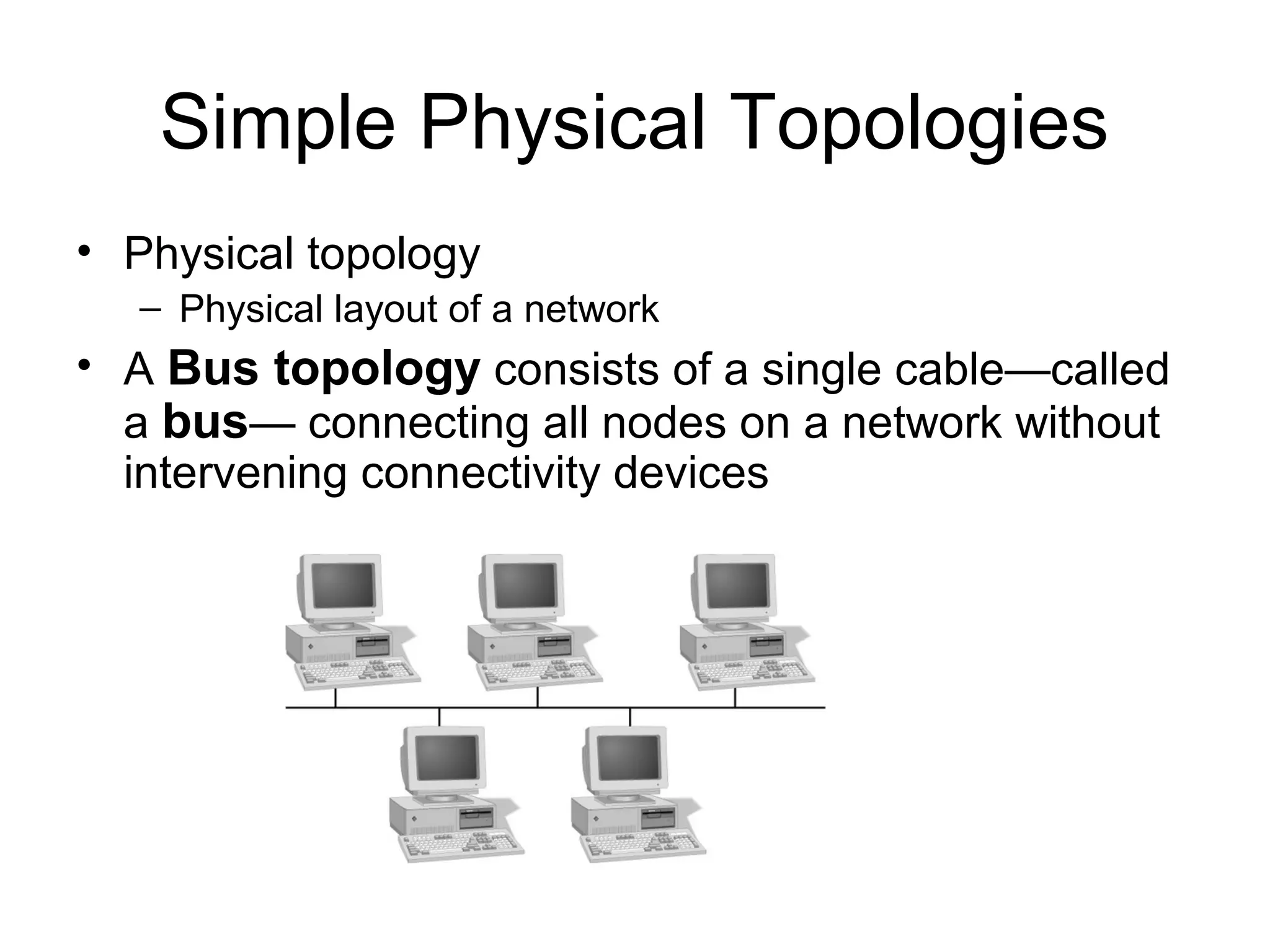
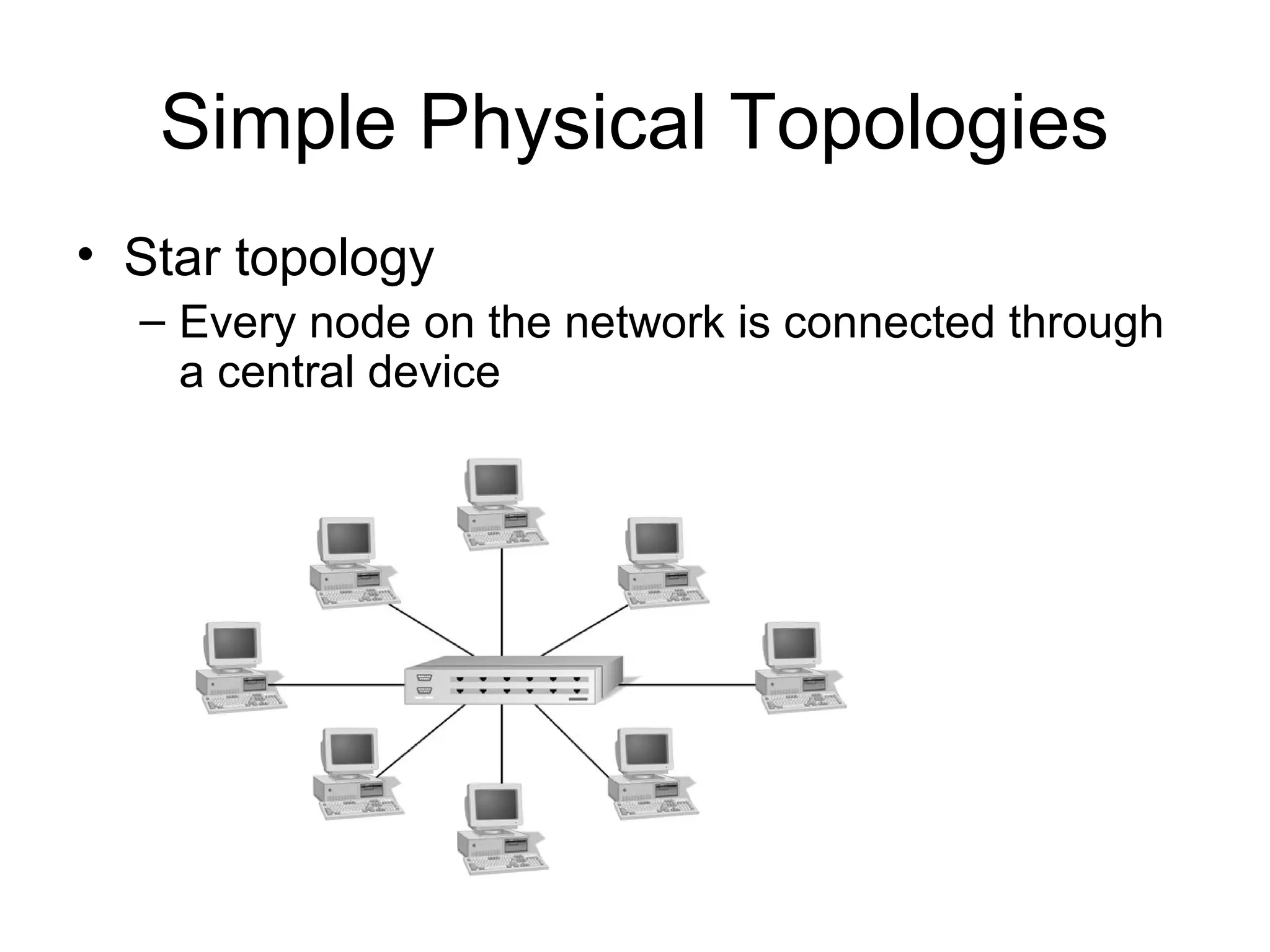
This document discusses various network topologies including bus, ring, star, and hybrid topologies. It describes the basic characteristics of each topology such as their physical layout, advantages, and disadvantages. It also covers backbone structures used to connect hubs, switches, routers and extend networks in daisy chain, distributed, collapsed, and parallel configurations. Finally, it notes that logical topologies like bus and ring may differ from the underlying physical topology.