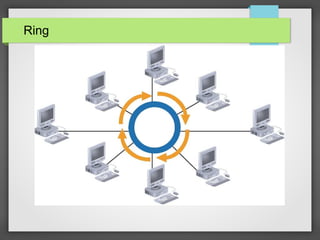
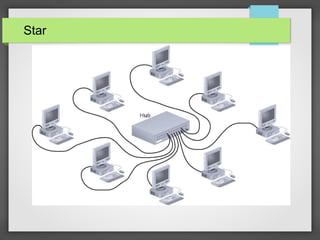
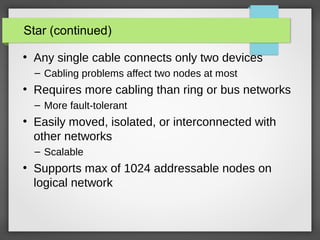
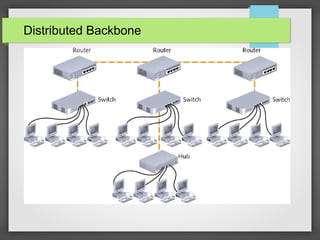
The document discusses different network topologies including bus, ring, and star configurations. It describes the physical layout and advantages and disadvantages of each. A bus topology uses a single cable to connect all nodes without intermediary devices. A ring topology connects each node to the two nearest in a circular formation. A star topology connects all nodes to a central hub device. Hybrid configurations like star-wired ring are also presented. Different logical topologies for data transmission are discussed, including bus and ring formats. Backbone structures for linking network components are outlined, such as daisy chains, distributed, and collapsed configurations.