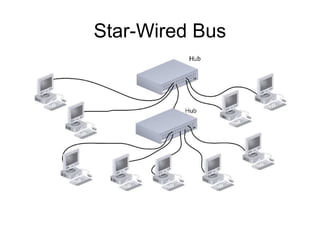
The document discusses several physical network topologies: bus, ring, star, mesh, tree, and various backbone network configurations. It provides details on the key characteristics of each topology type, including how they are structured, examples of how they are implemented, and their relative advantages and disadvantages. Hybrid topologies that combine elements of different standard topologies are also mentioned.