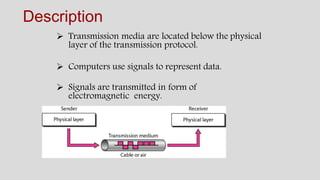
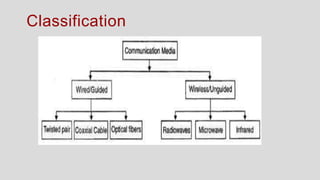
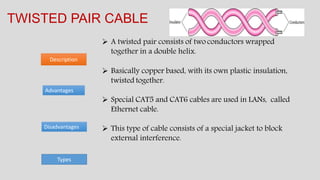
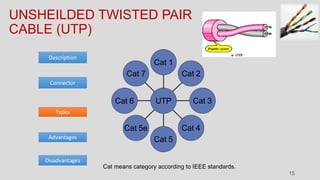
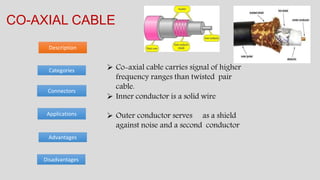
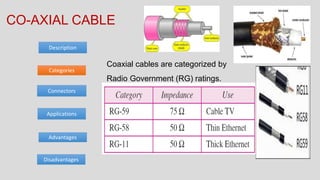
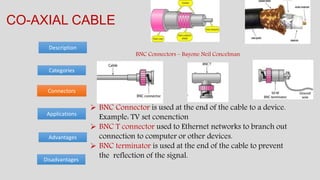
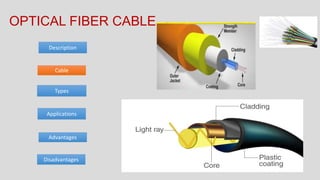
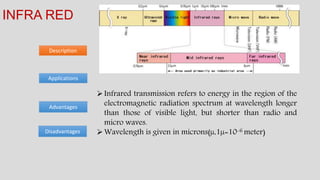
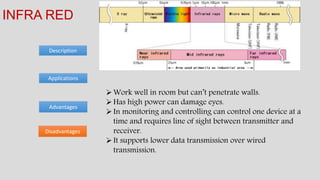
The document discusses various types of transmission media used in communication, including twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, optical fiber cables, and unguided/wireless media. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, such as cost, speed, susceptibility to interference, and installation complexity. The document also covers specific applications and technological characteristics related to each transmission medium.