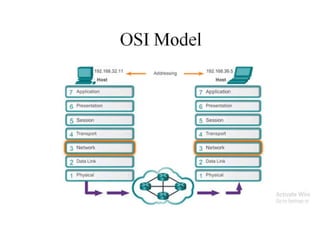
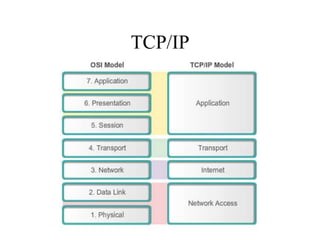
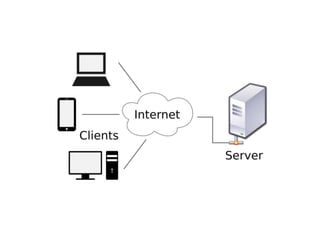
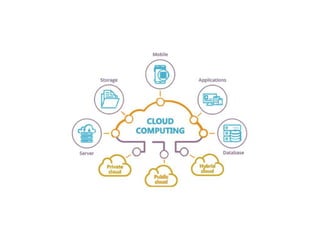
The document provides an overview of the internet as a global communication system that connects individual networks, enabling information exchange through various platforms like email, social media, and web browsing. It explains how to access the internet, types of internet services, and the essential hardware required, such as modems and routers. Additionally, it discusses the concept of cloud computing, its uses for file storage, sharing, and data backup.