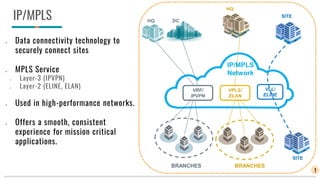
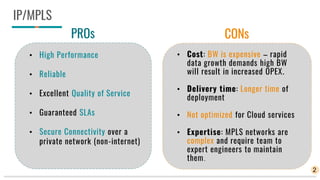
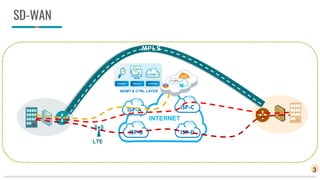
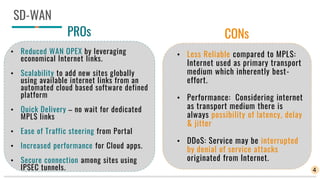
The document discusses IP/MPLS and SD-WAN technologies for connecting sites in a network. IP/MPLS uses MPLS services at layers 2 and 3 to securely connect sites with high performance and quality of service guarantees. SD-WAN brings together multiple connection types like MPLS, internet, and LTE into a single software-controlled network to reduce WAN costs while improving performance and security. For businesses, SD-WAN provides benefits of scalability, cost reduction, and ease of use, while MPLS is still needed for large enterprises with strict connectivity requirements. Both technologies will likely coexist with SD-WAN adoption increasing and MPLS use decreasing over time.