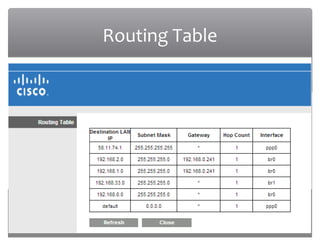
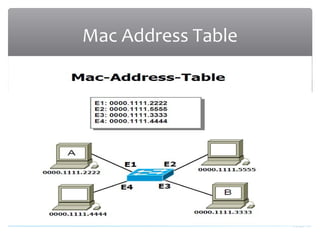
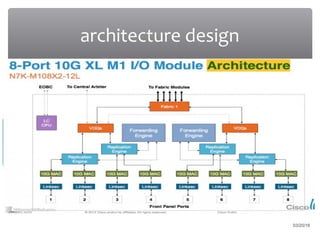
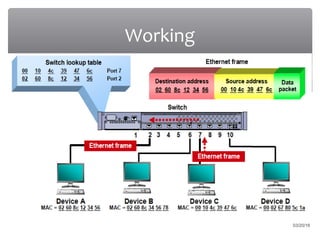
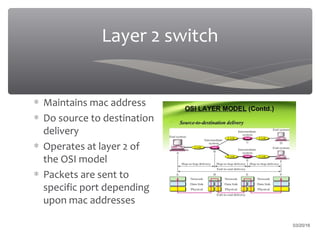
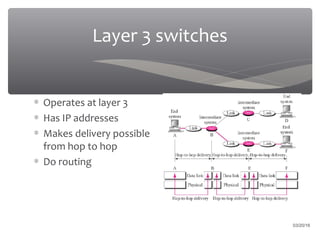
The presentation discusses various types of switches used in computer networks, detailing their functionalities, management features, and differences, such as modular and fixed configuration switches. It highlights the importance of switches over hubs for improved communication efficiency, security, and reliability. Future developments in switch technology are also mentioned, focusing on automation in determining application network requirements.