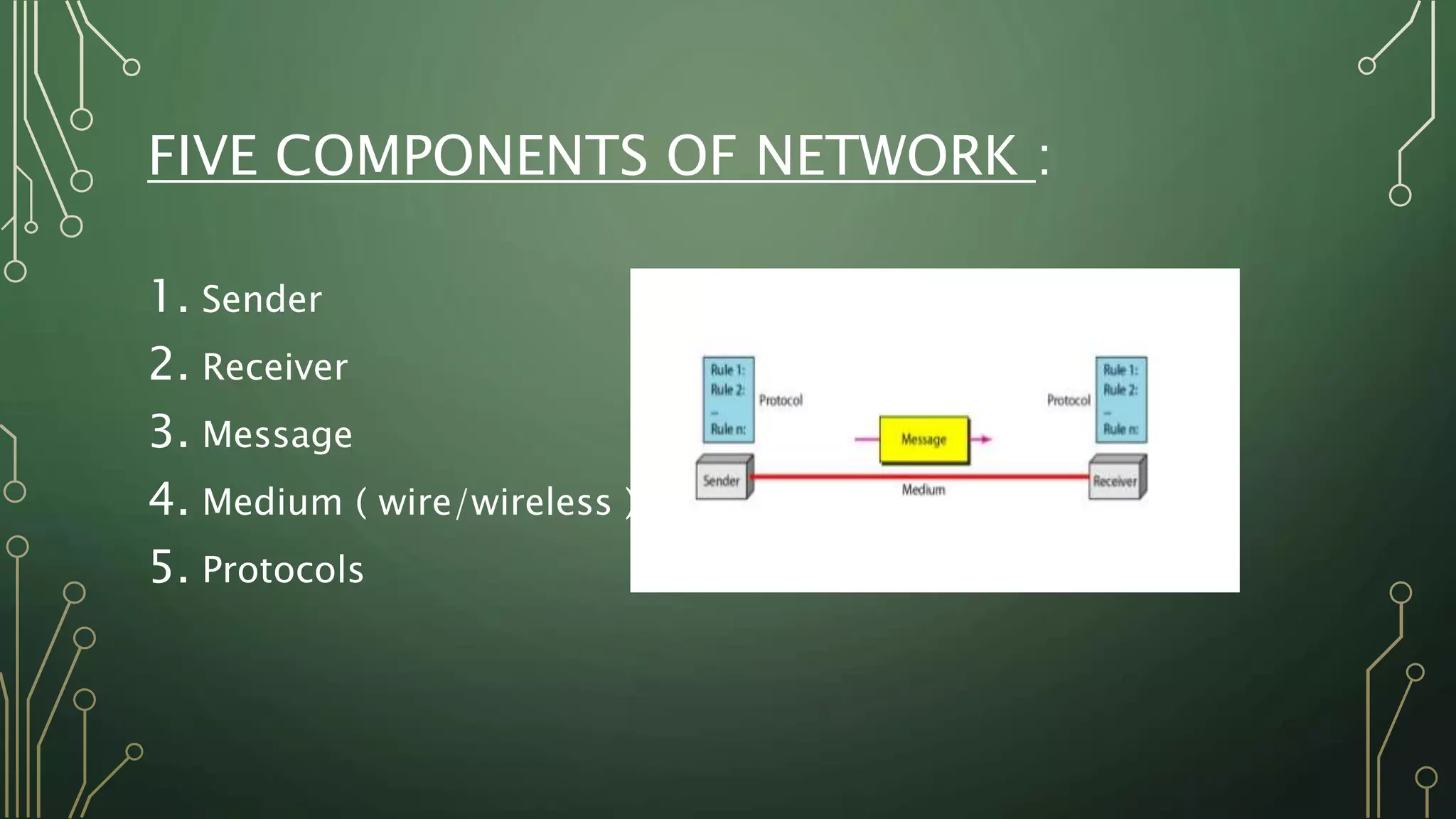
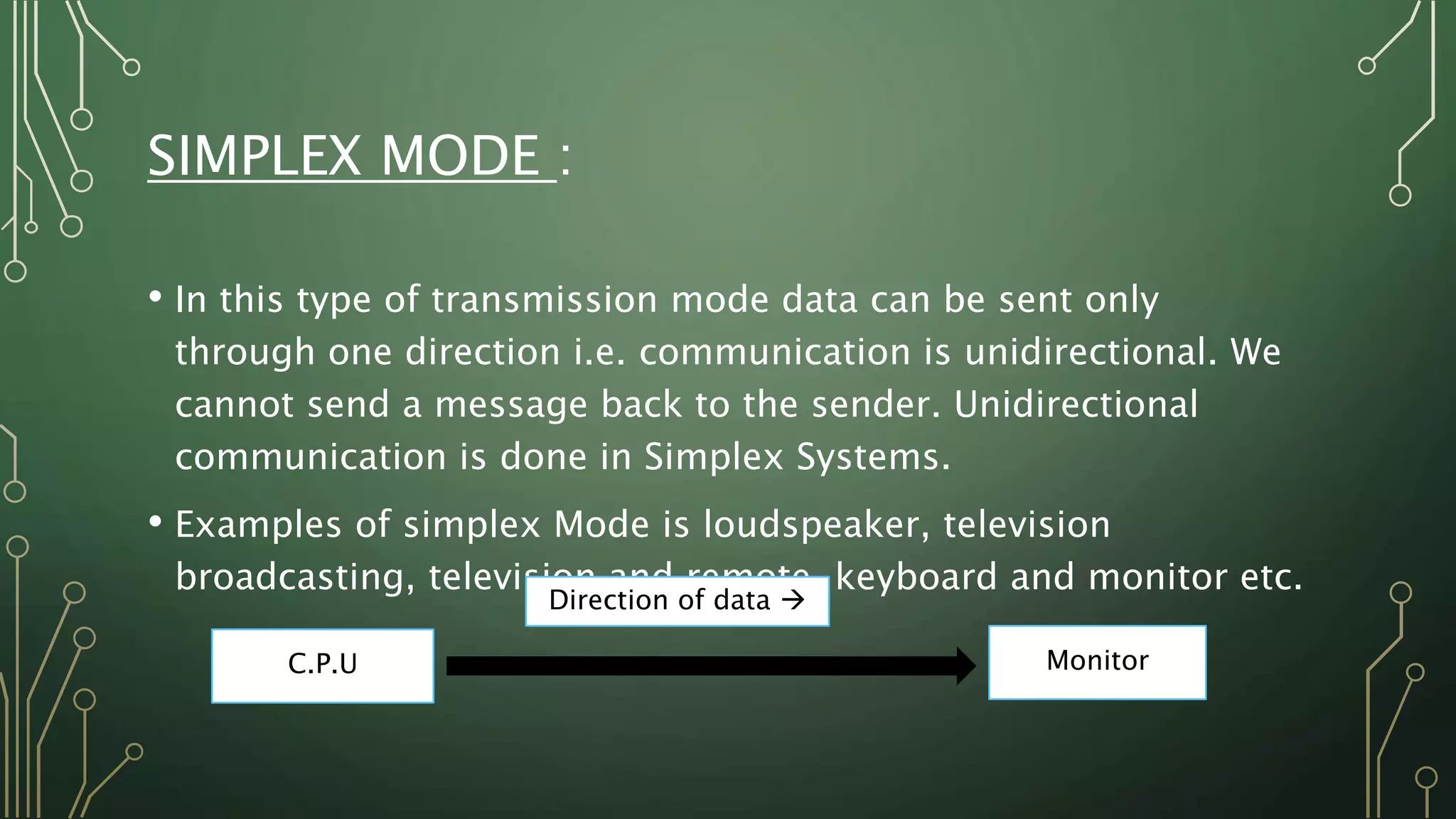
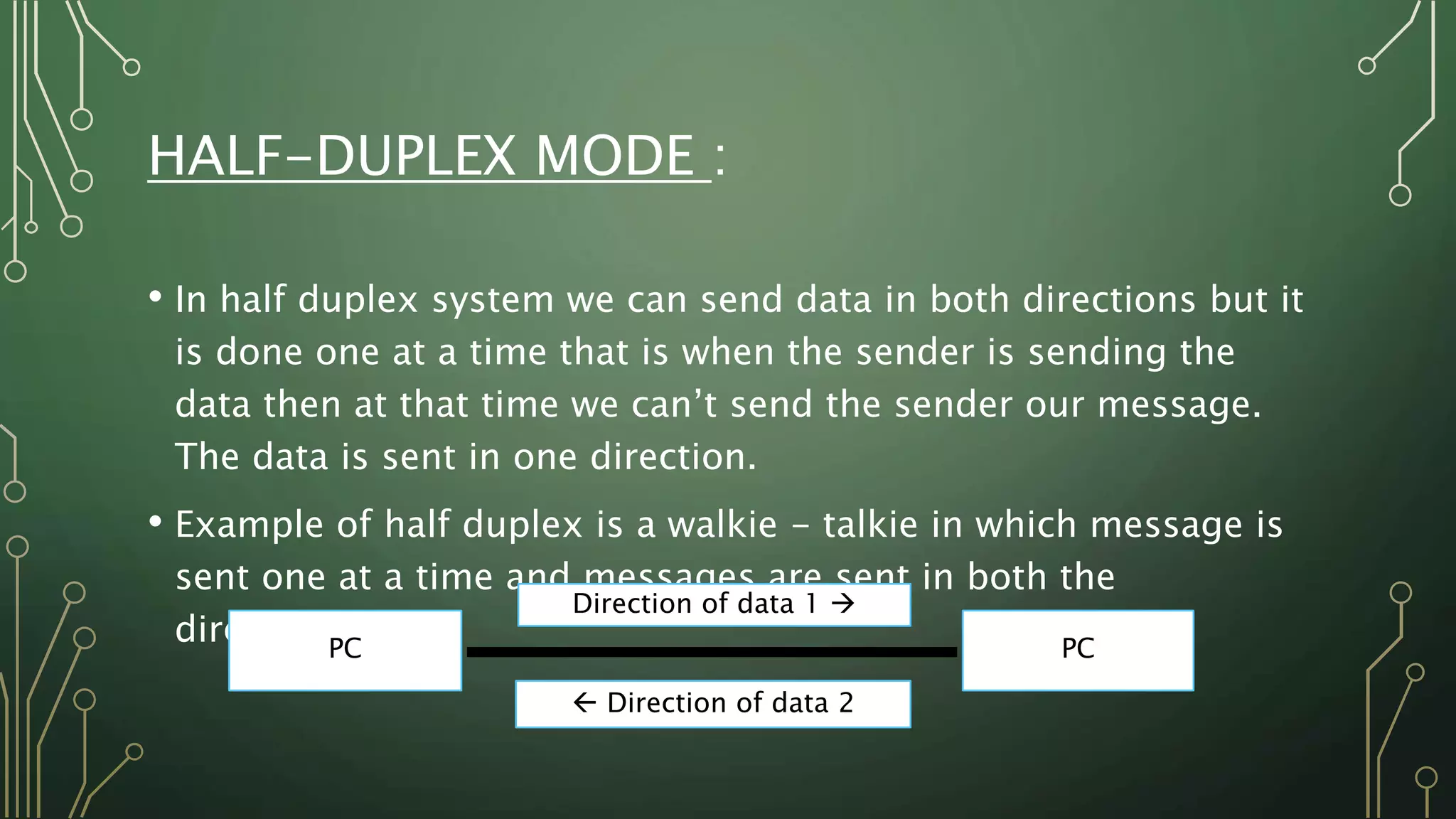
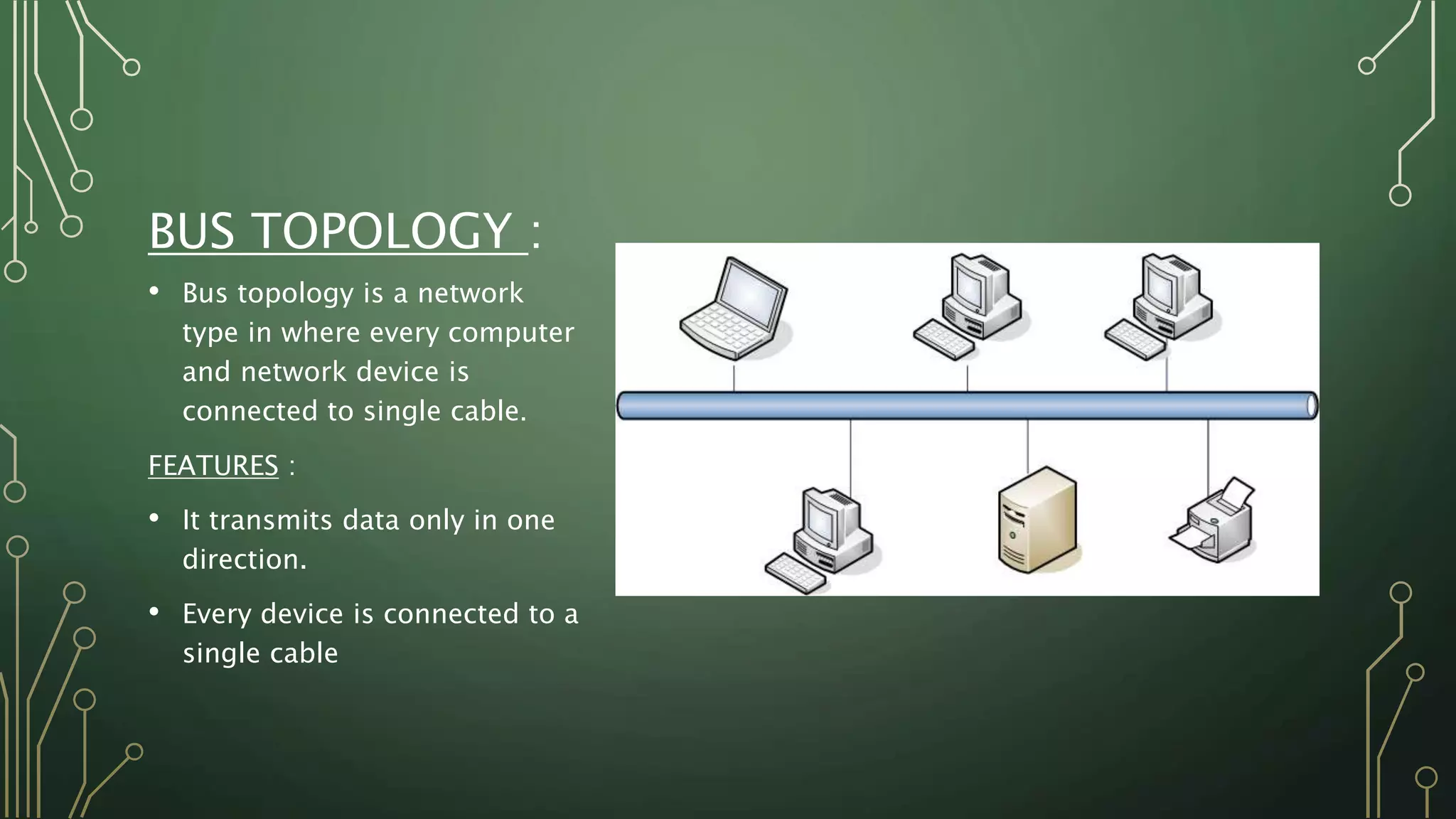
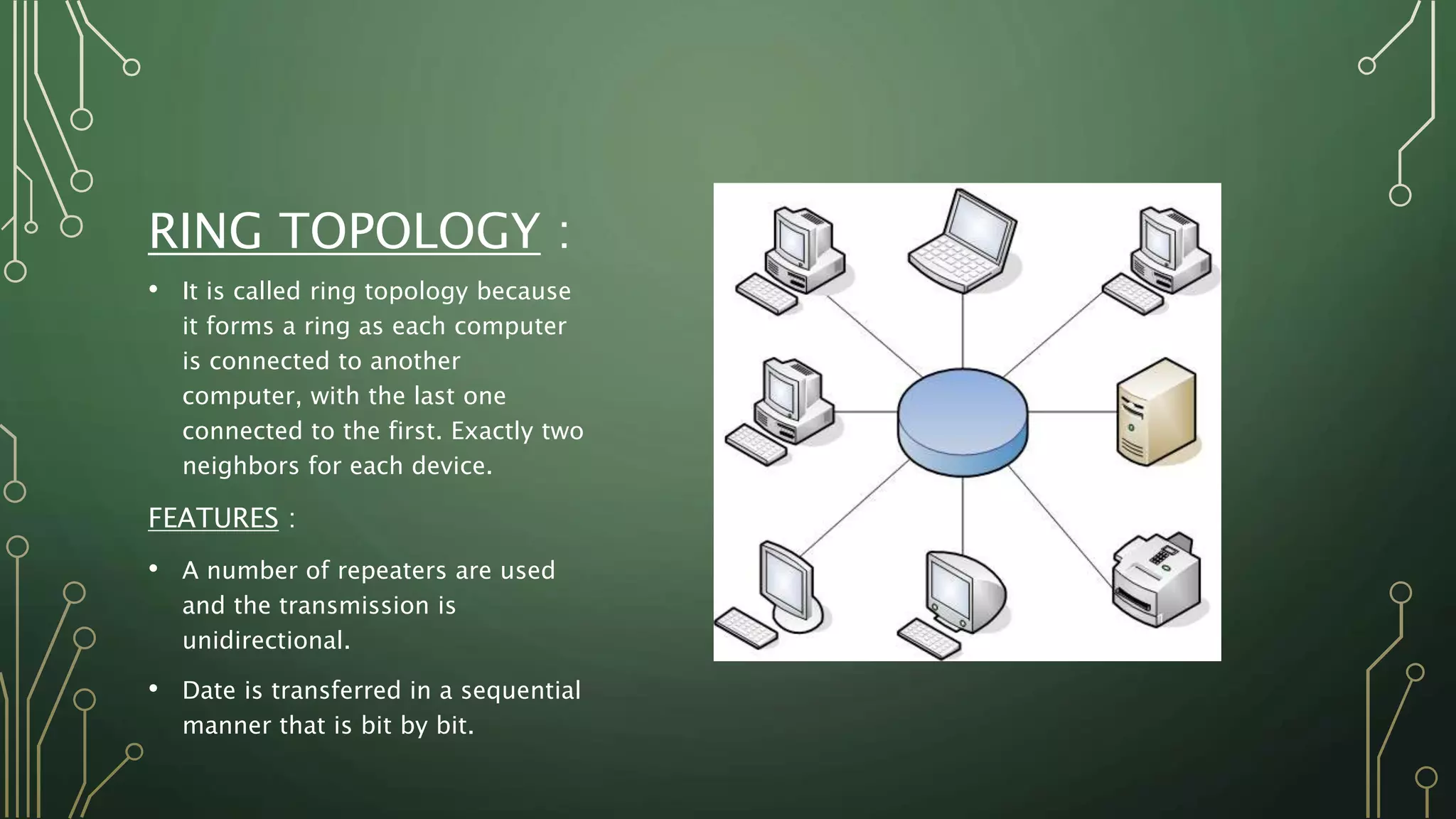
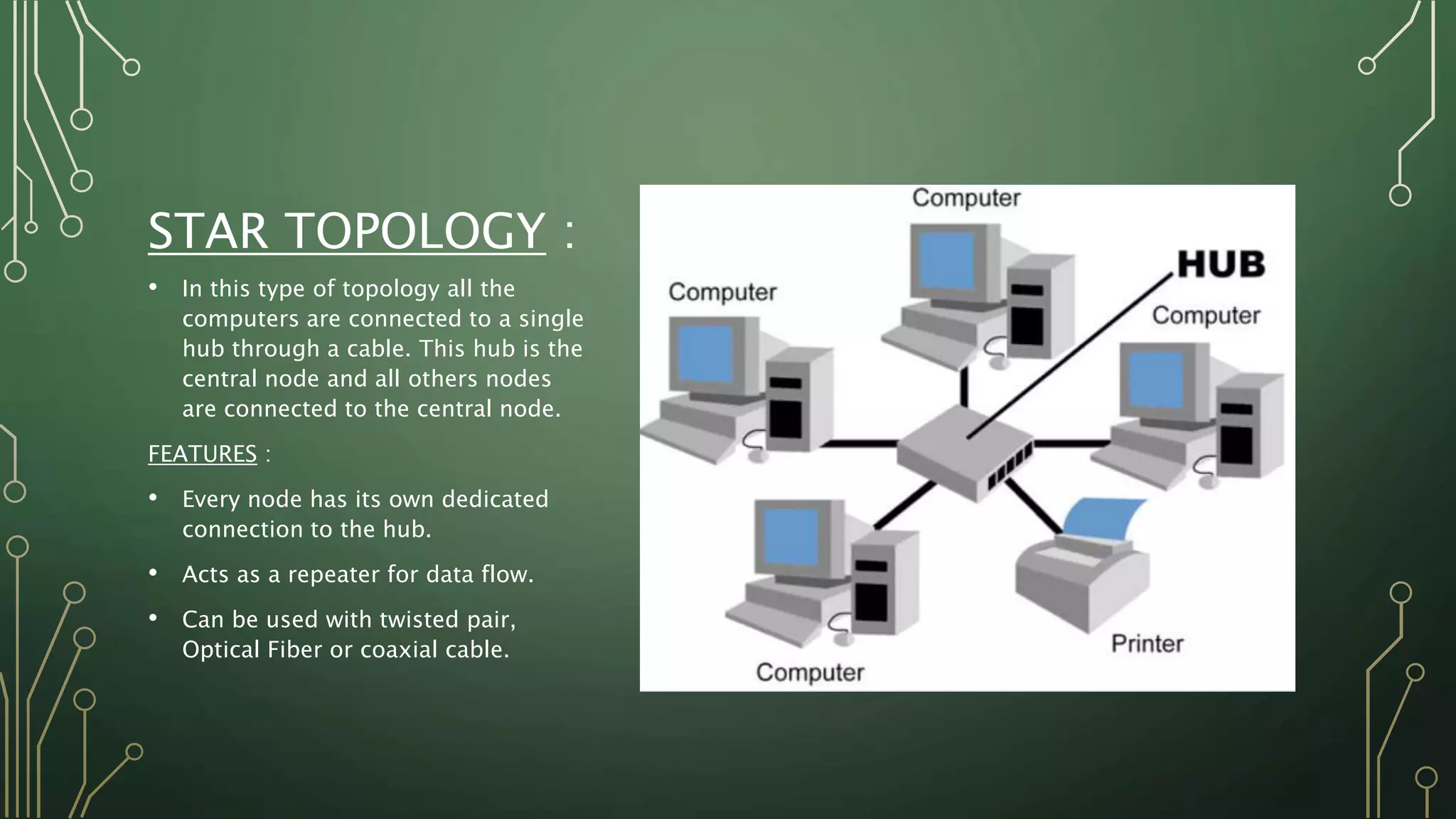
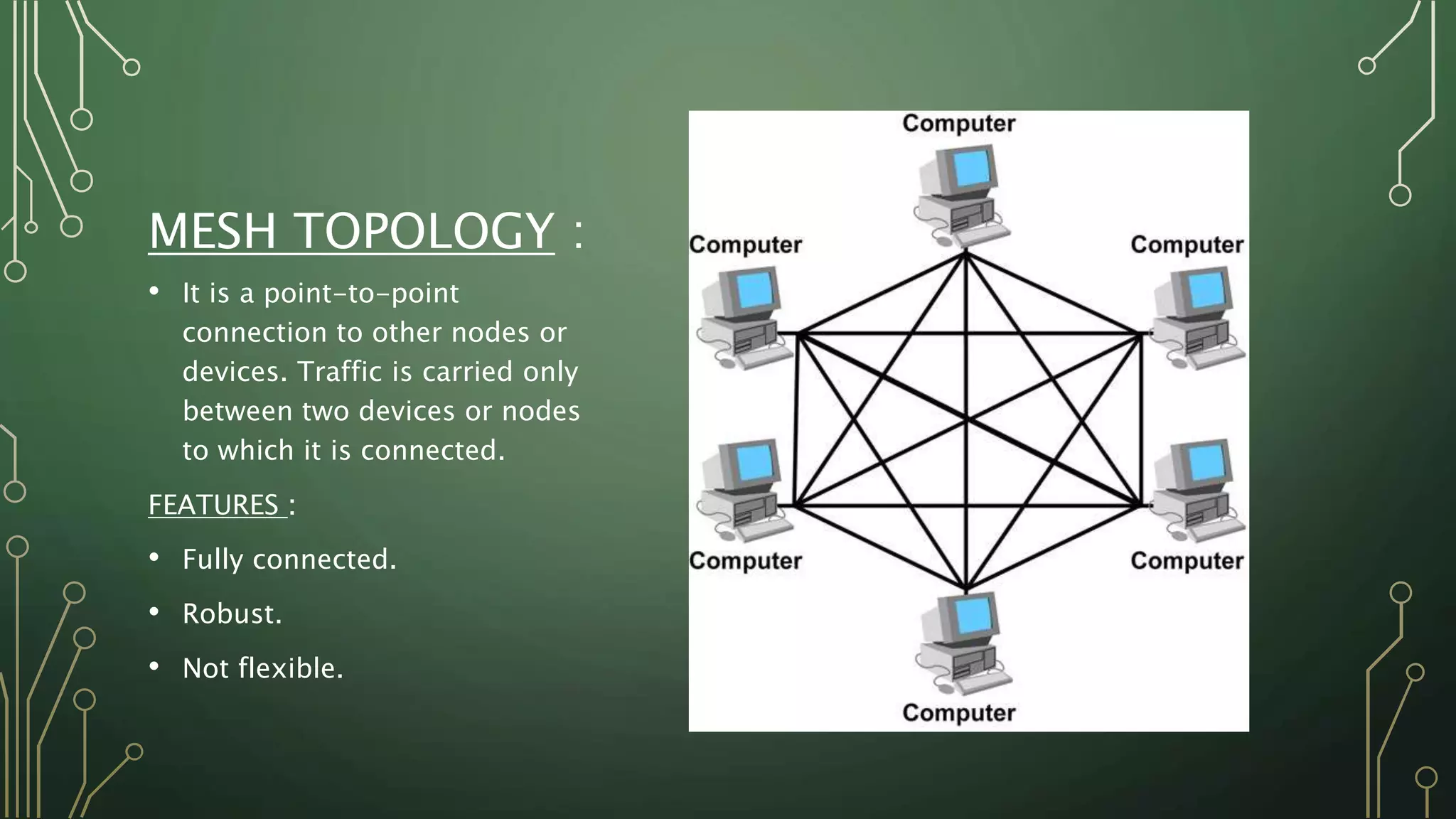
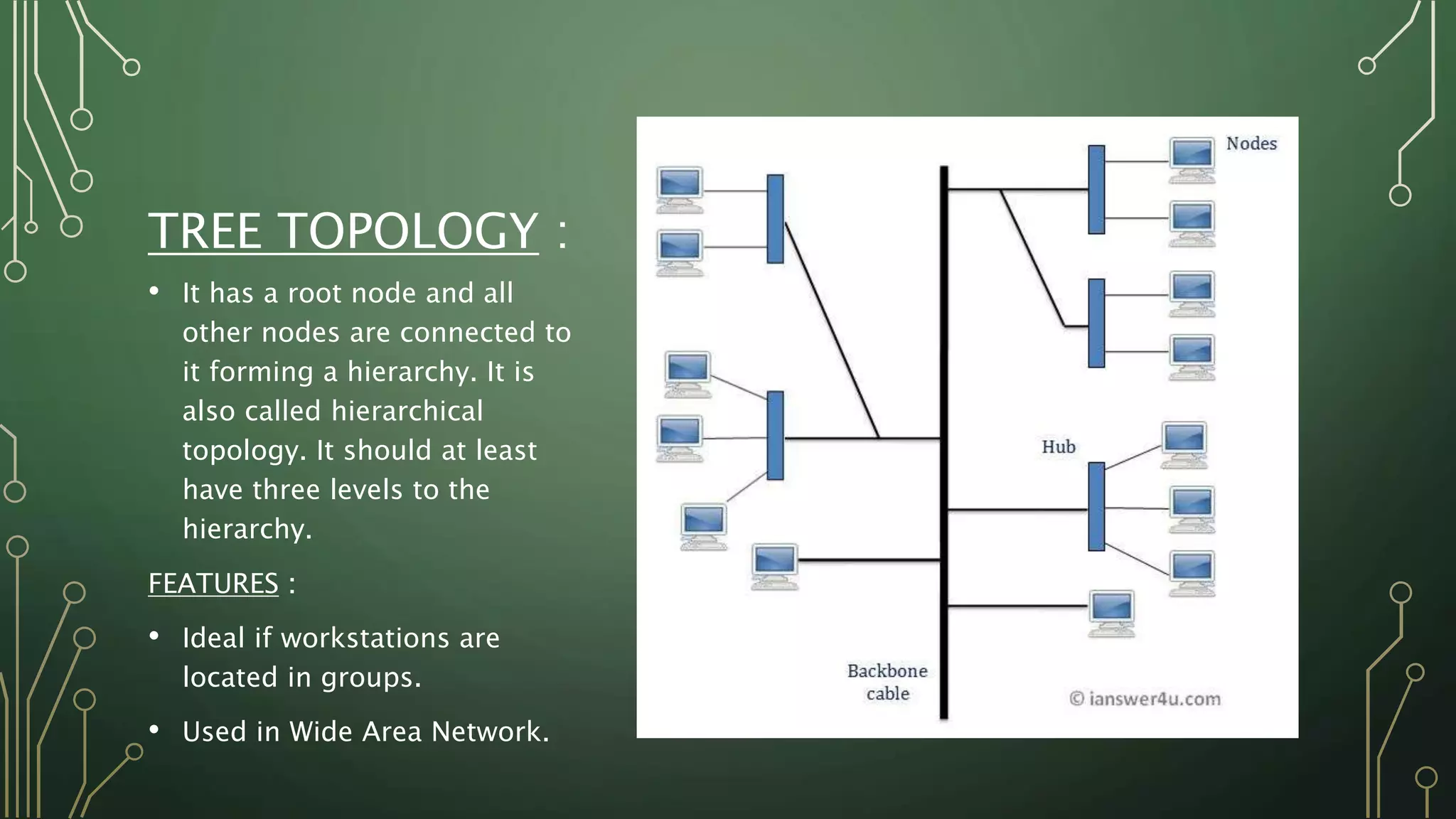
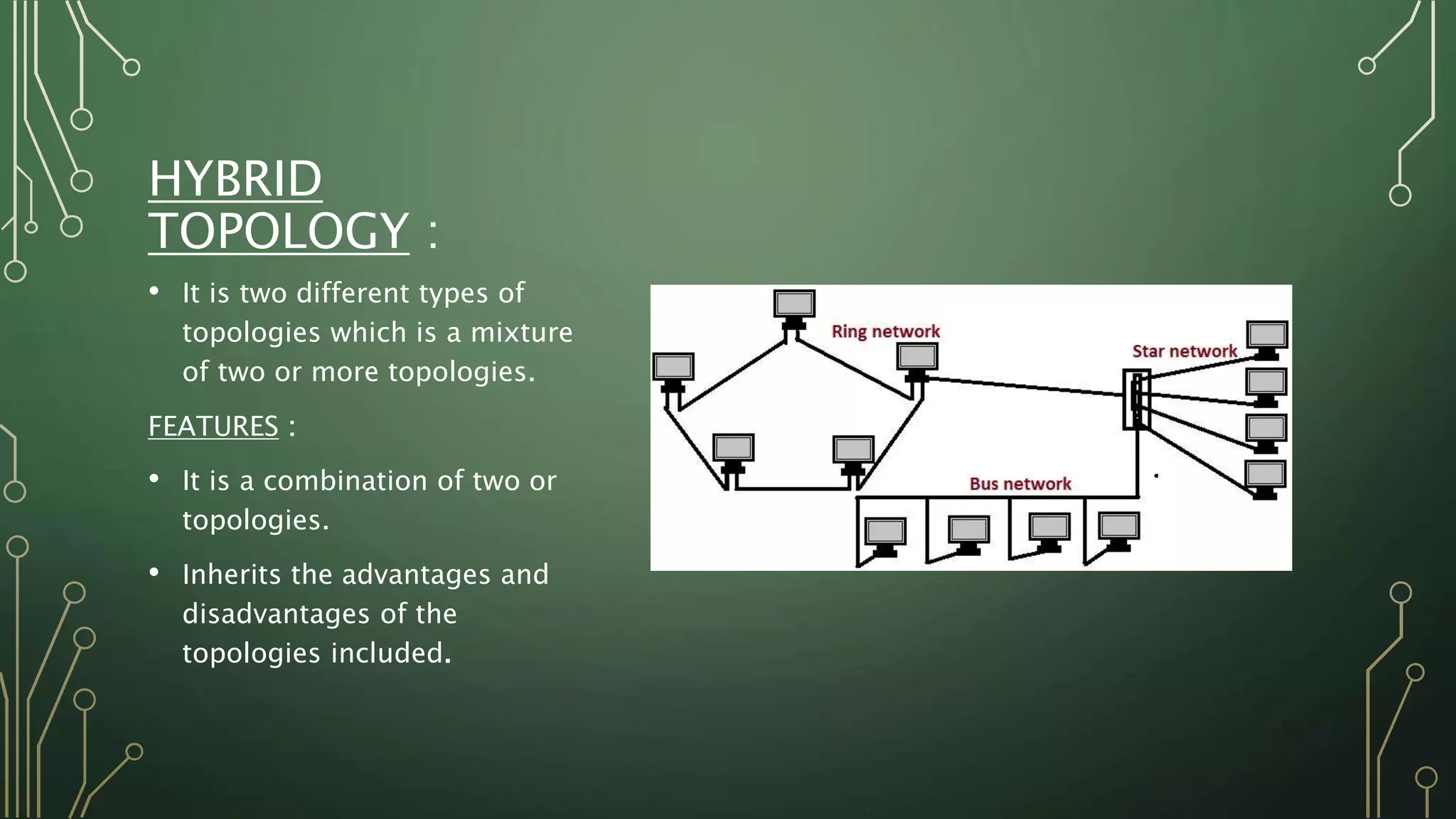
This document discusses computer networks and their basic components. It describes the three common network modes: simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. It also outlines the five main network topologies: bus, ring, star, mesh and tree. Each topology is defined and its advantages and disadvantages are provided. The document serves as an introductory overview of computer networks.