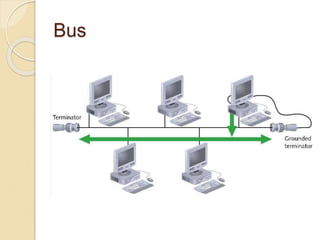
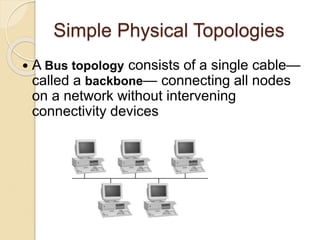
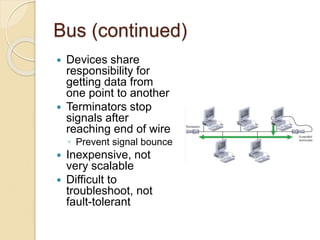
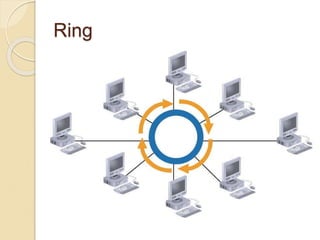
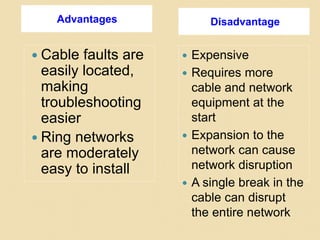
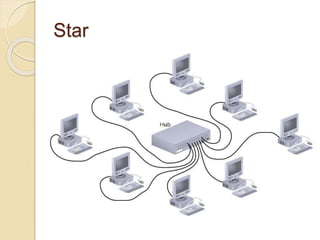
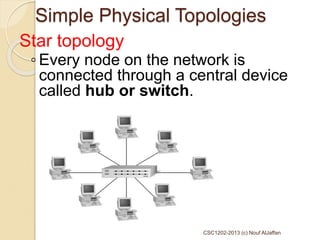
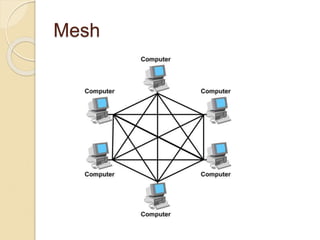
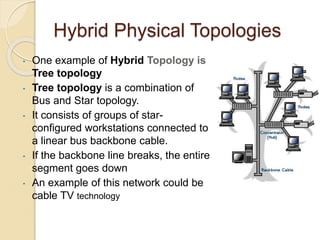
The document provides an overview of various computer network topologies, including bus, ring, star, mesh, and tree topologies. It discusses their physical layouts, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for network equipment and management. Additionally, it highlights the importance of selecting the appropriate topology based on network size, growth, and performance needs.