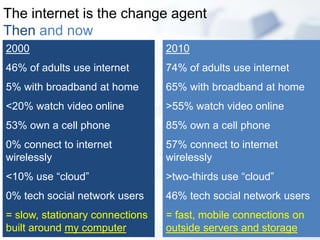
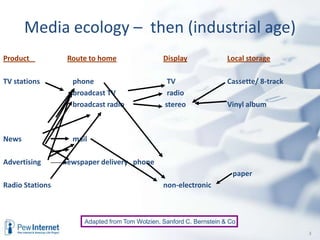
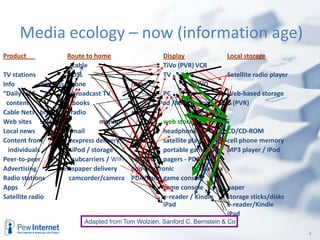
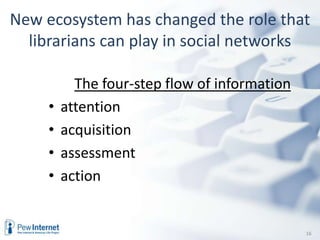
The document discusses the evolution of internet usage and media ecology from 2000 to 2010, highlighting significant changes in technology adoption and user behaviors, such as increased broadband access and the rise of social networking. It outlines implications for libraries to adapt by becoming nodes in social networks and teaching new literacies, emphasizing the importance of information curation and community engagement. The document concludes that effective social networks contribute to healthier, more engaged communities.