This document provides an overview of networking concepts including:
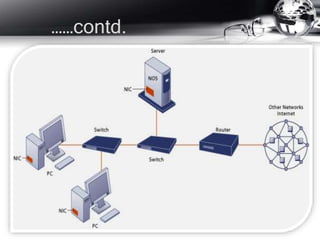
- What a network is and common terms like servers, switches, routers, and modems.
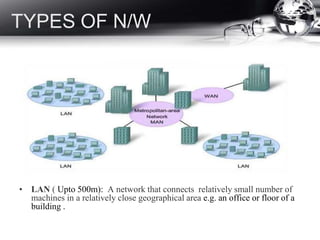
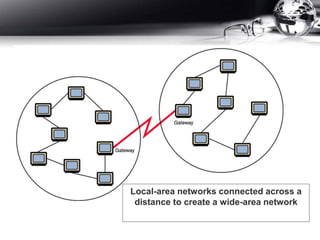
- Types of networks including LANs, MANs, and WANs.
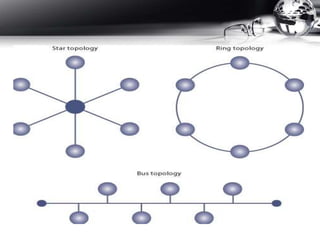
- Topologies like ring, star, and bus.
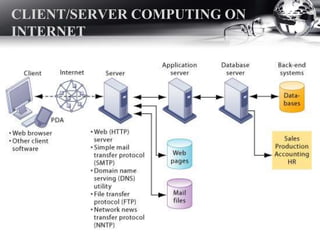
- The Internet as a global network and how connections are made via ISPs and technologies like DSL and cable modems.
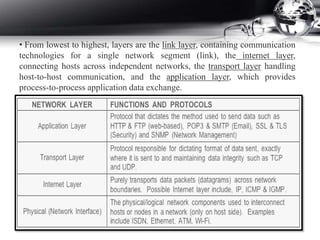
- The TCP/IP protocol suite and how it organizes networking into layers.
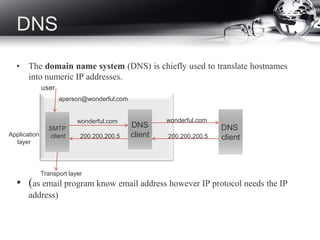
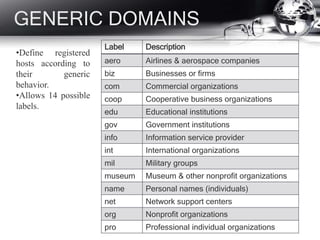
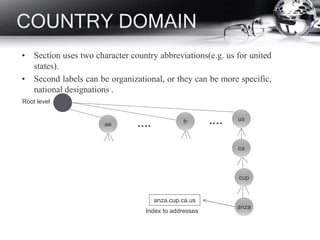
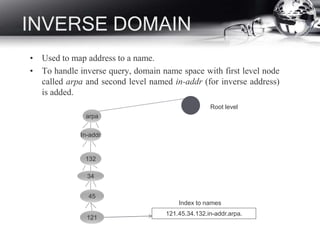
- DNS and how it translates names to IP addresses.
- Internet services like email, file transfer, and the World Wide Web.