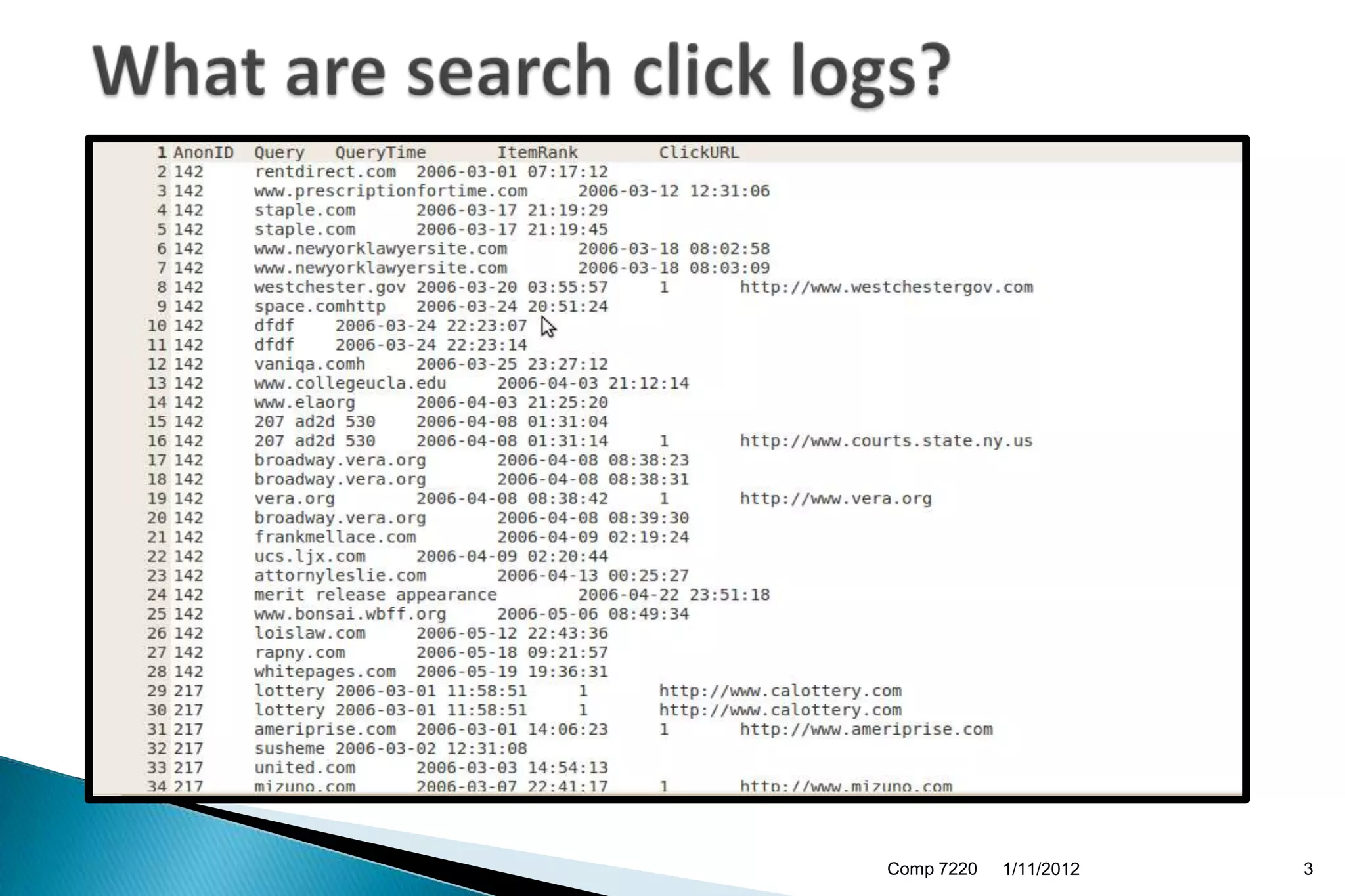
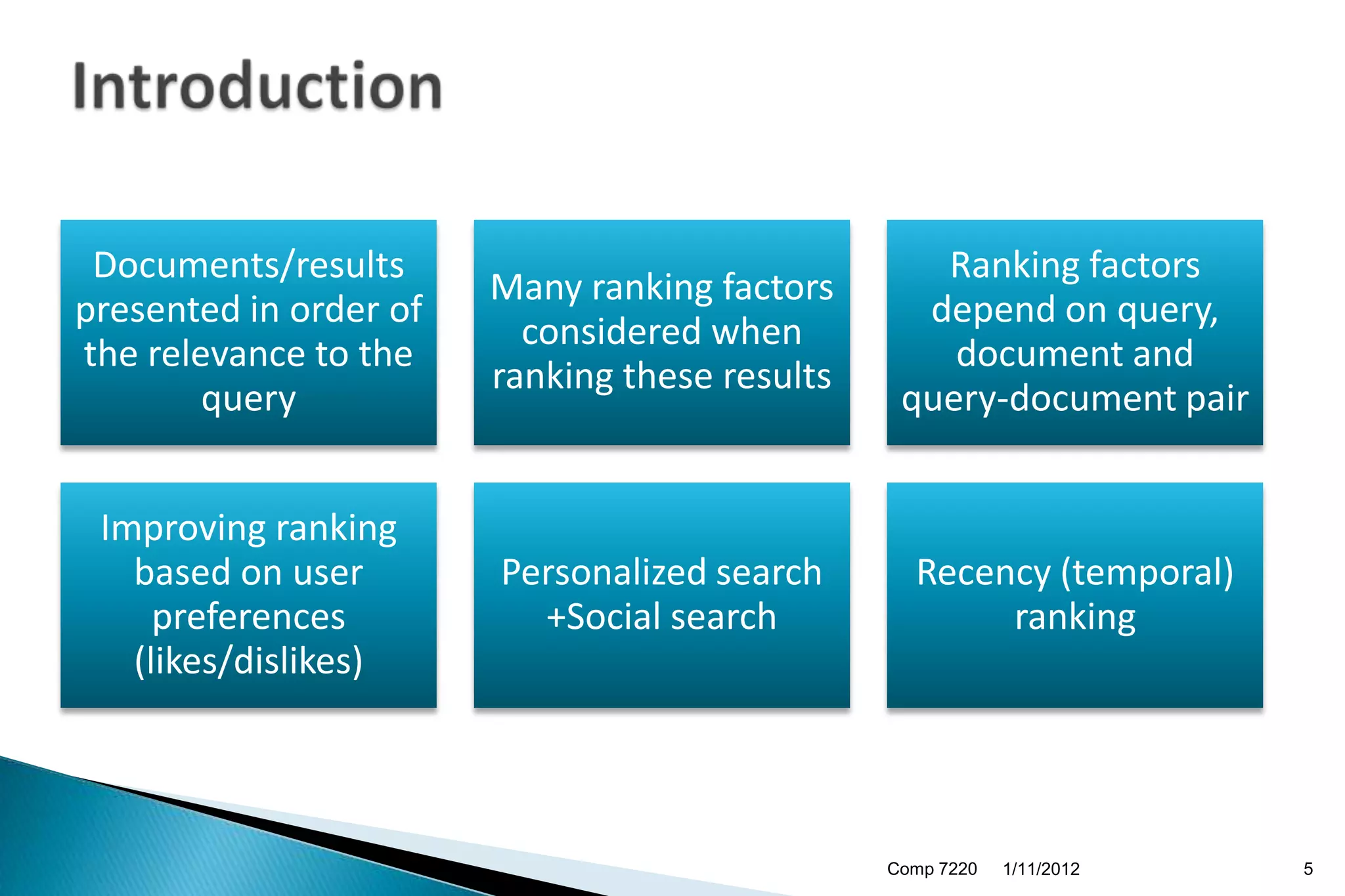
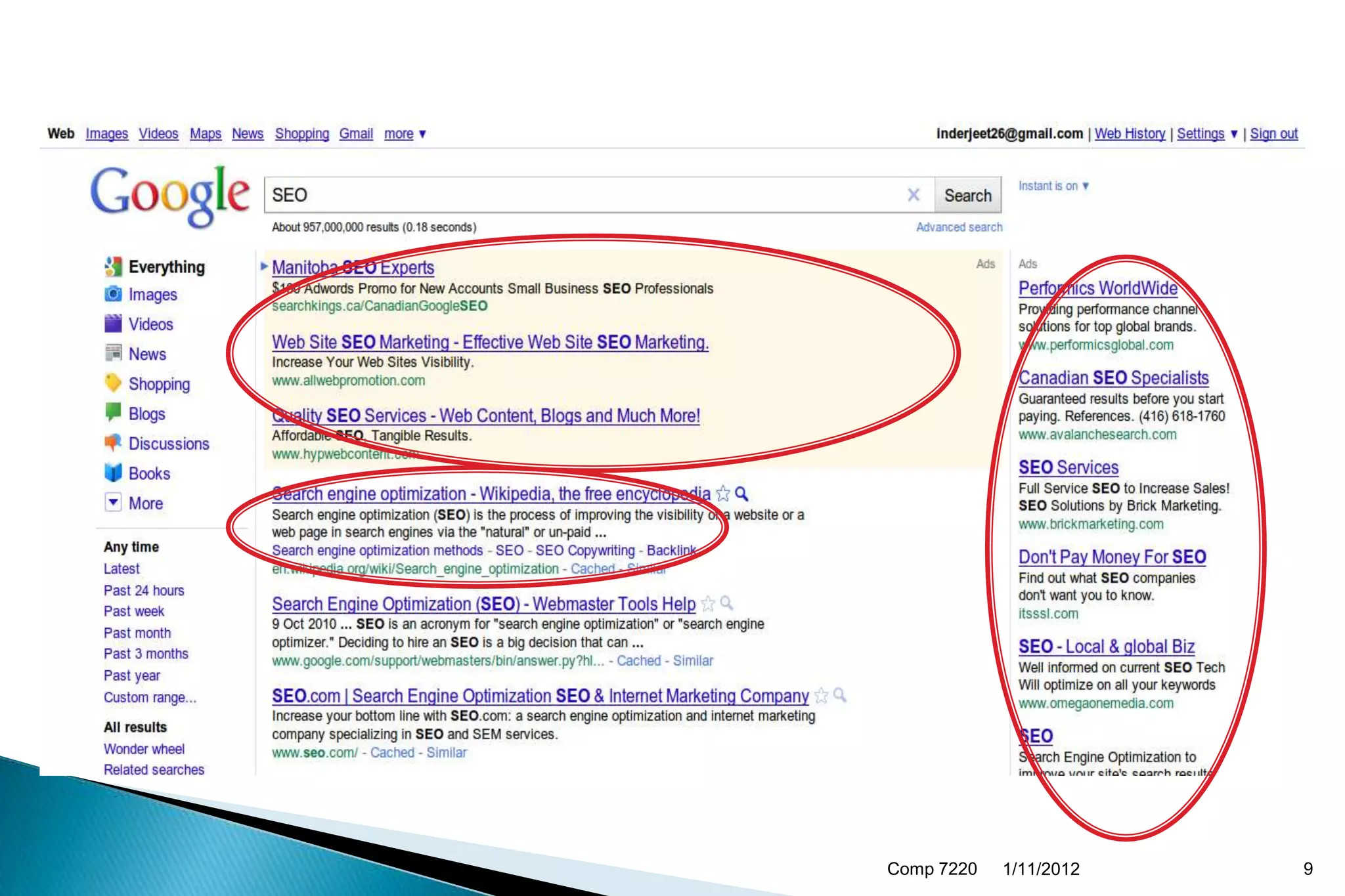
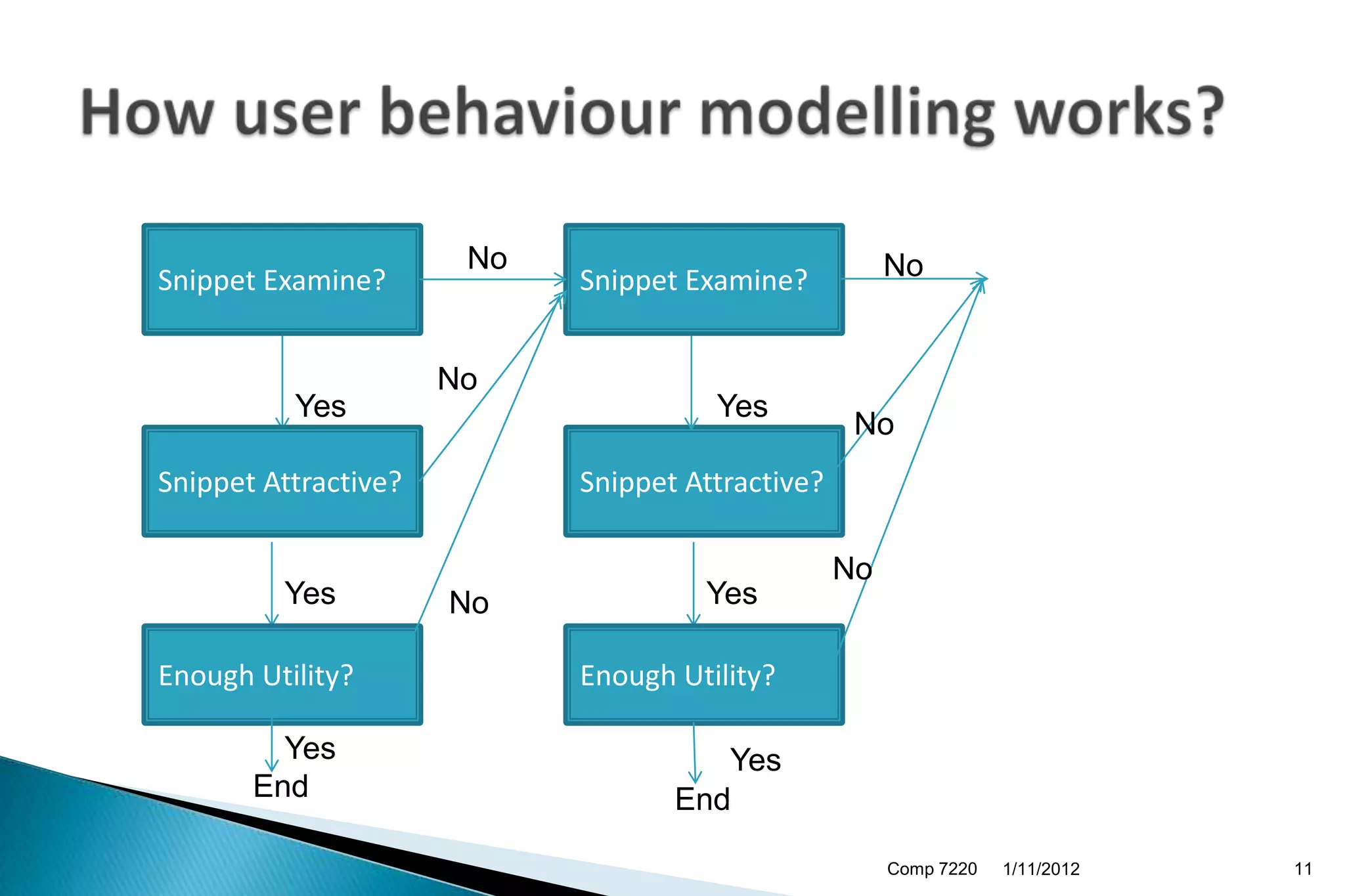
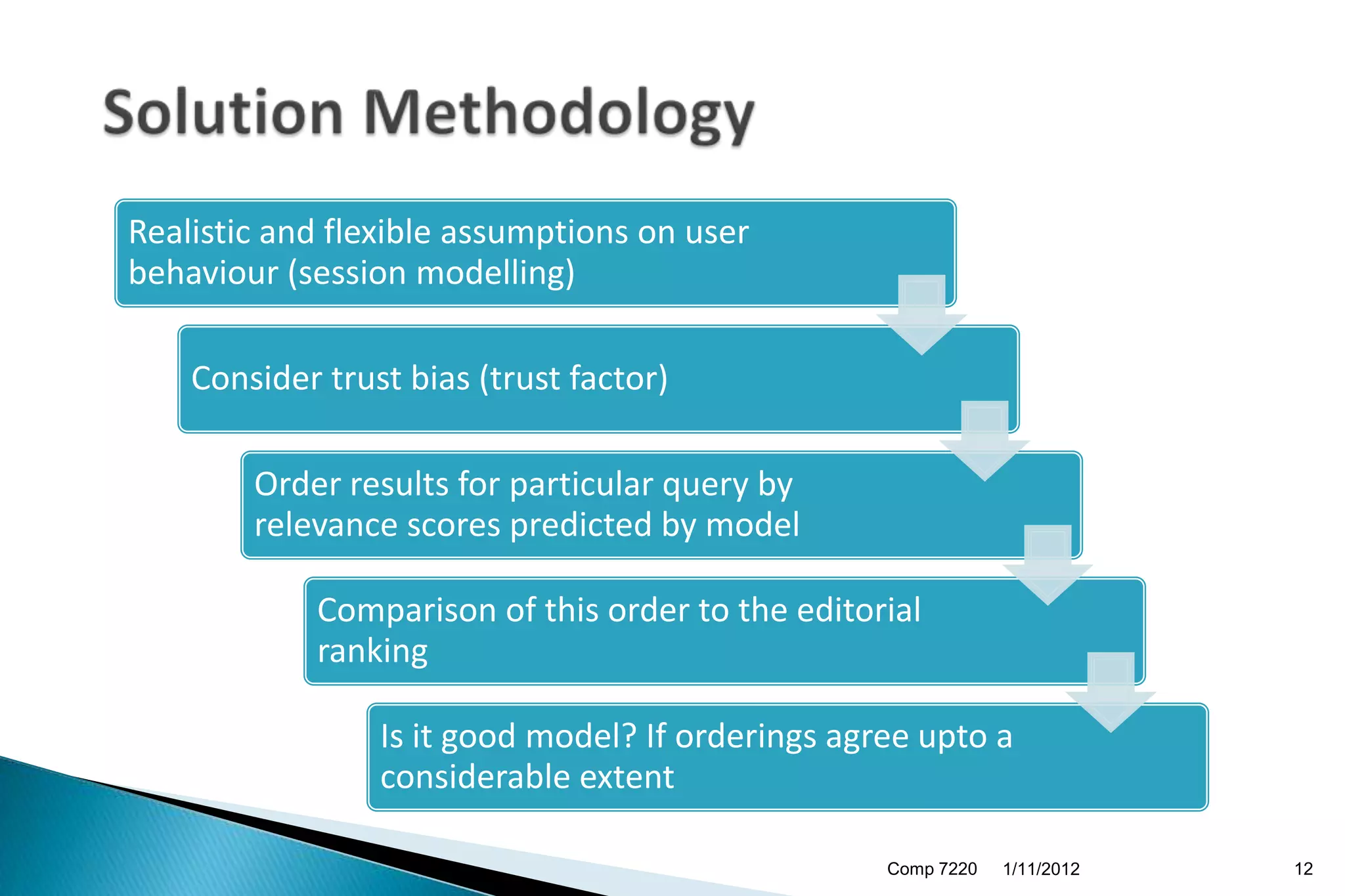
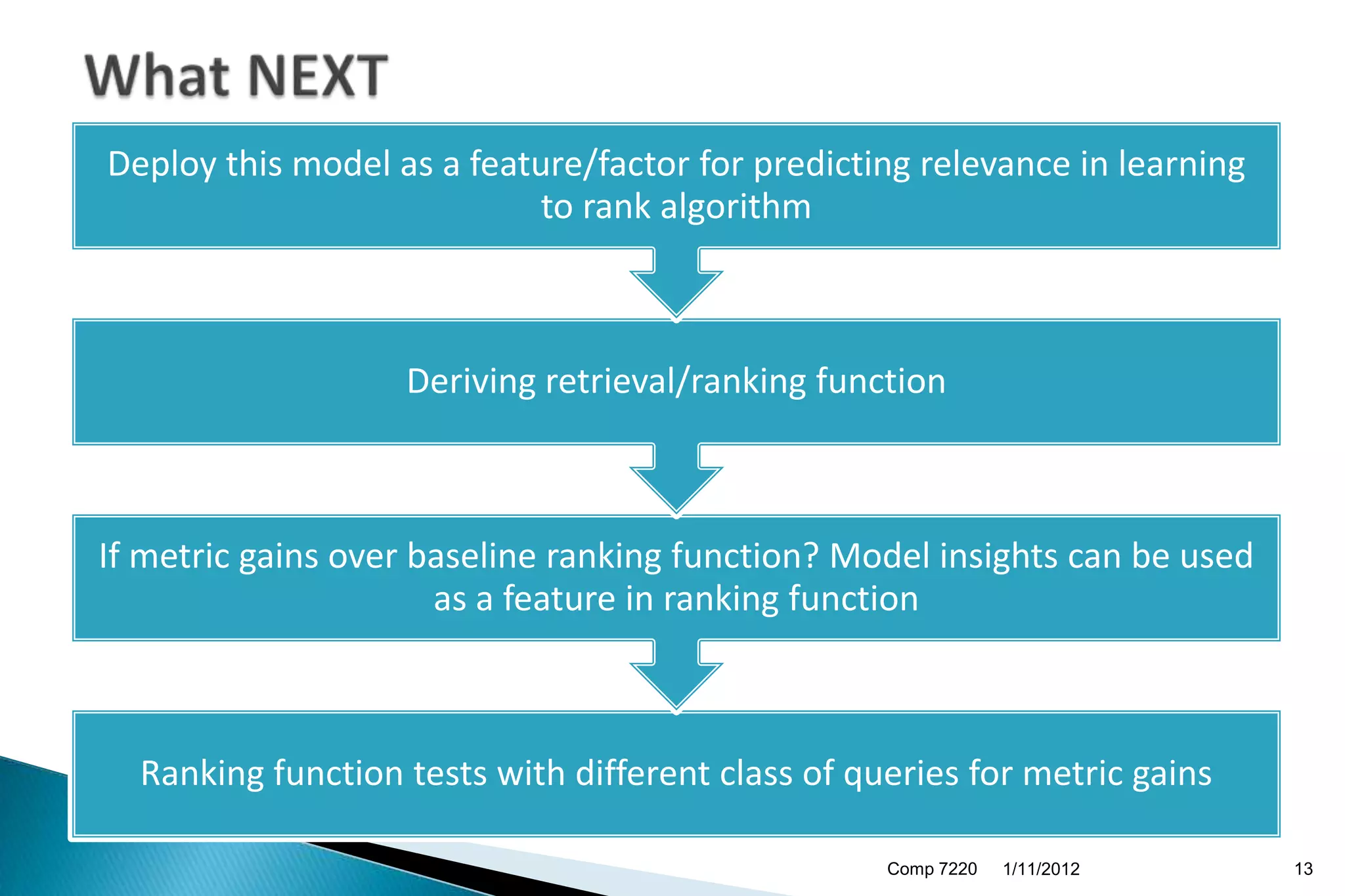
The document discusses search engine ranking and optimization. It introduces problems with existing ranking models such as not considering factors like trust bias. A new methodology is proposed that makes more realistic assumptions about user behavior, such as modeling user sessions and preferences for certain websites. The approach aims to improve search result ranking by incorporating additional ranking factors from click logs and evaluating the model using standard information retrieval metrics on search log and benchmark datasets.



![[David Green; blog]
Comp 7220 1/11/2012 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comp7220presentation-120111194046-phpapp01/75/Determining-Relevance-Rankings-from-Search-Click-Logs-6-2048.jpg)
![# of clicks received
[CIKM'09 Tutorial]
Comp 7220 1/11/2012 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comp7220presentation-120111194046-phpapp01/75/Determining-Relevance-Rankings-from-Search-Click-Logs-7-2048.jpg)


![[Guo et al., 2009]
[Chapelle and Zhang, 2009]
Comp 7220 1/11/2012 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comp7220presentation-120111194046-phpapp01/75/Determining-Relevance-Rankings-from-Search-Click-Logs-15-2048.jpg)

![[Tmcnet.com Blog]
Comp 7220 1/11/2012 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comp7220presentation-120111194046-phpapp01/75/Determining-Relevance-Rankings-from-Search-Click-Logs-17-2048.jpg)