Embed presentation


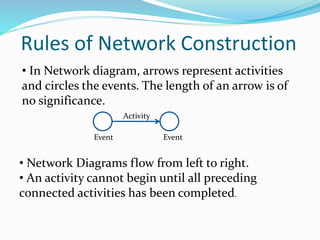
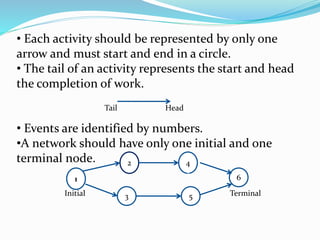

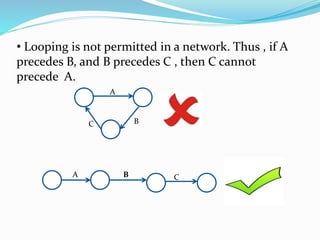



The document discusses rules for constructing network diagrams that represent project operations. Some key rules include: arrows represent activities and circles represent events; networks flow from left to right with activities only starting once all preceding activities are complete; each activity must start and end at a circle; event numbers increase from tail to head; networks can only have one initial and one terminal node; dummy and parallel activities are not permitted; and looping or burst events are also not allowed.







