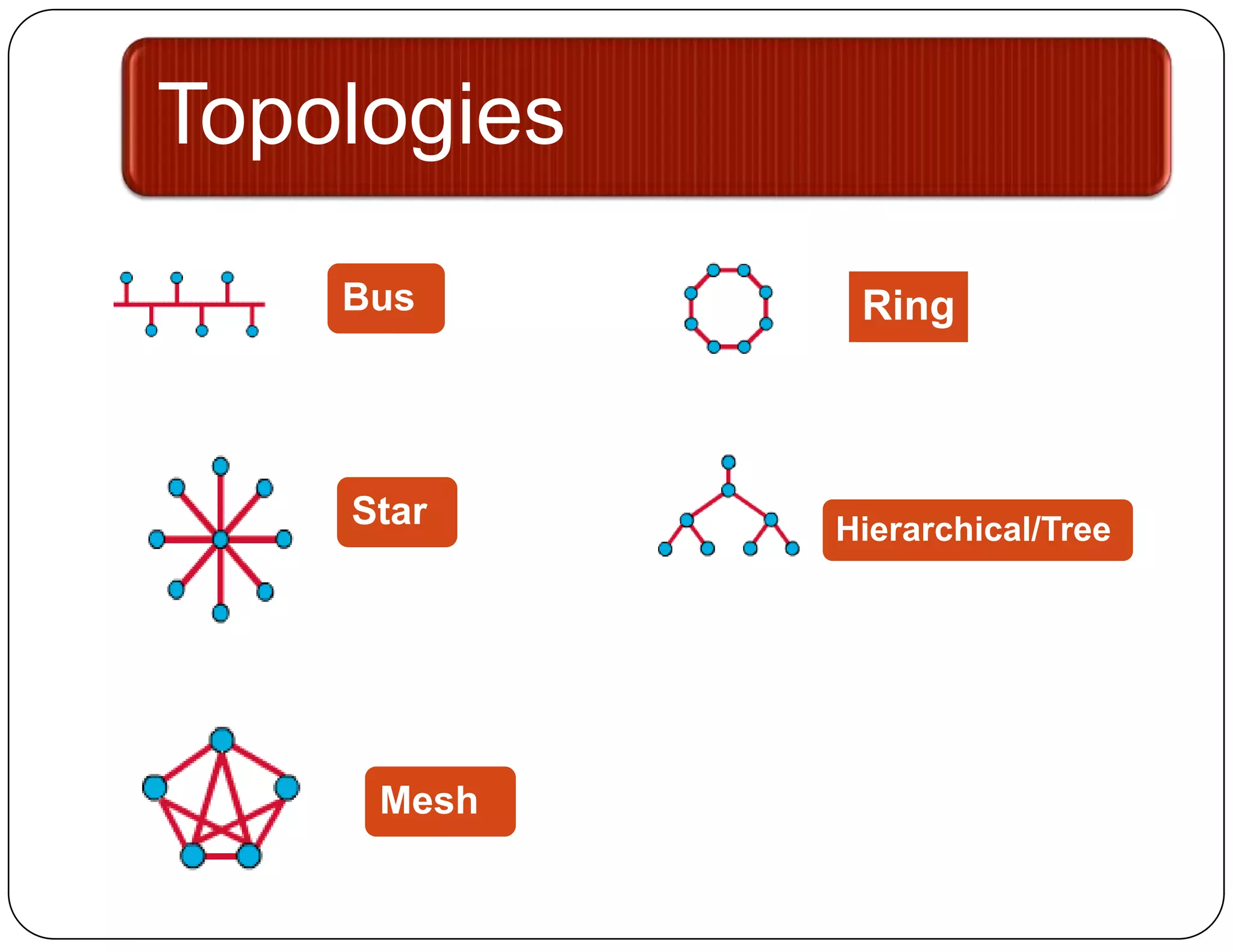
Network topologies determine how devices are physically connected in a network. There are several common topology types:
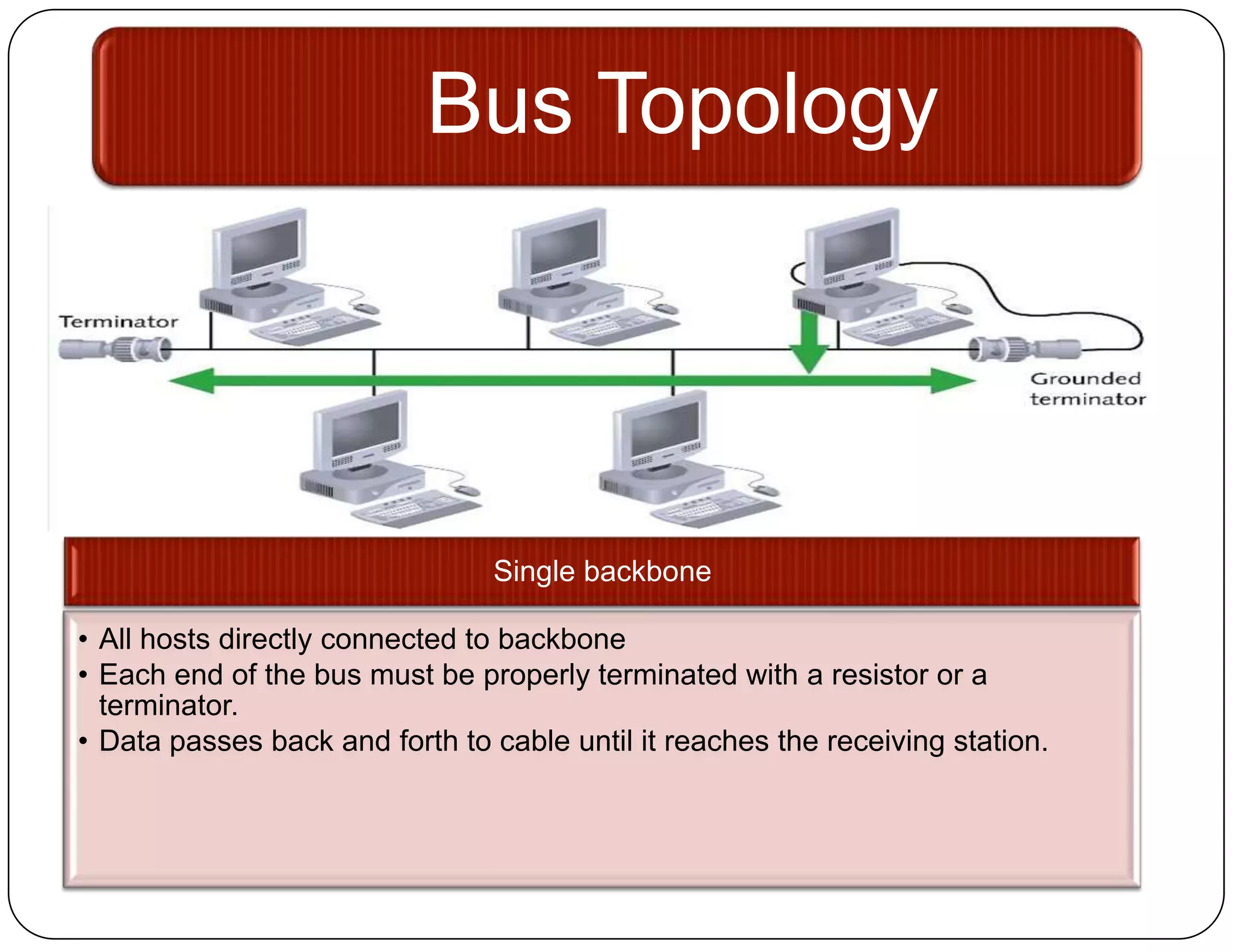
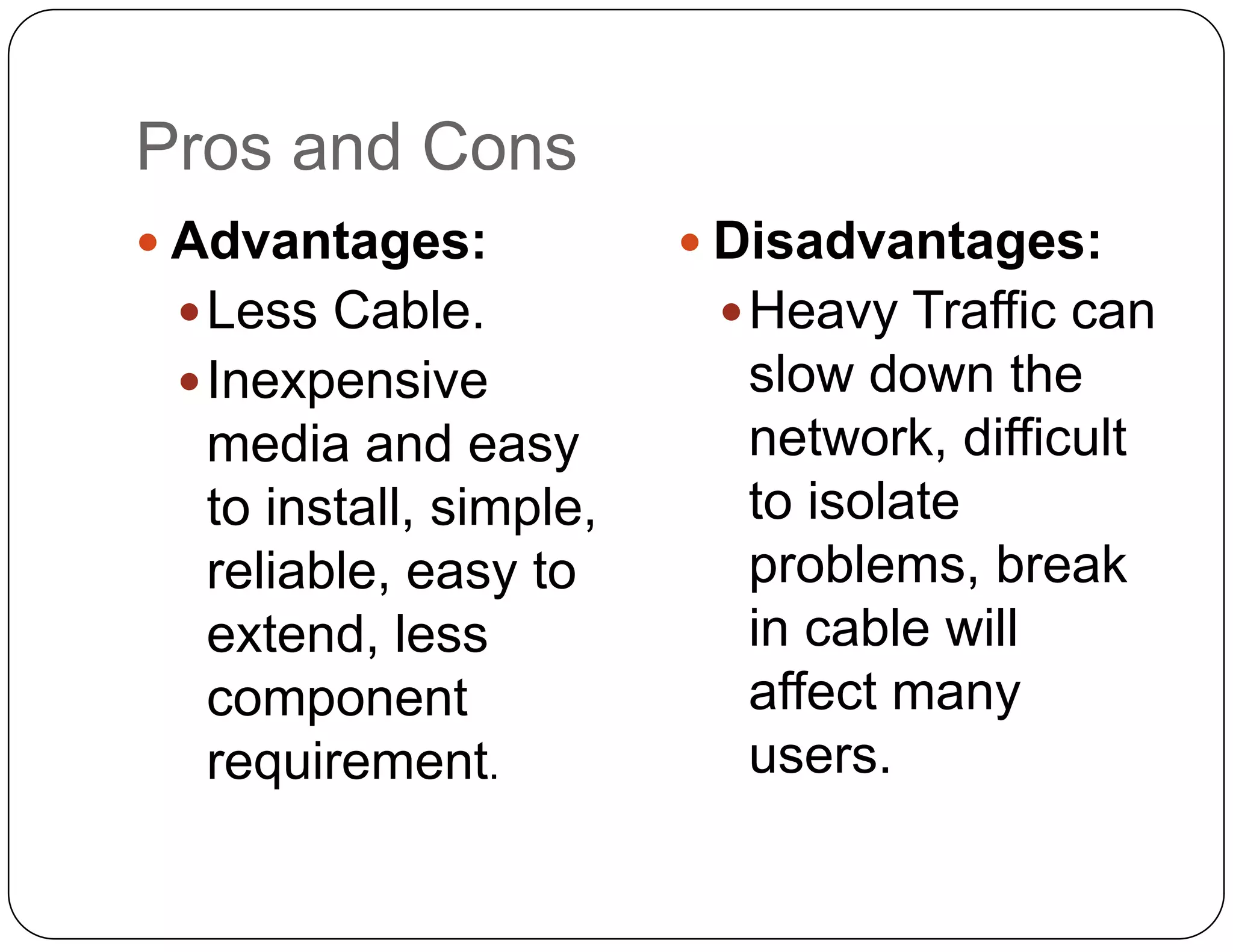
- Bus topology connects all devices to a single backbone cable. A break in the cable disrupts the entire network.
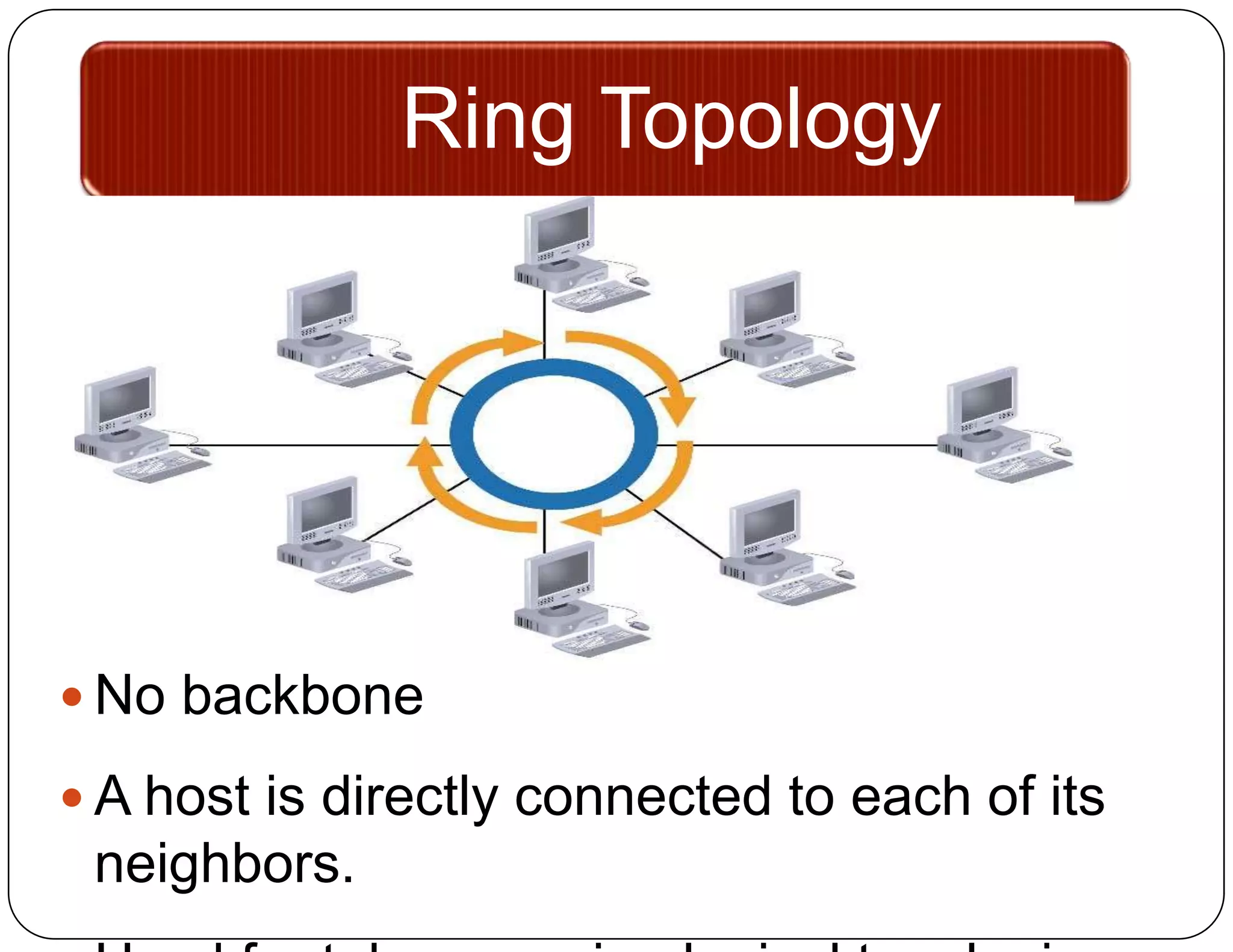
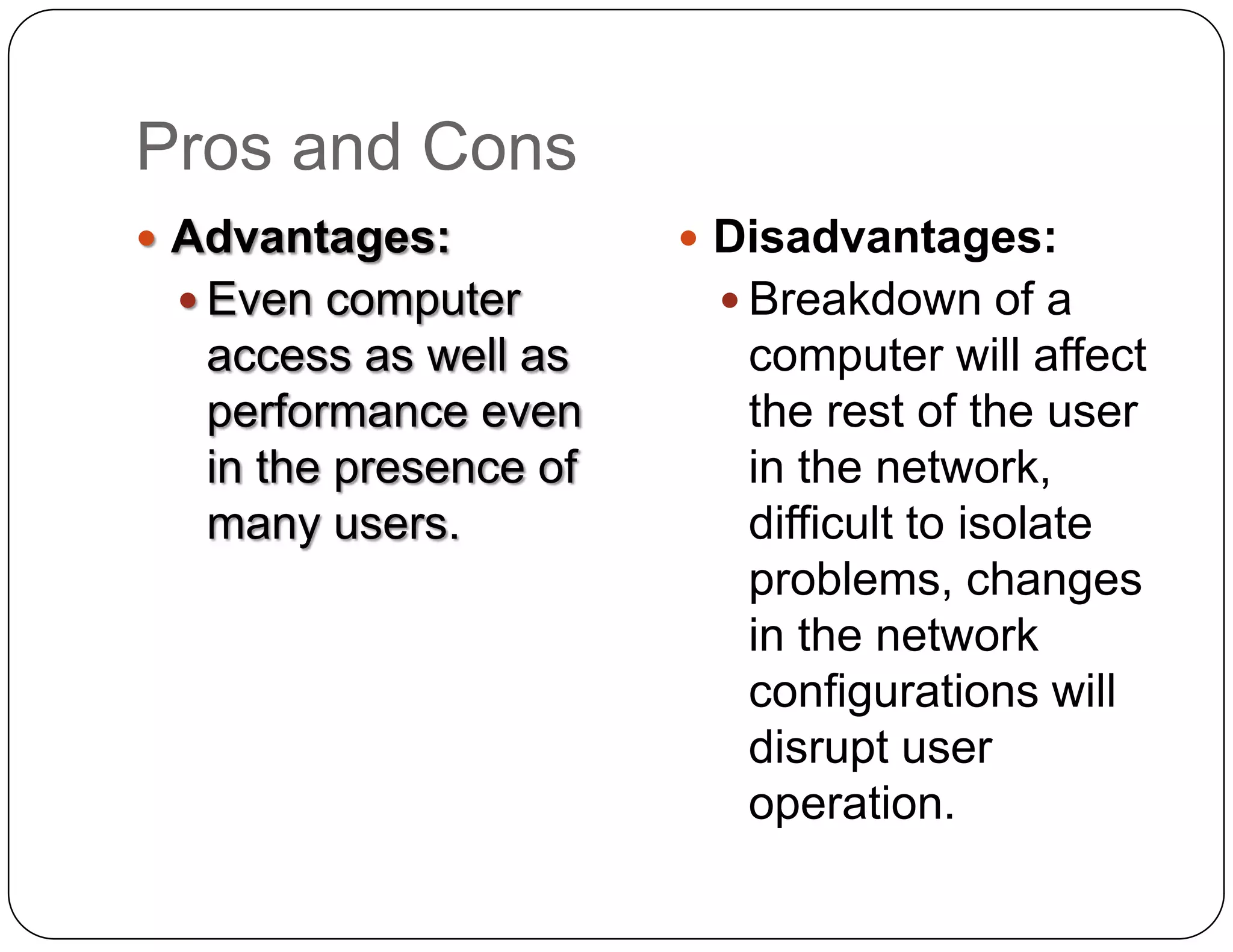
- Ring topology connects each device directly to its neighbors in a circular configuration. A break disrupts connections until the break is repaired.
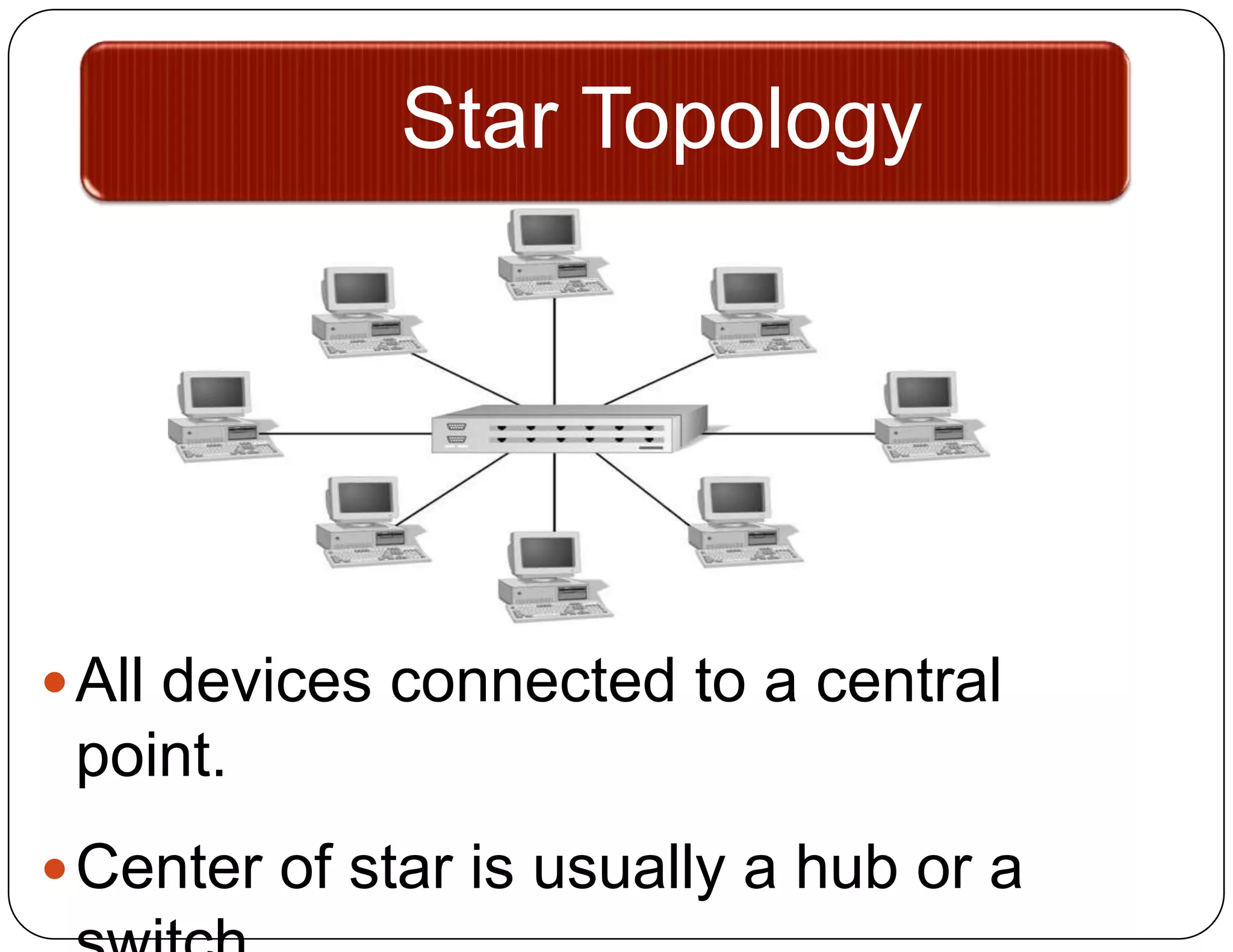
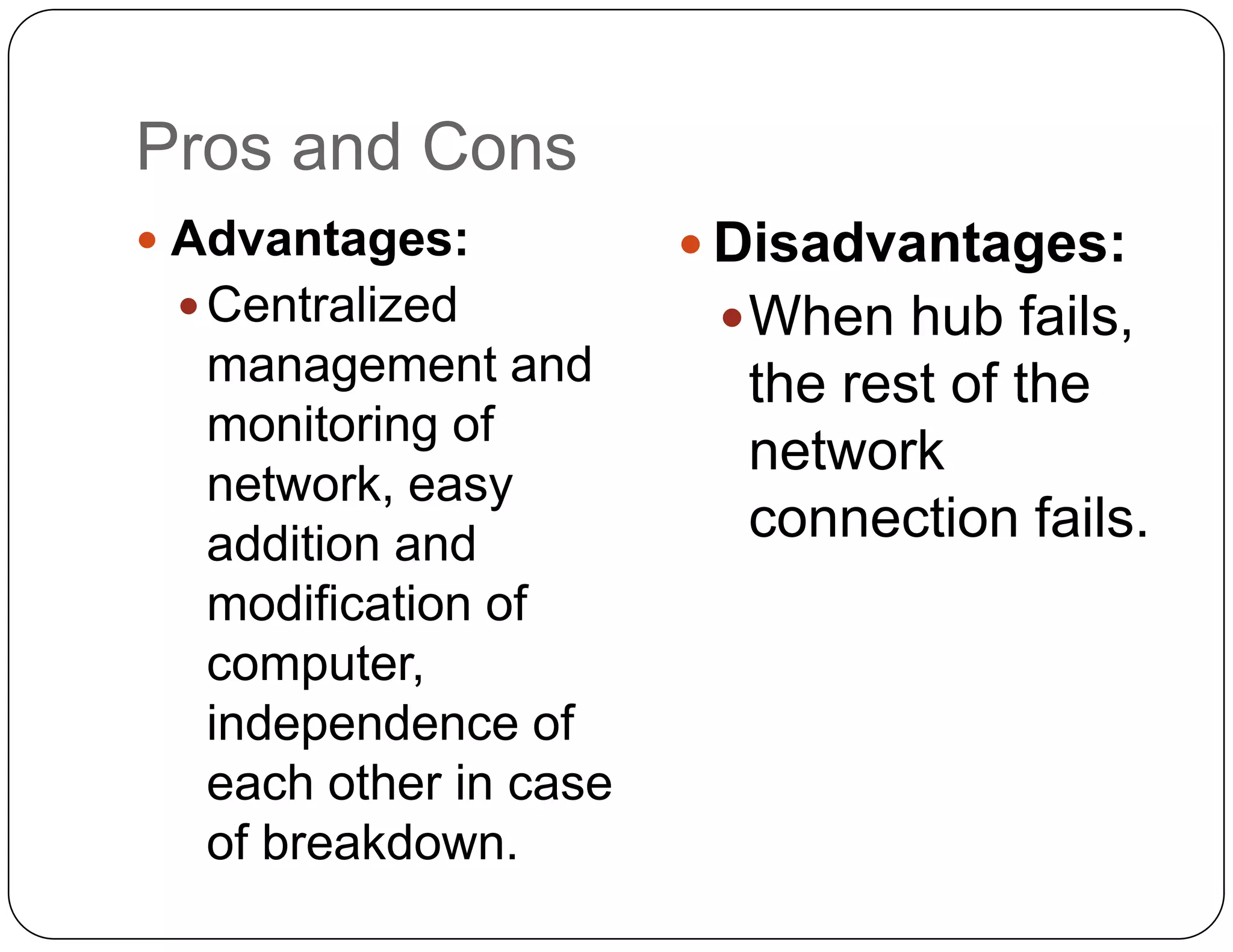
- Star topology connects all devices to a central hub or switch. Failure of the hub stops the entire network until repaired.
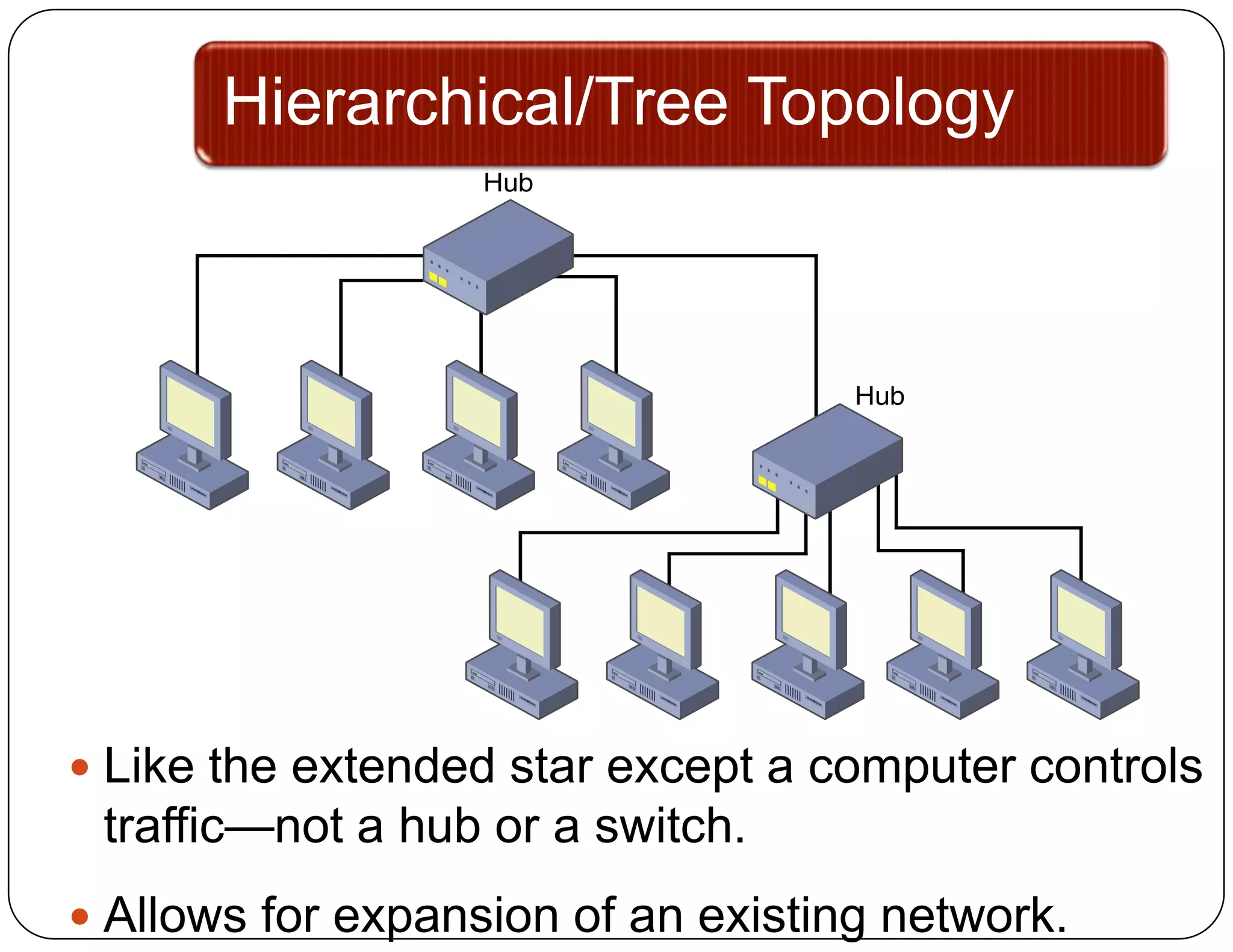
- Hierarchical/tree topology allows expansion by connecting devices in a branching structure with control points.
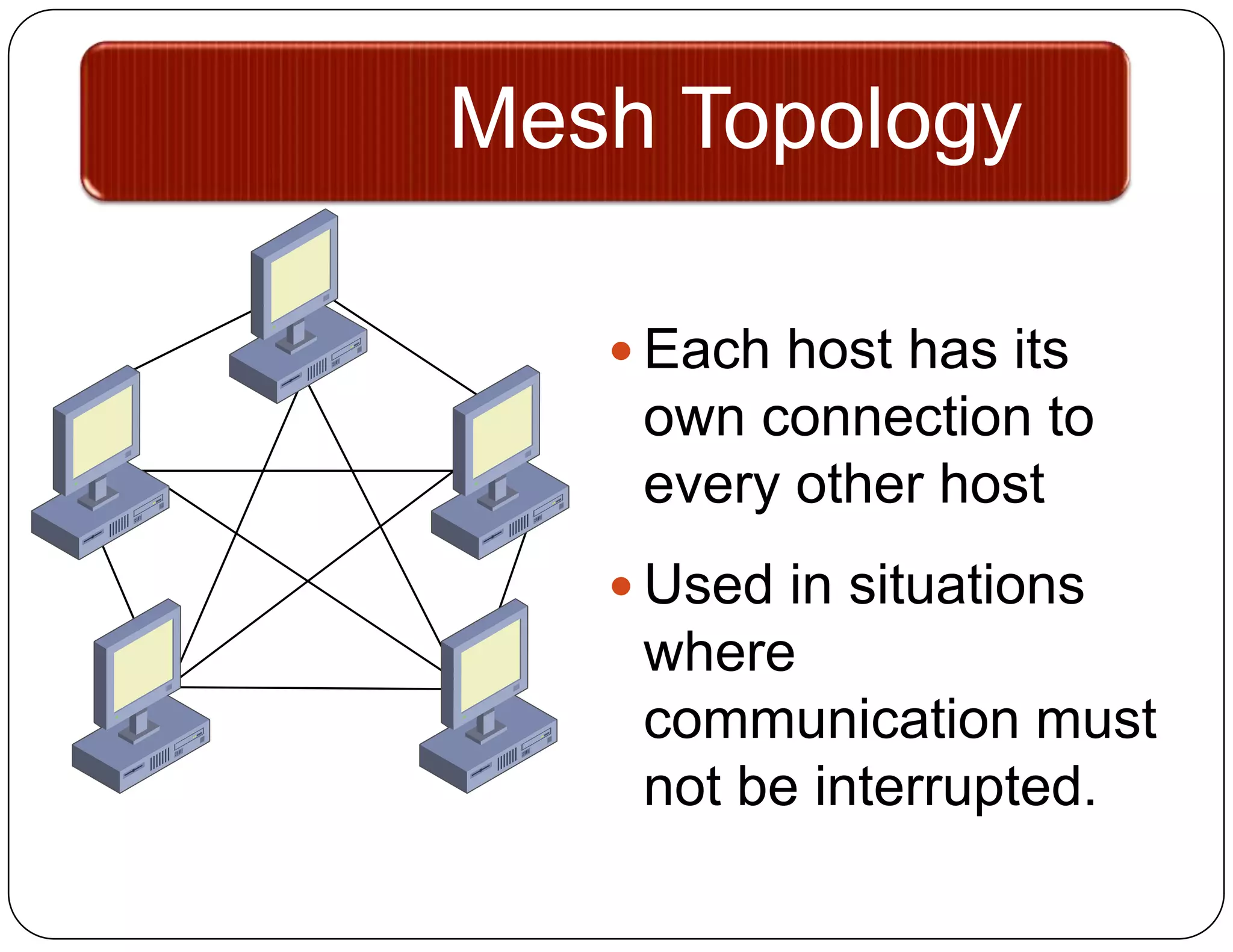
- Mesh topology fully connects each device to every other device for continuous communication if any connection fails.