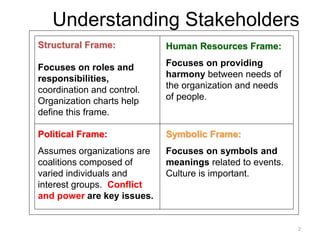
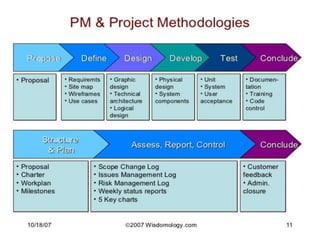
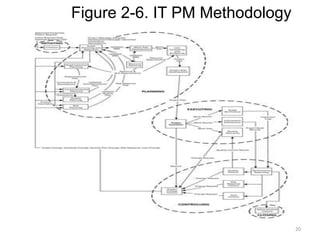
This document discusses the key processes involved in project management. It begins by explaining the importance of understanding stakeholders and their various needs and perspectives. It then discusses factors that help projects succeed, with executive support and user involvement being the most important. The document outlines the typical project management processes of initiation, planning, execution, control, and closure. It emphasizes the need for leadership, communication skills, and managing resources effectively. Developing an internal methodology tailored to an organization's specific needs is also recommended.