This document summarizes the use of neural networks for classification tasks. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of neural networks for classification. It also presents a case study on using a neural network to classify insurance customers as likely to renew or terminate their policies based on attributes like age and zip code. The neural network achieved higher accuracy than decision trees and regression analysis on the insurance data set.




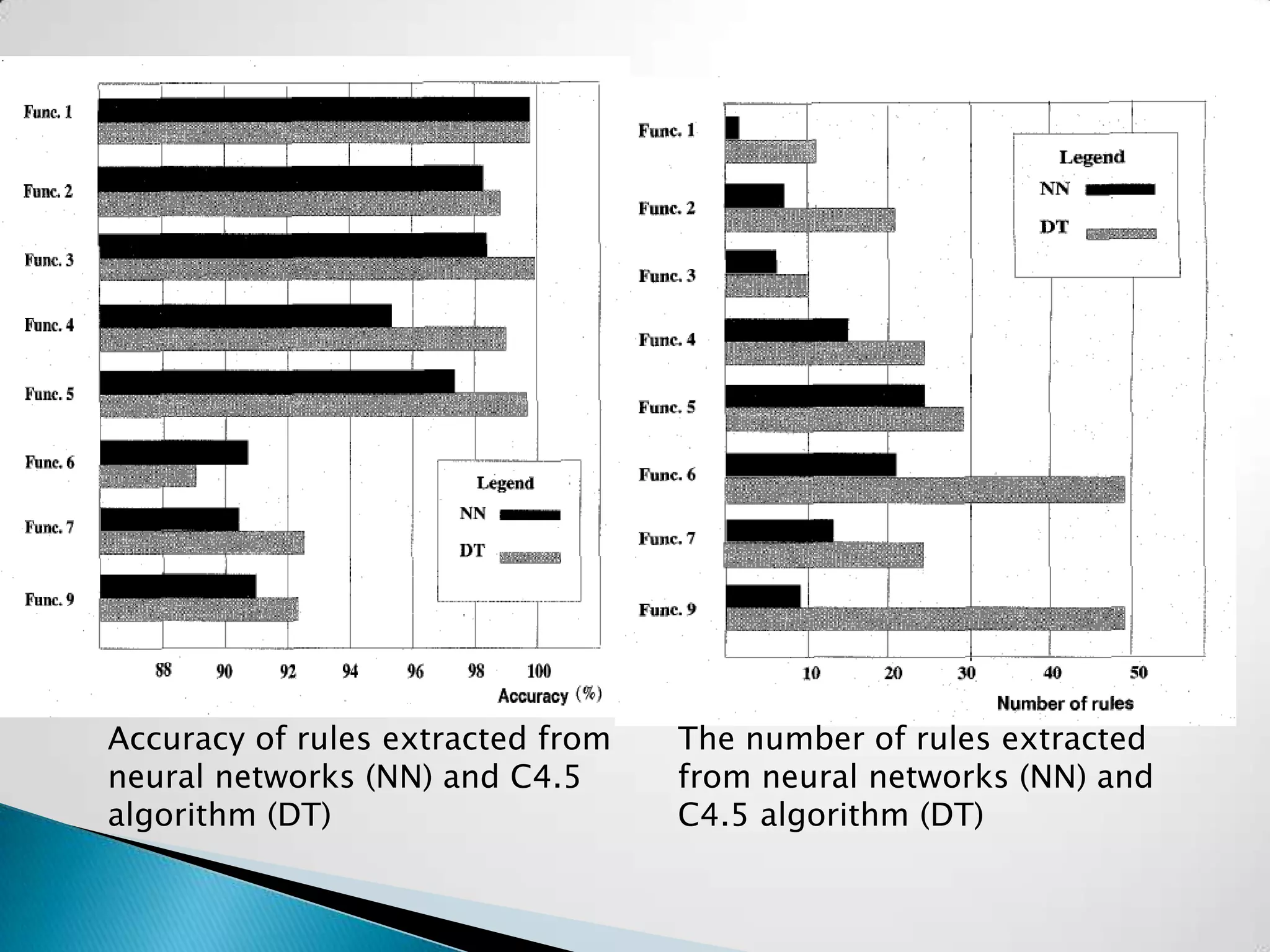
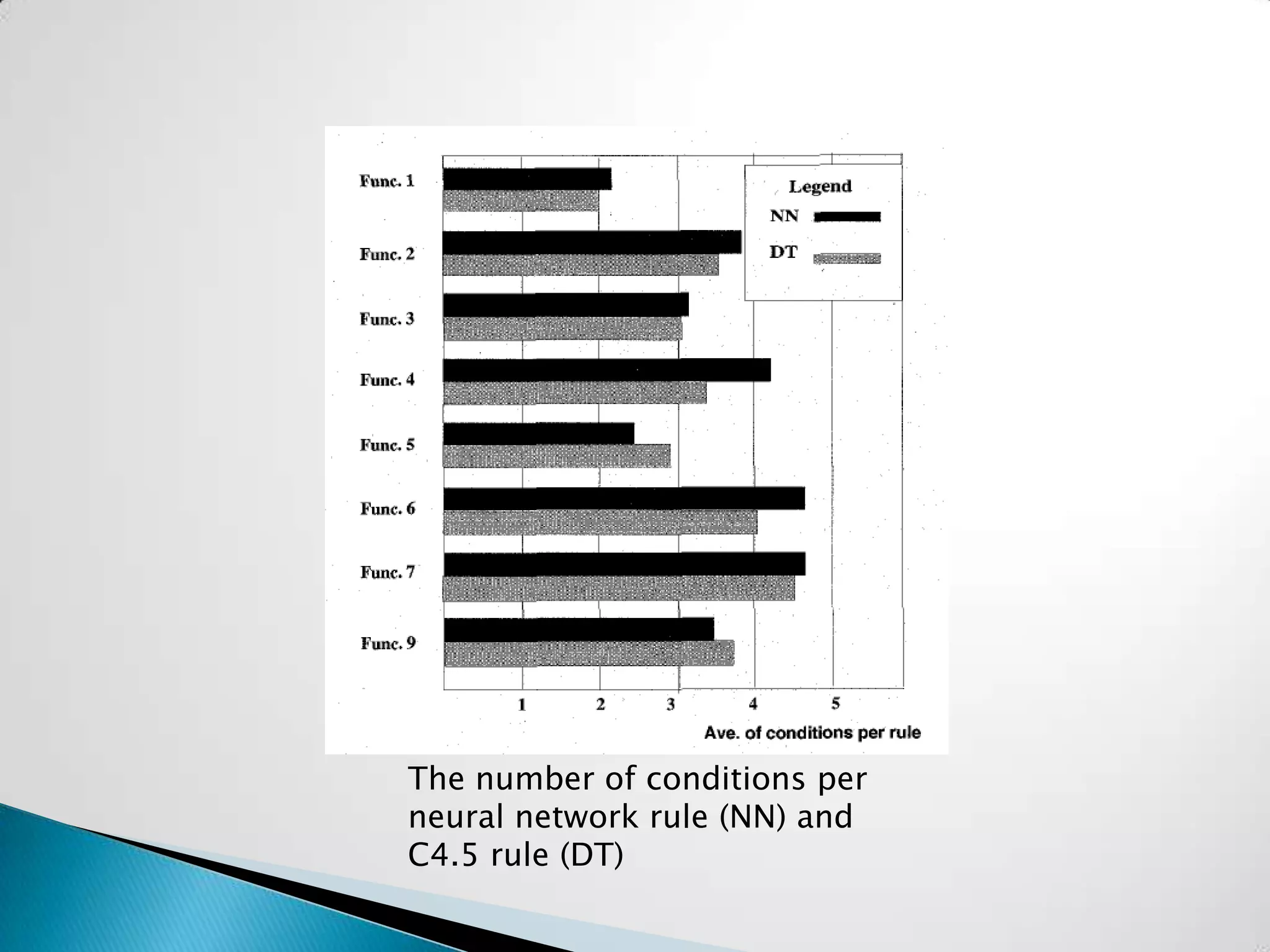
![ Comparison of Neural classifier [Lu et al.] and
decision tree classifier
People database consisting of 9 attributes
(age, elevel, zipcode .etc.) and 1 output (Group A
or Group B)
3 layer feed forward neural network (38 input
units, 6 hidden units and 1 output unit)
Tested and compared their approach on 8
classification problems used in earlier researches
Func 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralnetworks-120111193957-phpapp02/75/Neural-Network-Classification-and-its-Applications-in-Insurance-Industry-6-2048.jpg)