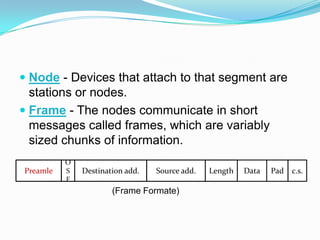
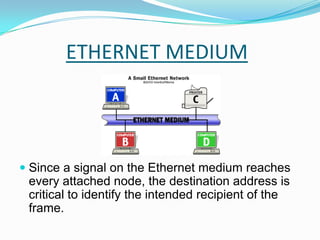
Ethernet is a widely used local area network technology that uses various cabling media like coaxial cable, twisted pair wires, and fiber optics. Devices on an Ethernet network communicate by sending short messages called frames which include information like destination and source addresses. Ethernet networks originally had limitations in distance and number of devices due to collisions that occurred when multiple devices sent frames simultaneously. These limitations were addressed through technologies like repeaters, bridges, and routers which helped segment networks and increase their size and overall performance. Modern switched Ethernet networks provide full-duplex communication allowing simultaneous transmission and reception to avoid collisions.