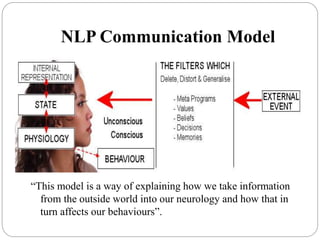
The document provides an overview of neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) including its connections to neurology, linguistics, and programming. NLP relates to how people think, process information through their senses, use language, and achieve goals. It involves principles like rapport, flexibility, and outcome-focused thinking. NLP can be used for self-development and overcoming challenges by changing behaviors and habits.