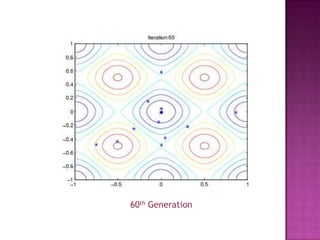
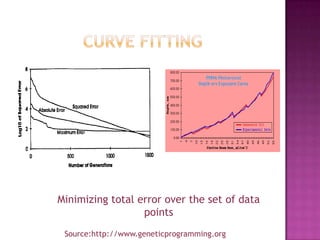
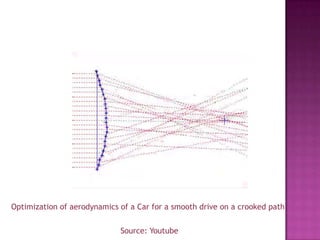
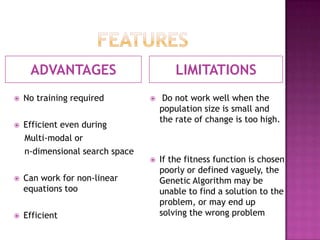
This document discusses genetic algorithms and their applications. It explains key concepts like genetic crossover, genetic algorithm steps to solve optimization problems, and how genetic algorithms mimic biological evolution. Examples are provided of genetic algorithms being used for tasks like predicting protein structure, automotive design optimization, and generating musical variations. Advantages and limitations of genetic algorithms are also summarized.