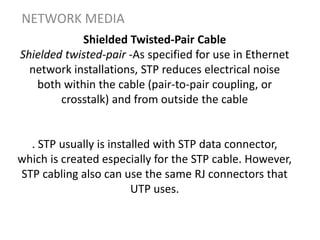
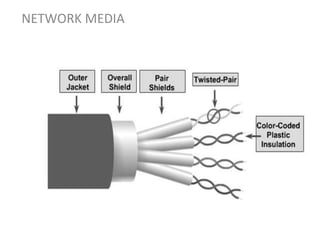
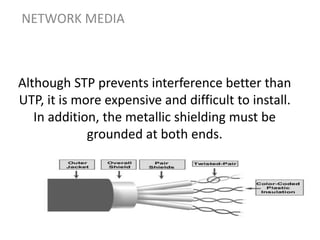
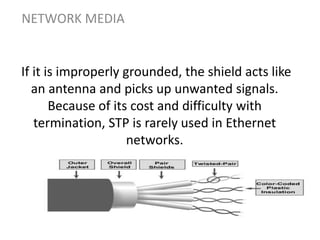
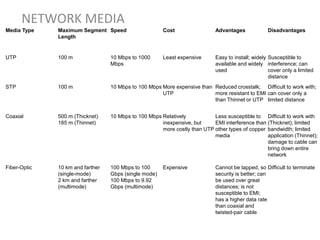
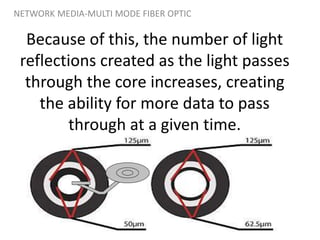
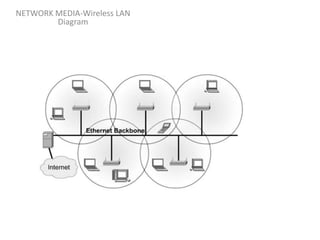
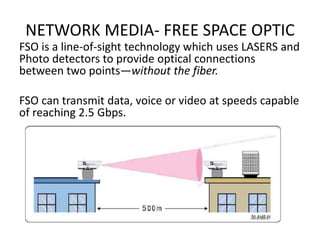
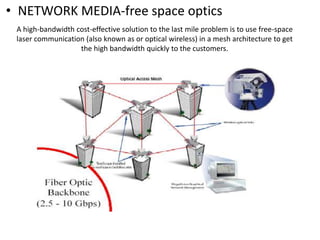
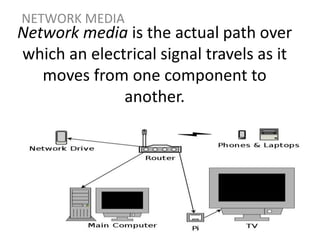
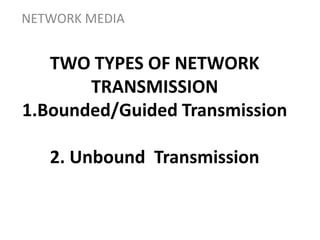
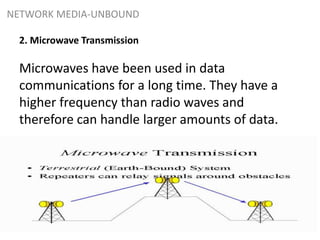
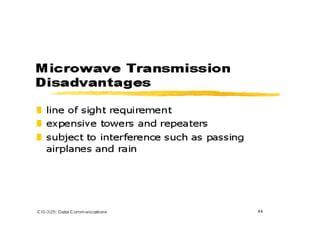
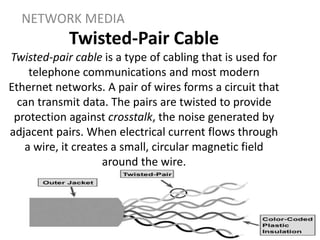
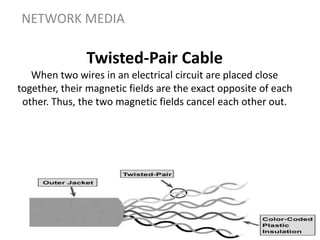
Network media refers to the physical paths over which electrical signals travel between network components. There are two types of network transmission: bounded/guided transmission, where signals are confined to a specific path using cables like twisted-pair, coaxial, or fiber-optic; and unbound transmission, which extends beyond cabling and includes radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves. Unbound transmission provides larger bandwidth and wide area capabilities but operates at very high frequencies. Common methods for reducing noise in network signals include signal averaging, analog filtering using passive low-pass and high-pass filters, and active filters which incorporate amplifying components.























![Commonly used types of UTP cabling are as follows:
Category 4—Used in Token Ring networks. Can transmit data at
speeds up to 16 Mbps.
Category 5—Can transmit data at speeds up to 100 Mbps.
Category 5e —Used in networks running at speeds up to 1000
Mbps (1 gigabit per second [Gbps]).
Category 6—Typically, Category 6 cable consists of four pairs of
24 American Wire Gauge (AWG) copper wires. Category 6 cable
is currently the fastest standard for UTP.
NETWORK MEDIA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ictinframodule4networkmediapresentation1-160306205121/85/networkmedia-presentation1-31-320.jpg)