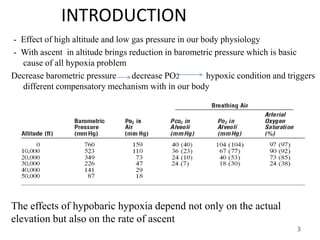
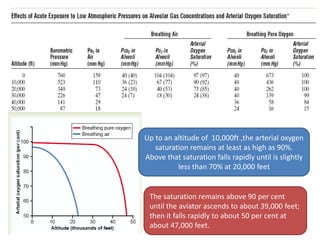
This document discusses physiology adaptations to high altitudes. It begins with an introduction on how decreasing barometric pressure with increased altitude causes hypoxic conditions. It then discusses how alveolar PO2 and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin decrease with altitude. The body acclimates to low PO2 through increased pulmonary ventilation, erythropoiesis, diffusing capacity, tissue capillarization, and cellular adaptations. Chronic mountain sickness can occur if exposed too long at high altitudes. Natives at high altitudes have genetic adaptations like increased chest sizes and cardiac outputs that allow them to tolerate low oxygen environments.


![ALVEOLAR Po2 AT DIFFERENT ELEVATIONS
Carbon dioxide and water vapor dilute the oxygen in the alveoli
In high altitude, alveolar PCo2 falls from 40 mm Hg [sea level] to
lower values[ in acclimatized falls to about 7mm Hg]
4
Mt.EVEREST
8848m 760 mm Hg
253 mm Hg 47 mm Hg[water vapor]
7 mm Hg [PCo2]
40mm Hg[PO2]
159 mm Hg[PN2]
Some alveolar oxygen is continually
absorbed into pulmonary capillaries leaving
35 mm Hg pressure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highaltitudephysiology01-191222150824/85/High-altitude-physiology01-4-320.jpg)
![• ACUTE EFFECT OF HYPOXIA
At 10000 feet = hyperventilation leading to respiratory alkalosis
Above 12000 feet = drowsiness, lassitude, mental and muscles
fatigue sometimes headache, occasionally nausea and sometimes
euphoria
Above 18000 feet = effects progress to a stage of twitching or
seizure
Above 23000 feet = loss of consciousness [coma] followed
shortly there after by death
6
In 15000 feet, unacclimatized aviator stays
1hr
Mental proficiency
Falls to about 20% of normal
After 18 hrs
Within seconds of ascends increase in SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITIES so increase in HR and BP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highaltitudephysiology01-191222150824/85/High-altitude-physiology01-6-320.jpg)


![Acclimatization to low po2
Altitude tolerance due different compensatory
mechanism
Pulmonary ventilation:
9
Low po2
hyperventilation
Decrease in pco2
40 to 15 mm Hg
Respi.
alkalosis
Metabolic
compensation
kidneys
Optimum [H+] and
[HCO3-] of plasma and
CSF
PH of blood and
CSF Increases
Inhibits respi. Center via
decline chemoreceptor
stimulation
After 2-5 days
inhibitions fades
away
Respiratory
center stimulated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highaltitudephysiology01-191222150824/85/High-altitude-physiology01-9-320.jpg)
![Increase number of RBC
• Endogenous erythropoietin level raises two peak
level [first 48 hrs of altitude]
• Level gets falls after following 4 days as ventilatory
response increases
• Increased Hematocrit =45% to 60%
• Increased hemoglobin concentration=15gm/dl to
20gm/dl
• There is increase 2,3 Diphospho glycerate, shifts
oxygen dissociation curve to right unlike respiratory
alkalosis
The net effect is a small increase P50,lowers affinity
between 02 and Hb
However increase in P50 value is limited
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highaltitudephysiology01-191222150824/85/High-altitude-physiology01-10-320.jpg)
![ Diffusing capacity:
• Normal value=21 ml/mm Hg/min
• Increases by three fold after acclimatization
• Rise diffusing capacity is due to combine effects of:
i. Increase in pulmonary capillary volume leading to increase in
surface areas of capillaries.
ii. Increase in lung air volume leading more expansions of lung
iii. Increases in pulmonary arterial blood pressure.
Tissue capillarity:
• Increase in systemic capillaries[Angiogenesis] in non pulmonary
tissues
• Most seen in active tissue exposed to chronic hypoxia
Capillary density in right ventricular increases markedly because of
effects of hypoxia and excess work load on right ventricle.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highaltitudephysiology01-191222150824/85/High-altitude-physiology01-11-320.jpg)


![ADAPTATIONOFNATIVESINHIGHALTITUDES
• Many native people in Andes and Himalayan live at above 13000
feet
• One group in Peruvian Andes lives at an altitude of 17500 feet.
• Natives are superior to even the best acclimatized low landers in all
aspect of acclimatization.
• Acclimatization of the natives begins in infancy ,natives are
genetically adapted to encounter the surrounding.
Barrel-shaped increased chest size and whereas body size is
decreases giving high ratio of ventilatory capacity to body mass
Their heart from birth onward pumps extra amount of CO output
At high altitude arterial PO2 is 40 mmHg which is less but
quantity of oxygen in arterial blood is greater than low landers.
Venous PO2 in high altitude natives is only 15 mmHg[30 mm
Hg] less than low landers [46 mm Hg]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highaltitudephysiology01-191222150824/85/High-altitude-physiology01-14-320.jpg)
