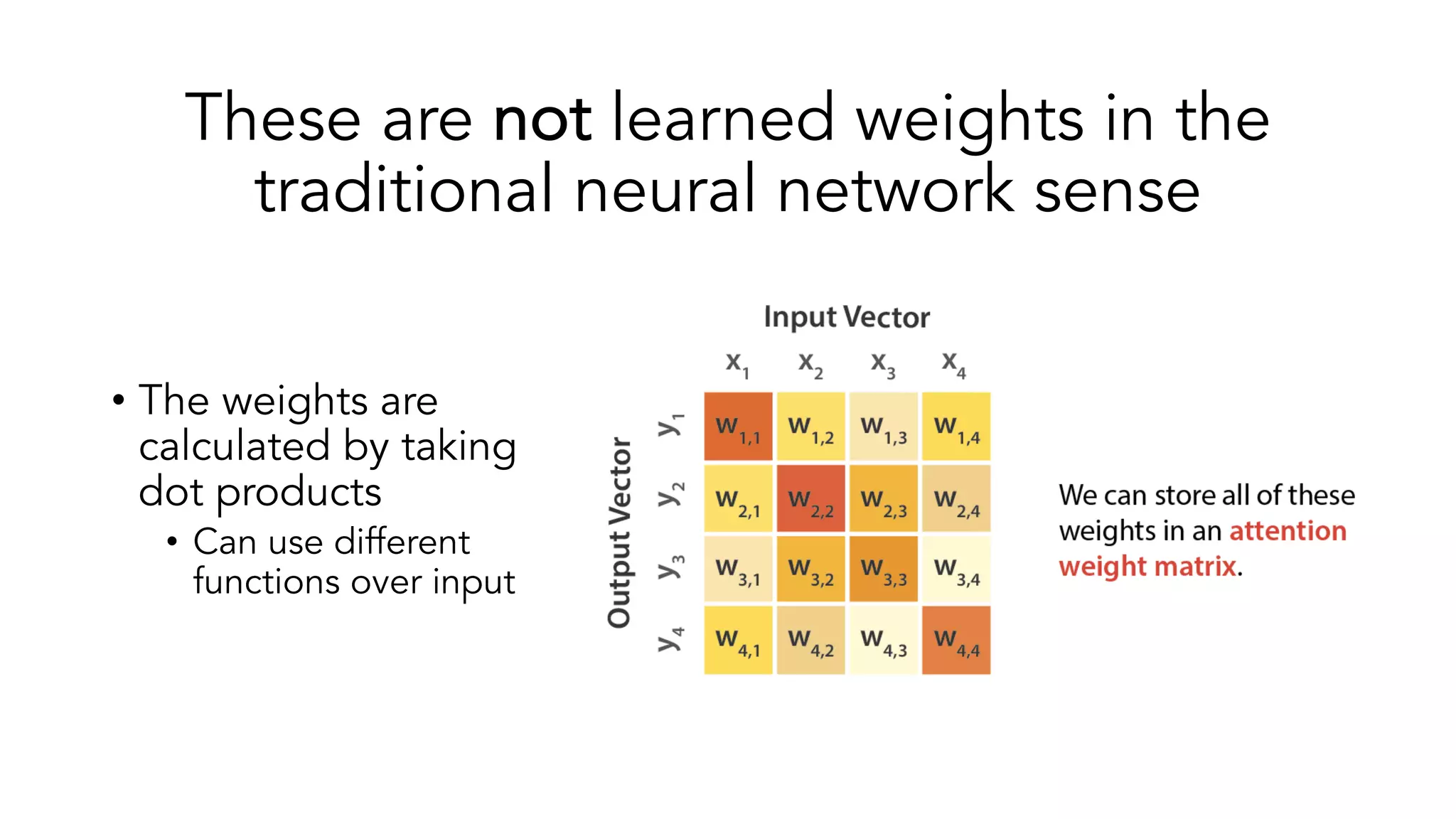
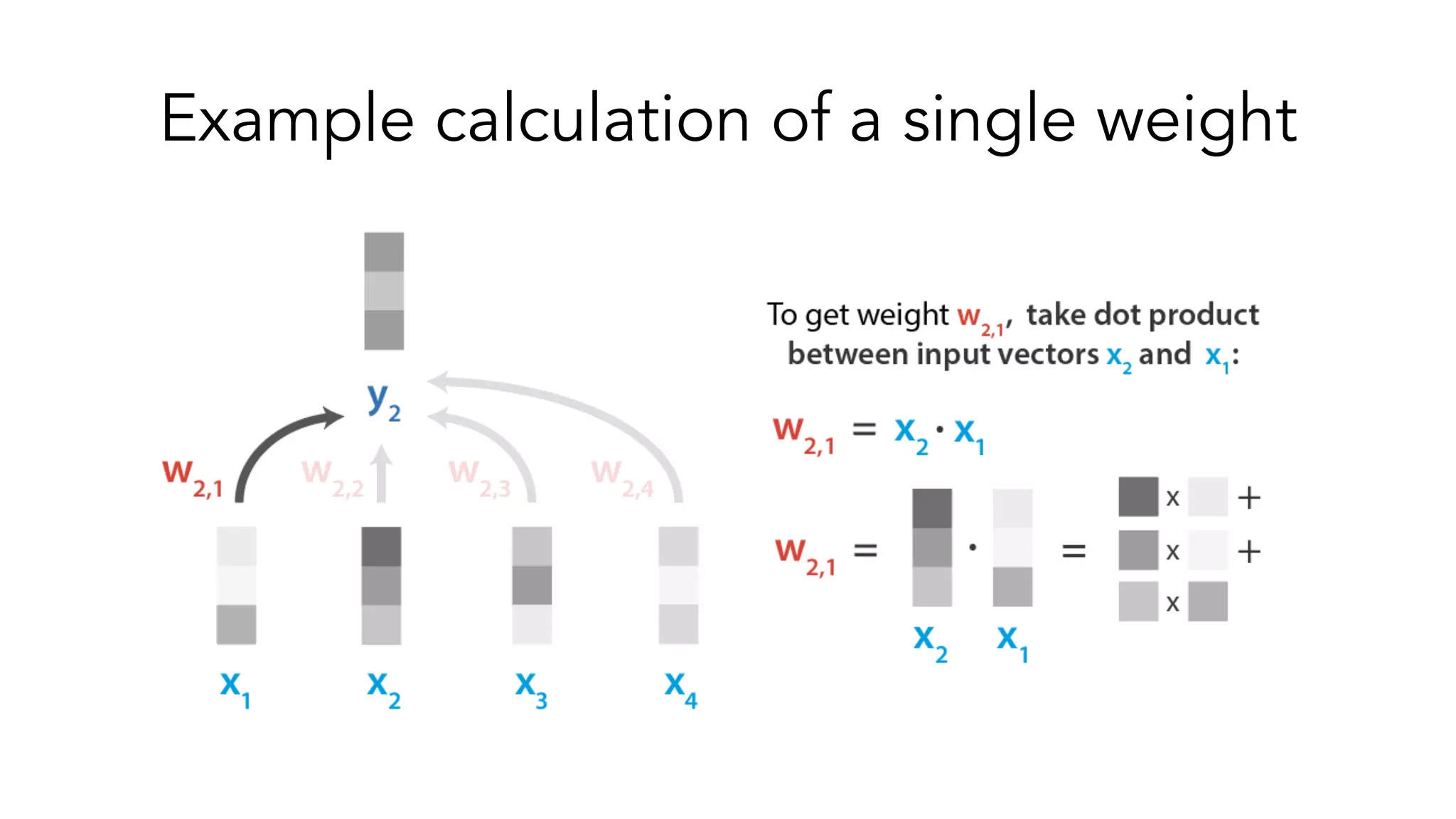
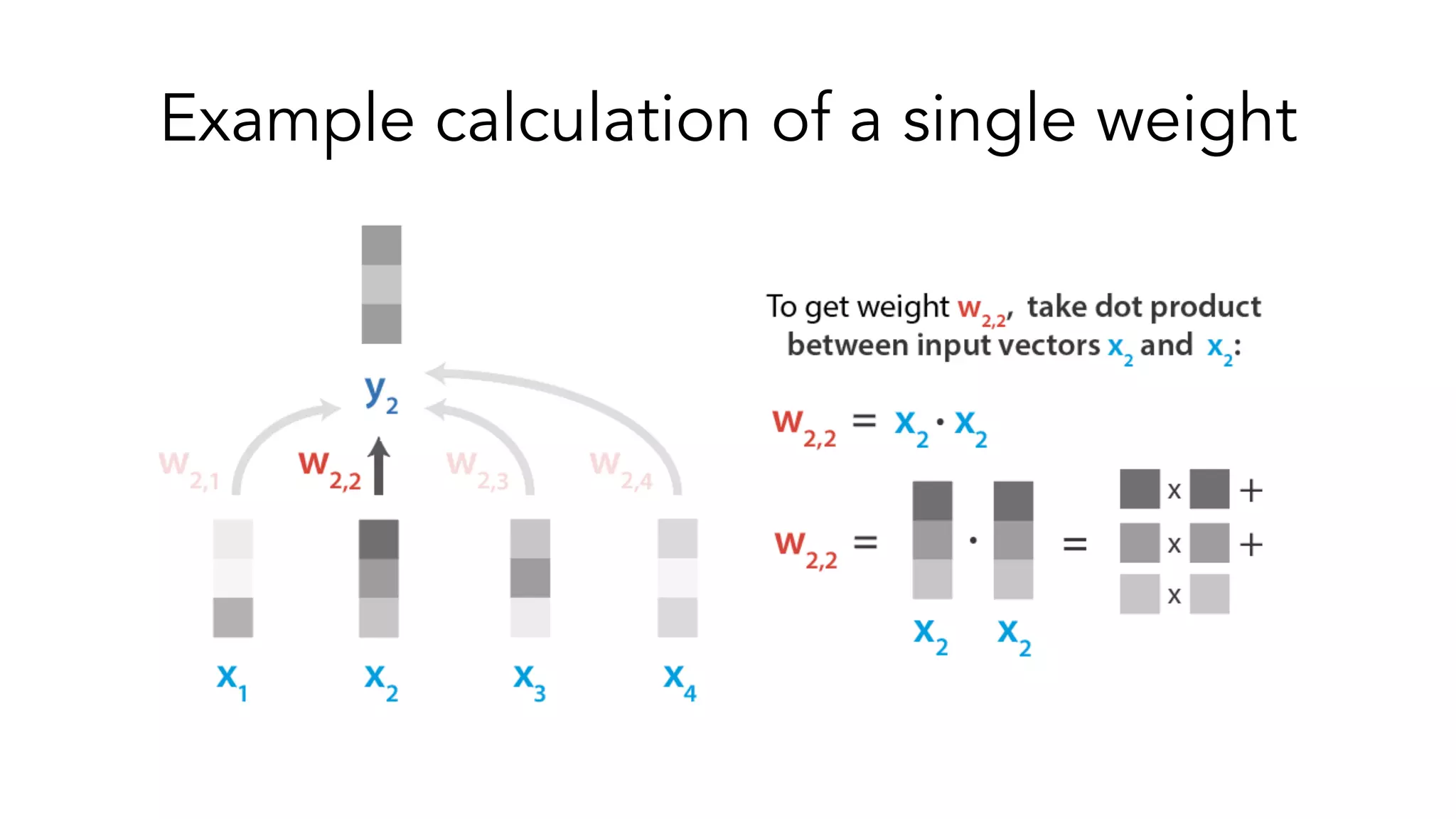
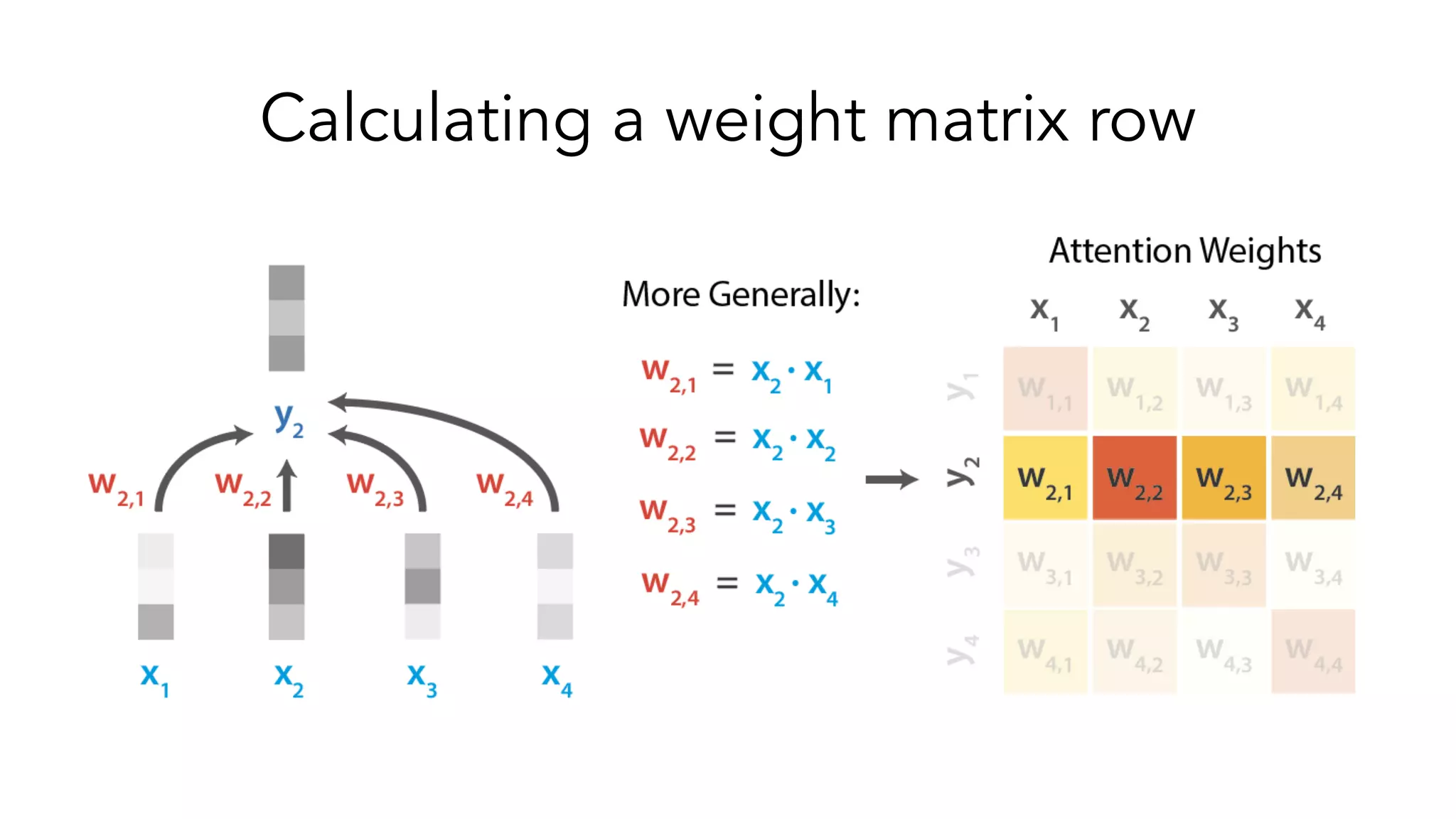
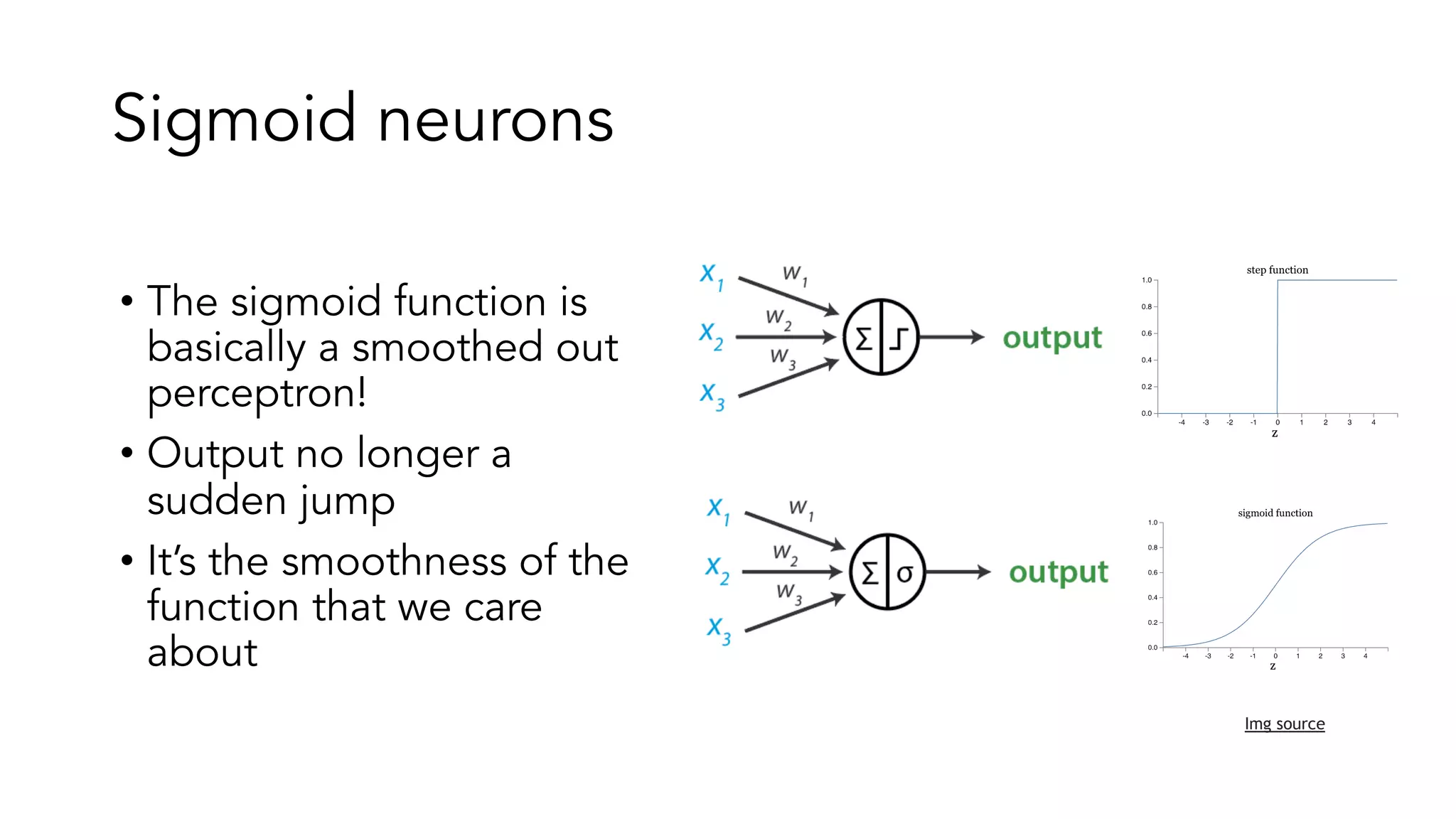
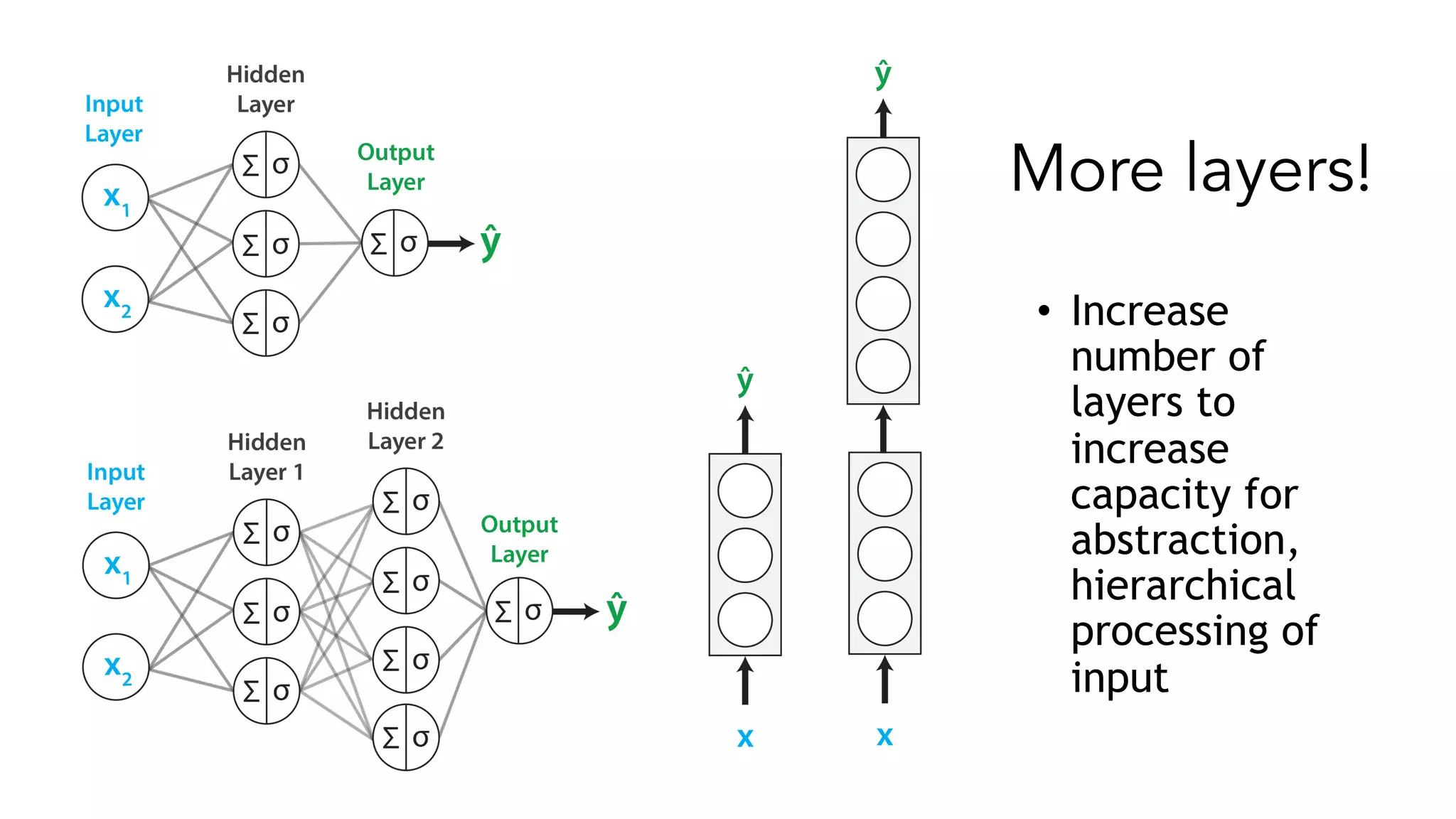
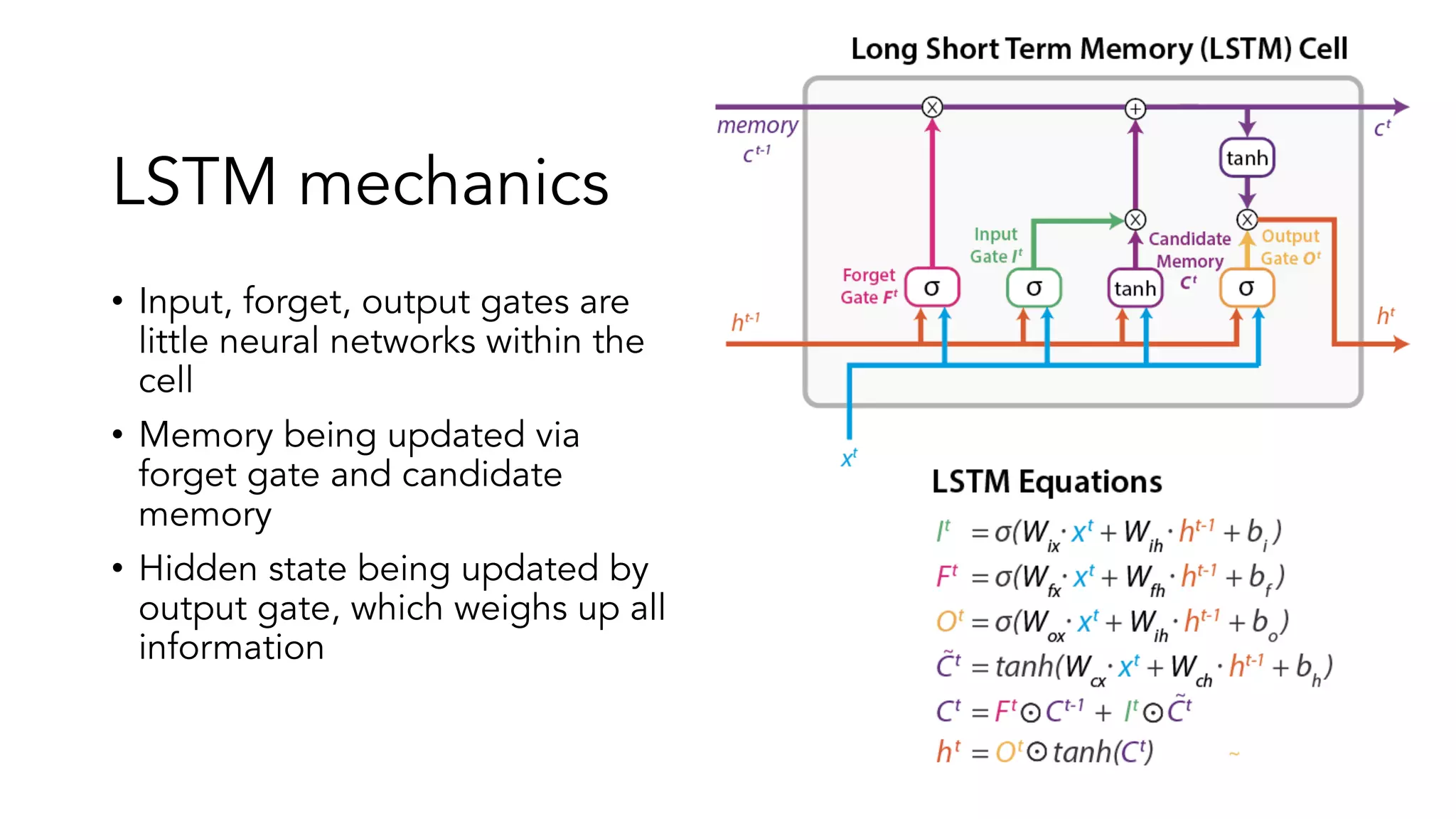
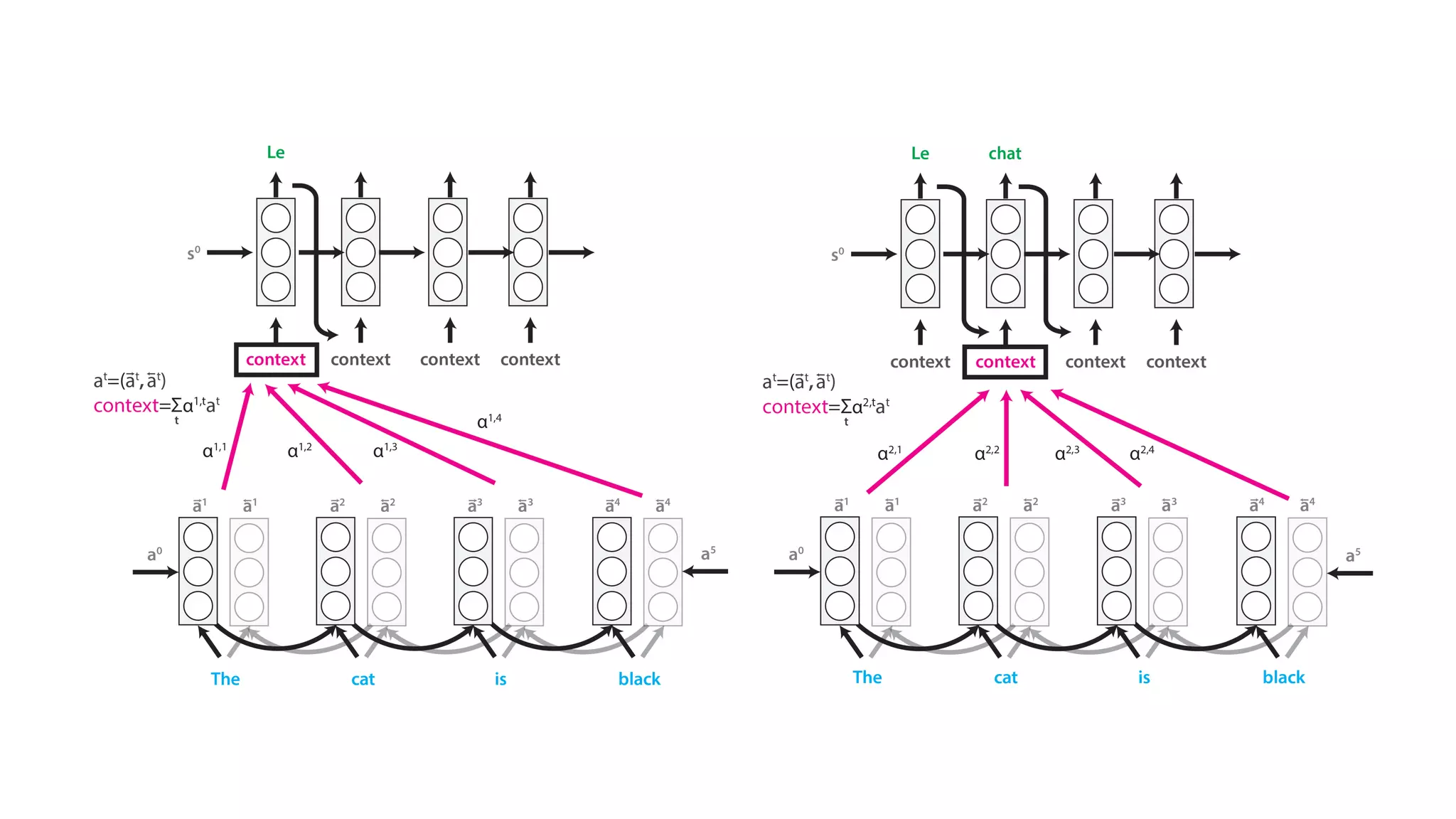
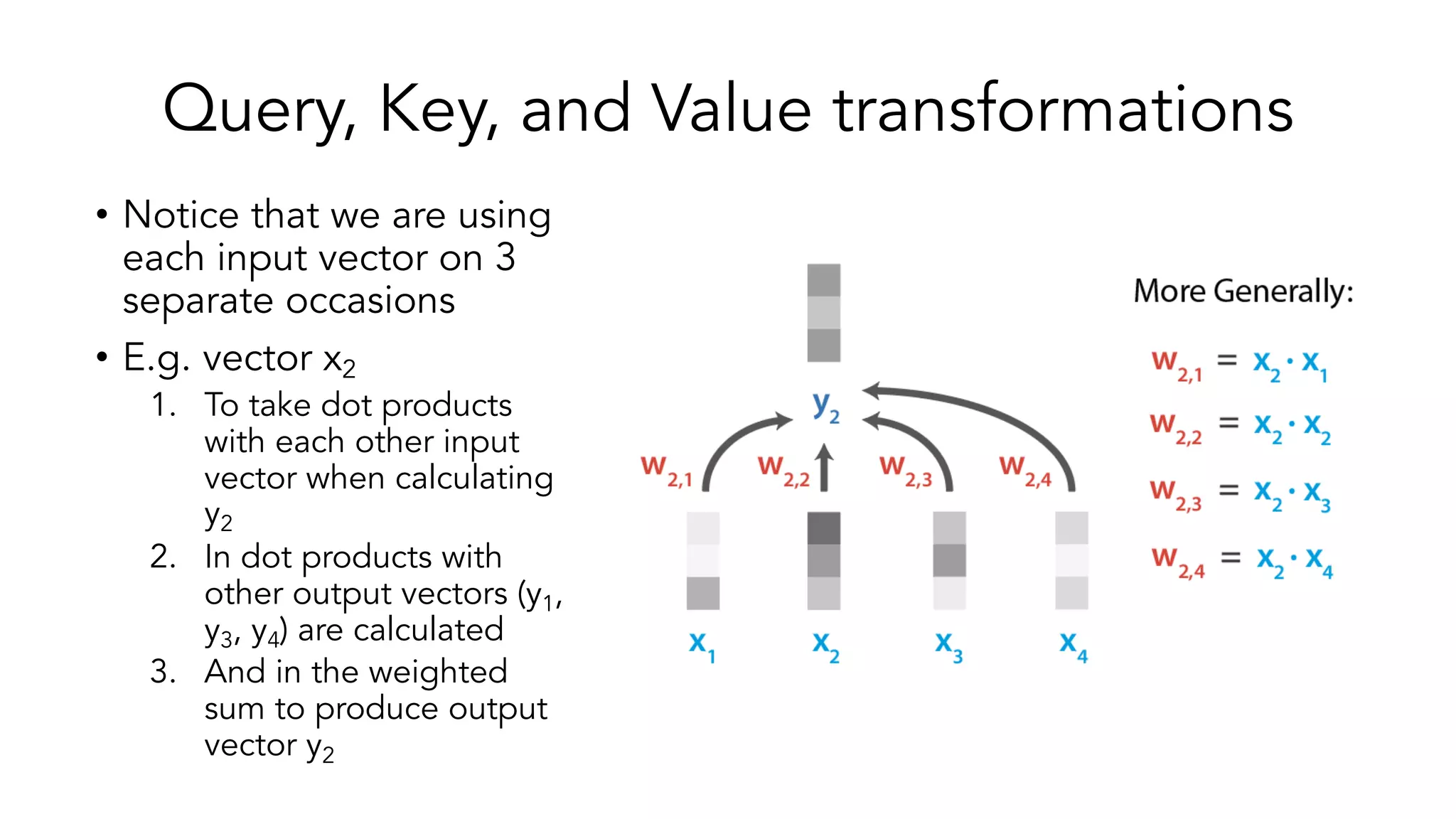
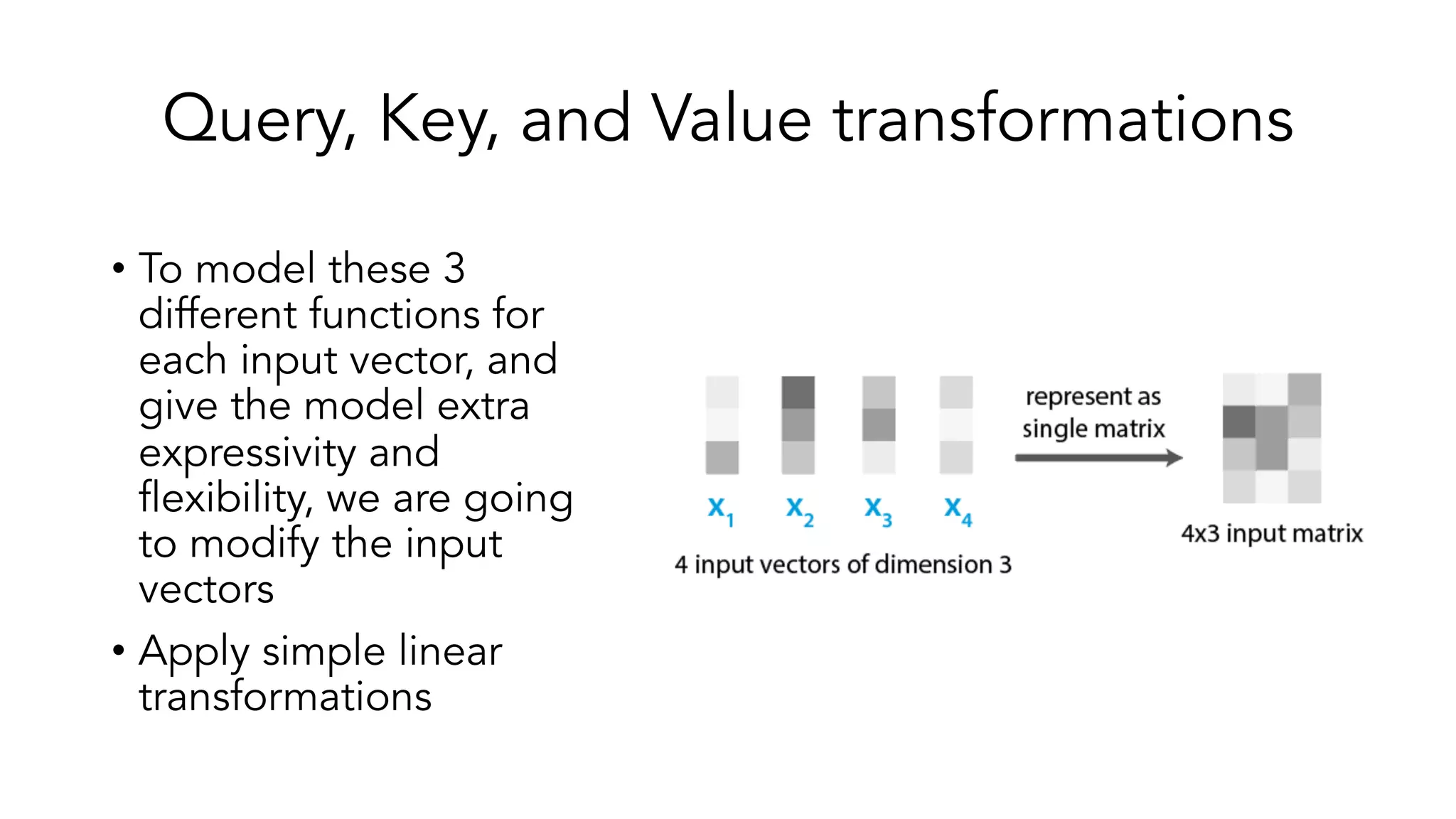
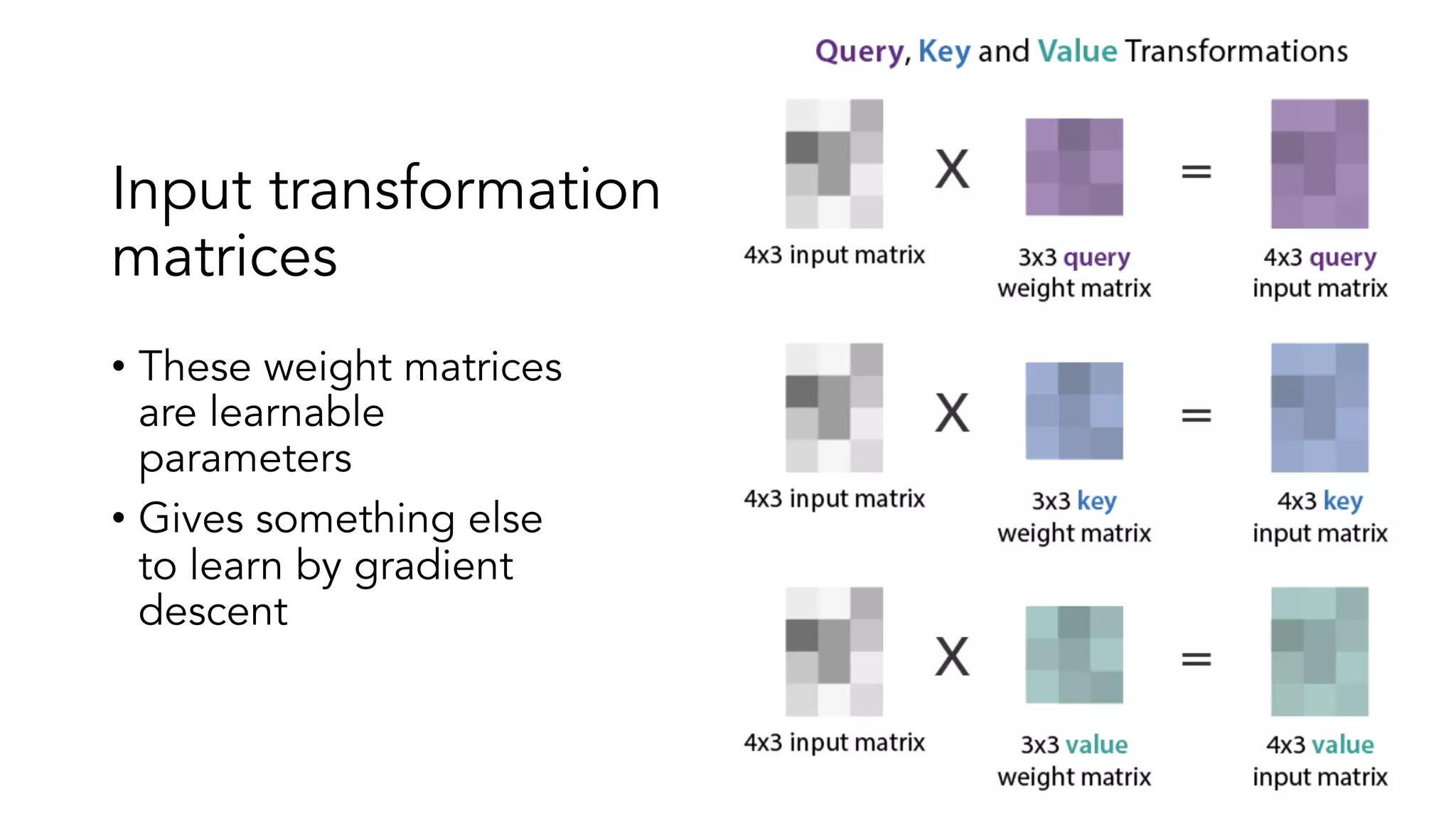
The document covers a tutorial on sequence modeling using deep learning, focusing on concepts such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs), gated mechanisms like GRUs and LSTMs, and advancements like encoder-decoder models and attention mechanisms. It highlights practical applications, including building a language model for 'Game of Thrones,' and the emerging importance of transformers in NLP. The tutorial provides a comprehensive overview of foundational neural network concepts, different types of sequential data, and their applications in various fields.




![Less conventional sequence data
• Activity on a website:
• [click_button, move_cursor, wait,
wait, click_subscribe, close_tab]
• Customer history:
• [inactive -> mildly_active ->
payment_made -> complaint_filed
-> inactive -> account_closed]
• Code (constrained language) is
sequential data – can learn the
structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningforsequences-191217160716/75/Sequence-Modelling-with-Deep-Learning-7-2048.jpg)