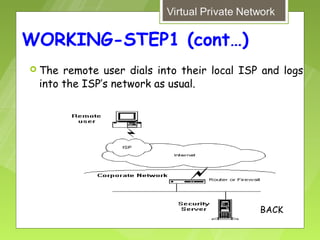
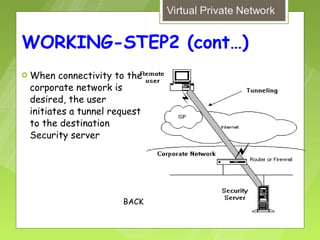
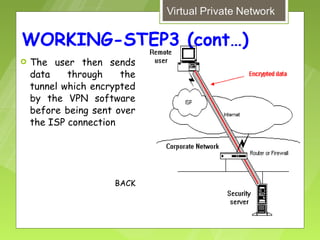
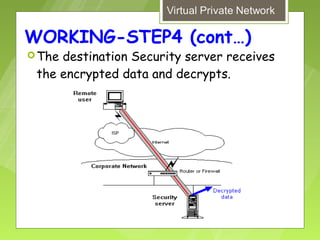
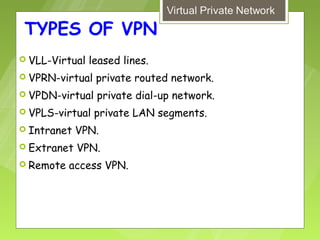
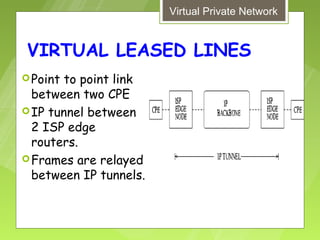
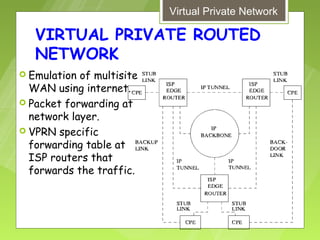
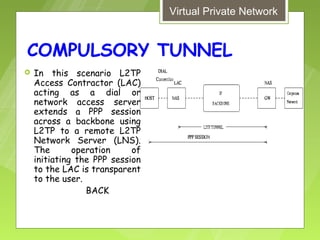
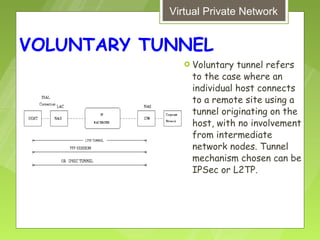
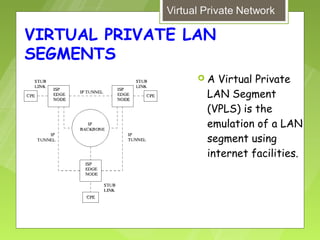
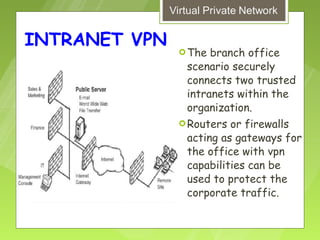
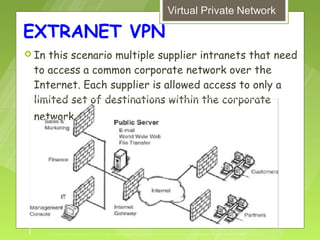
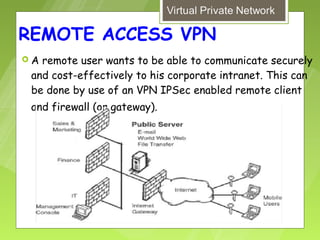
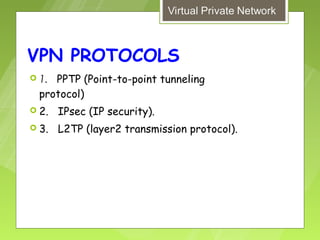
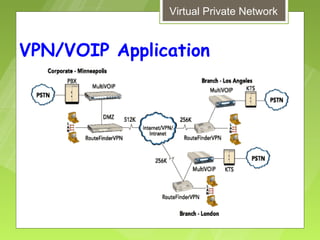
This document discusses virtual private networks (VPNs). It defines a VPN as a network that uses the open infrastructure of the internet to transmit data between corporate sites. It describes the need for VPNs to allow remote employees, growing corporations, and developing business relations to securely access corporate databases. The document outlines the basic working of VPNs through encrypted tunnels between remote users or sites and destination security servers. It also lists different types of VPNs and the protocols and hardware used to implement VPNs.