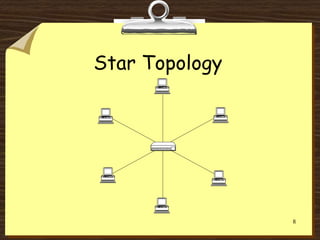
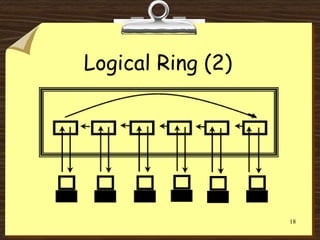
This document discusses various network topologies, including physical topologies like bus, ring, star, mesh, and extended star. It also covers logical topologies like logical bus and logical ring. Bus topology is inexpensive but has single point of failure issues. Ring topology has high speed but requires more cable. Star topology is easy to expand and manage but has higher installation costs. Mesh topology improves fault tolerance but is expensive to implement. Hybrid topologies combine elements of different physical topologies.