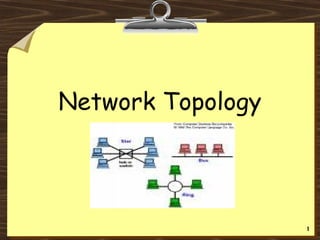
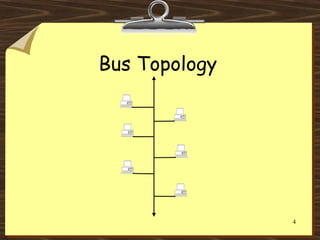
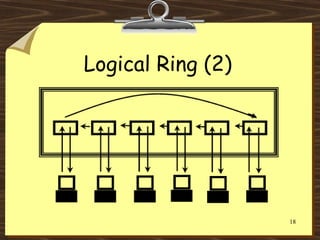
This document discusses various network topologies including bus, ring, star, mesh, extended star, and hybrid topologies. It also distinguishes between physical and logical topologies. A physical topology refers to the actual layout and wiring of the network, while logical topology refers to how data is transmitted through the network. For example, while a network may have a star-shaped physical topology with cables connecting devices to a central hub, the hub may use a logical bus or ring topology to transmit data internally.