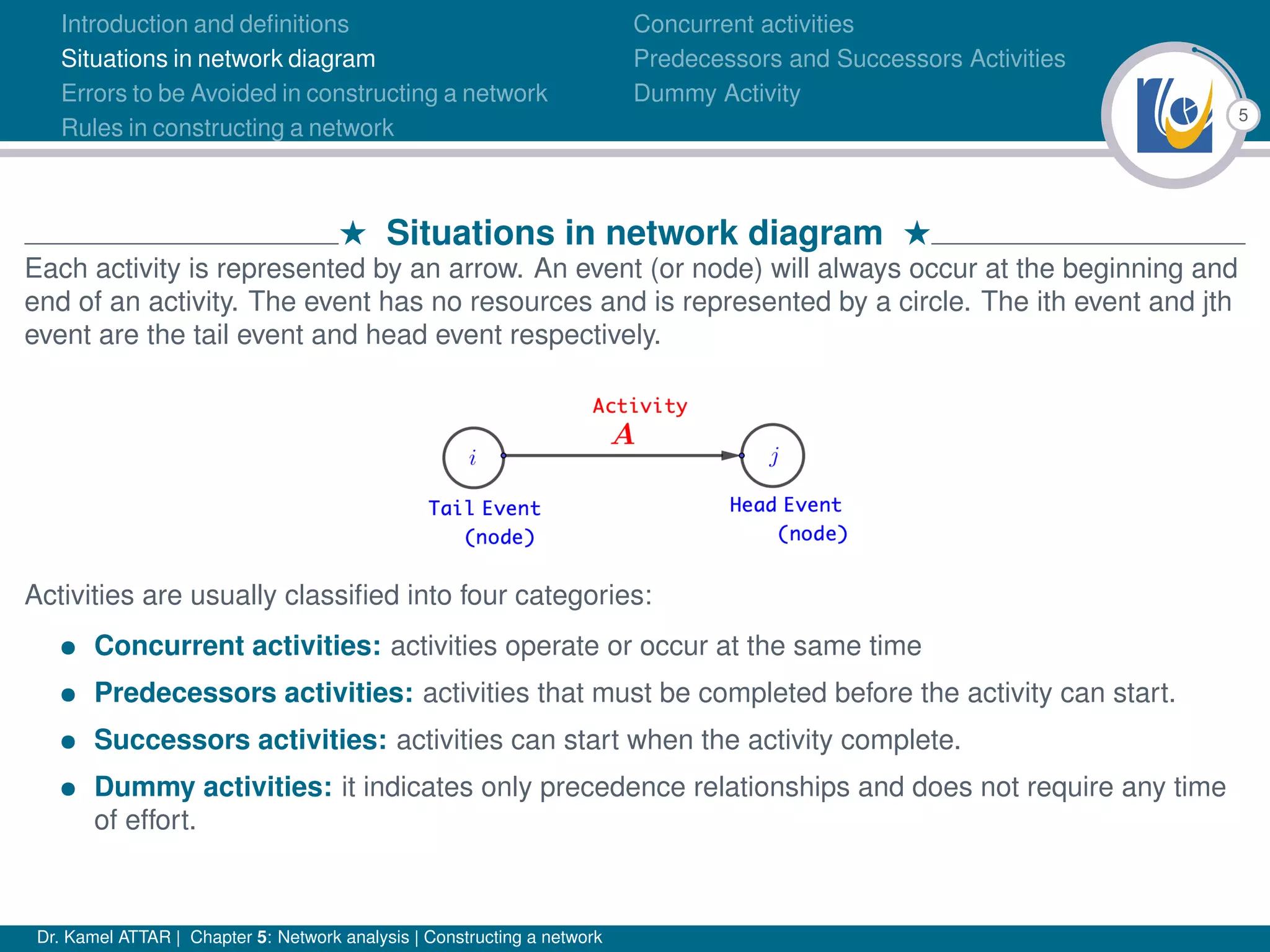
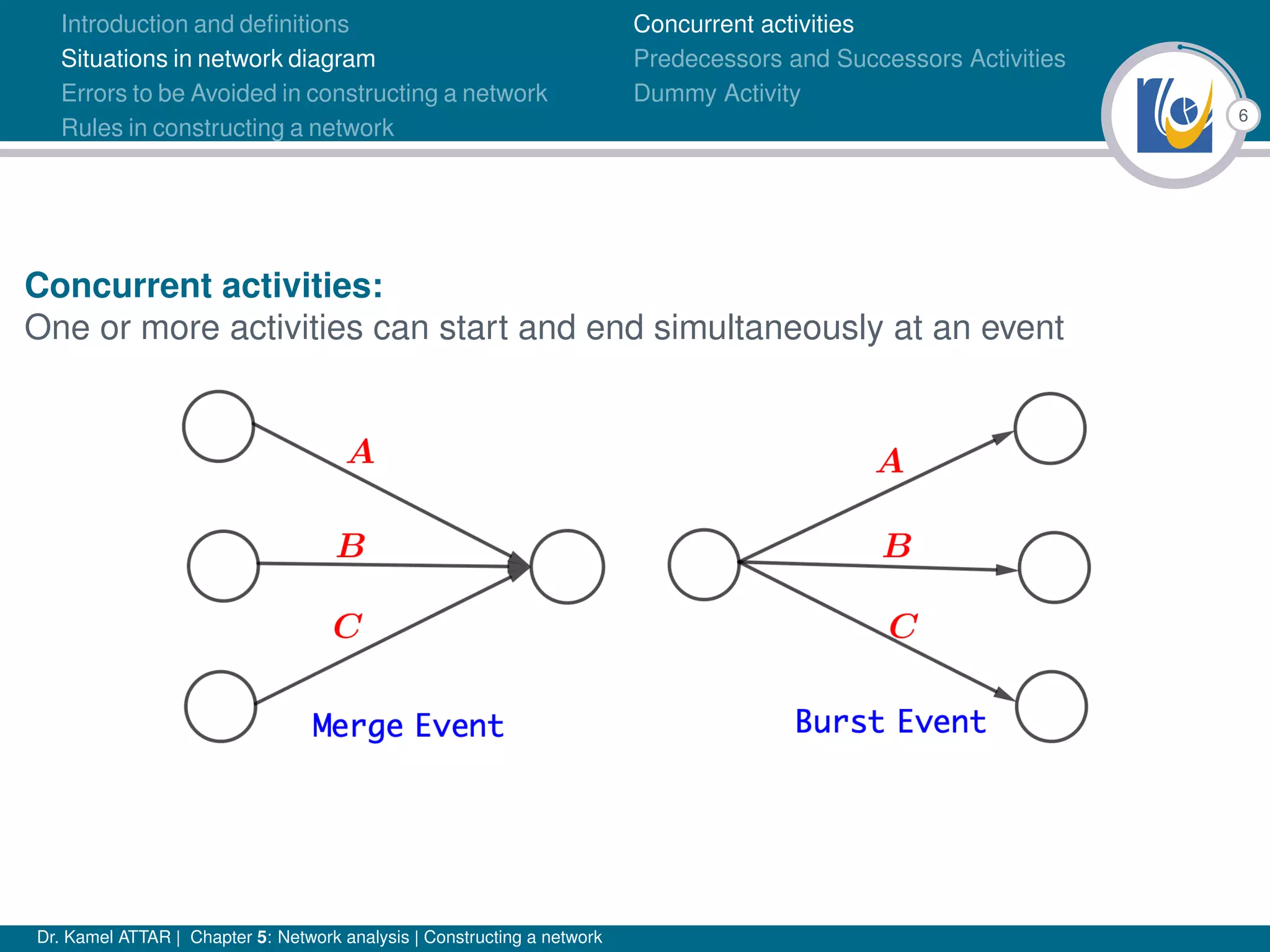
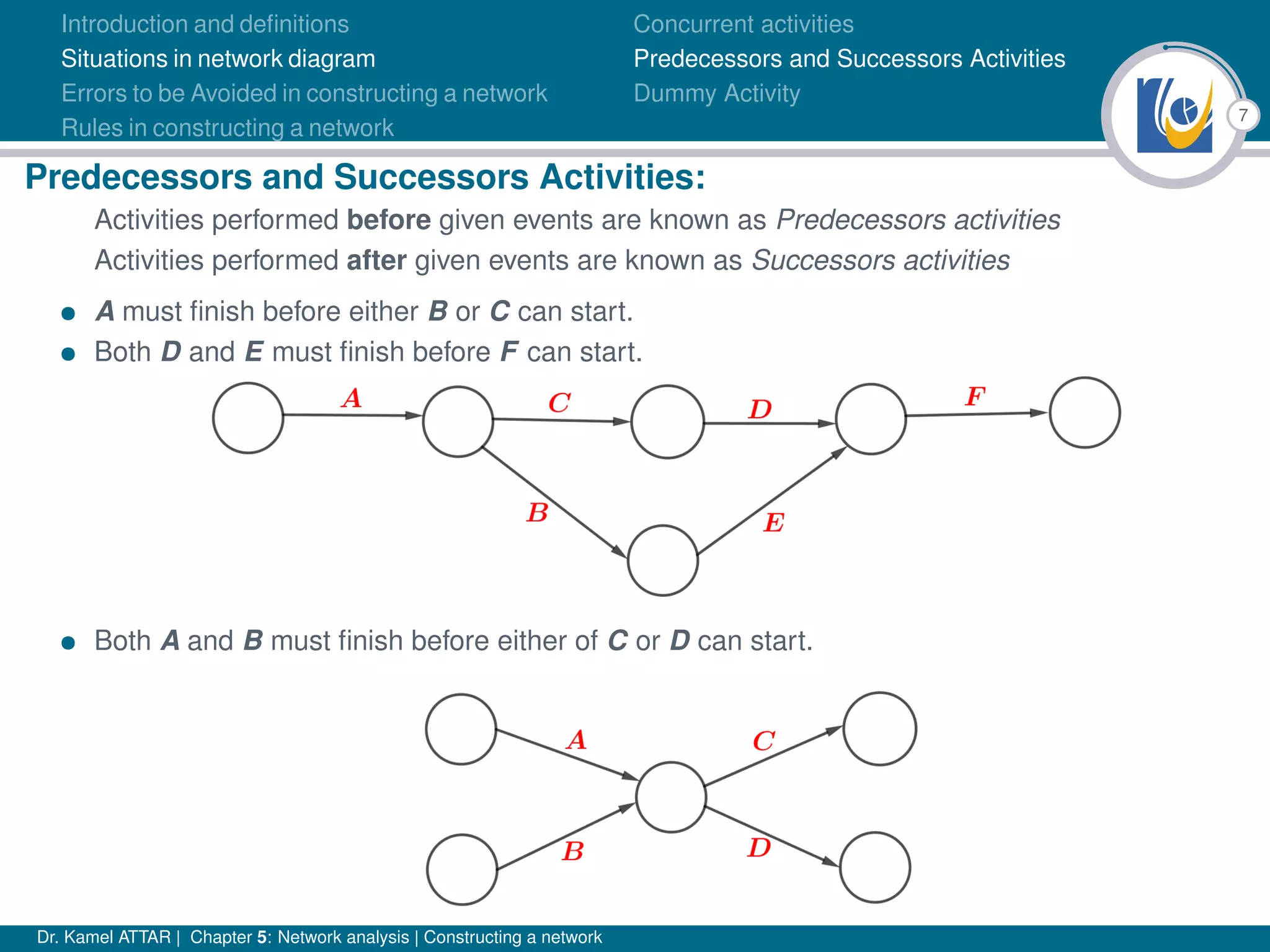
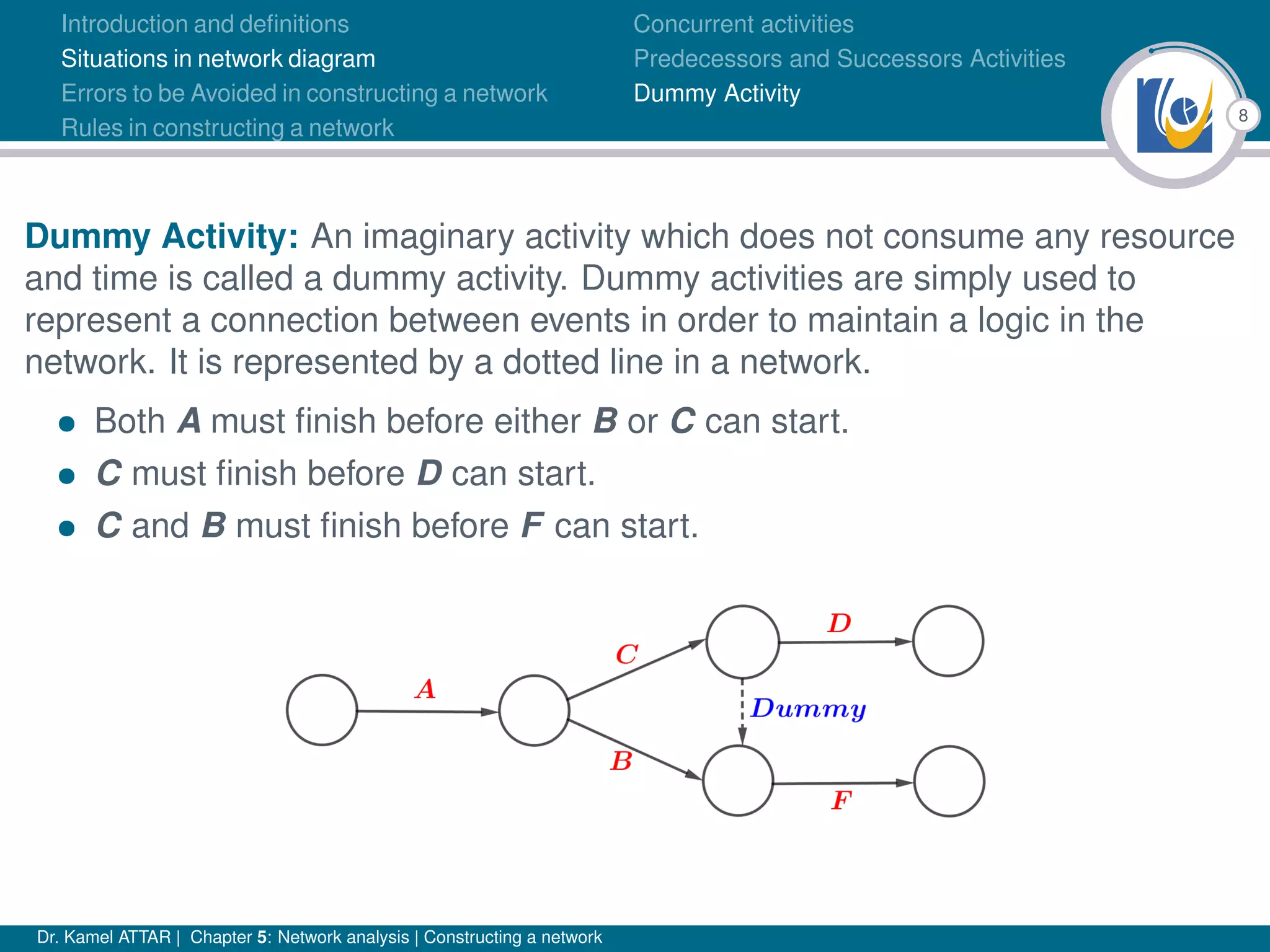
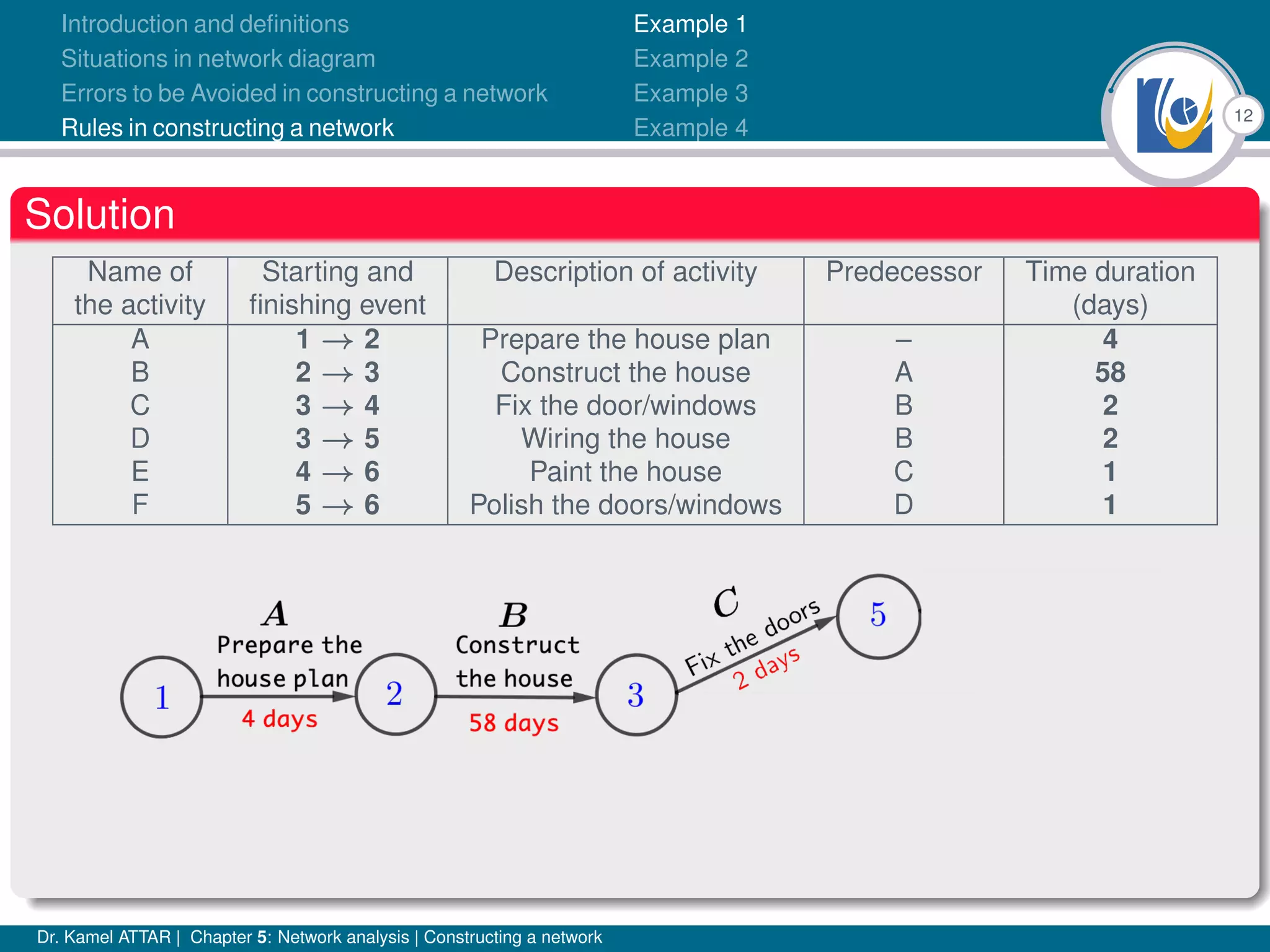
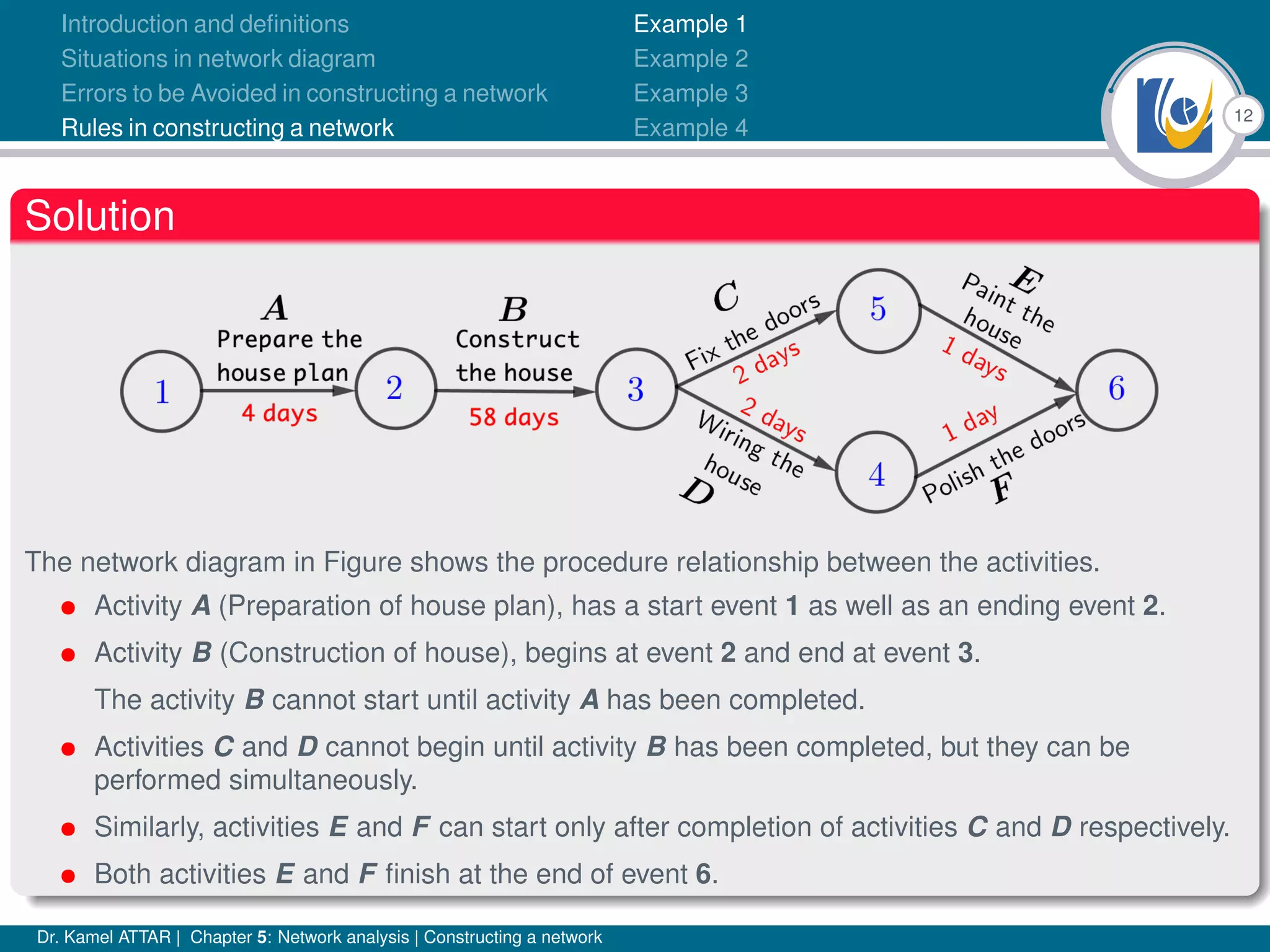
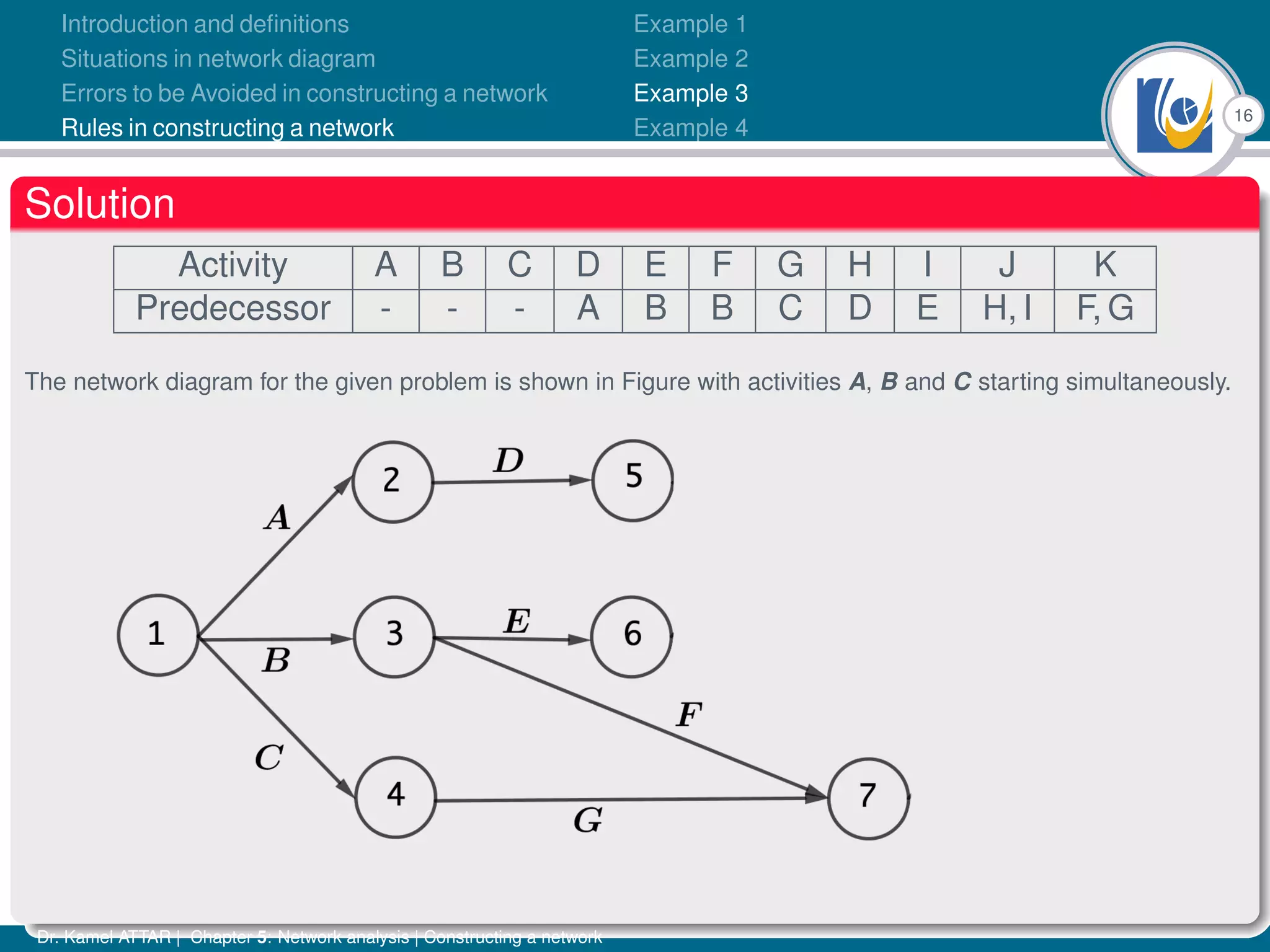
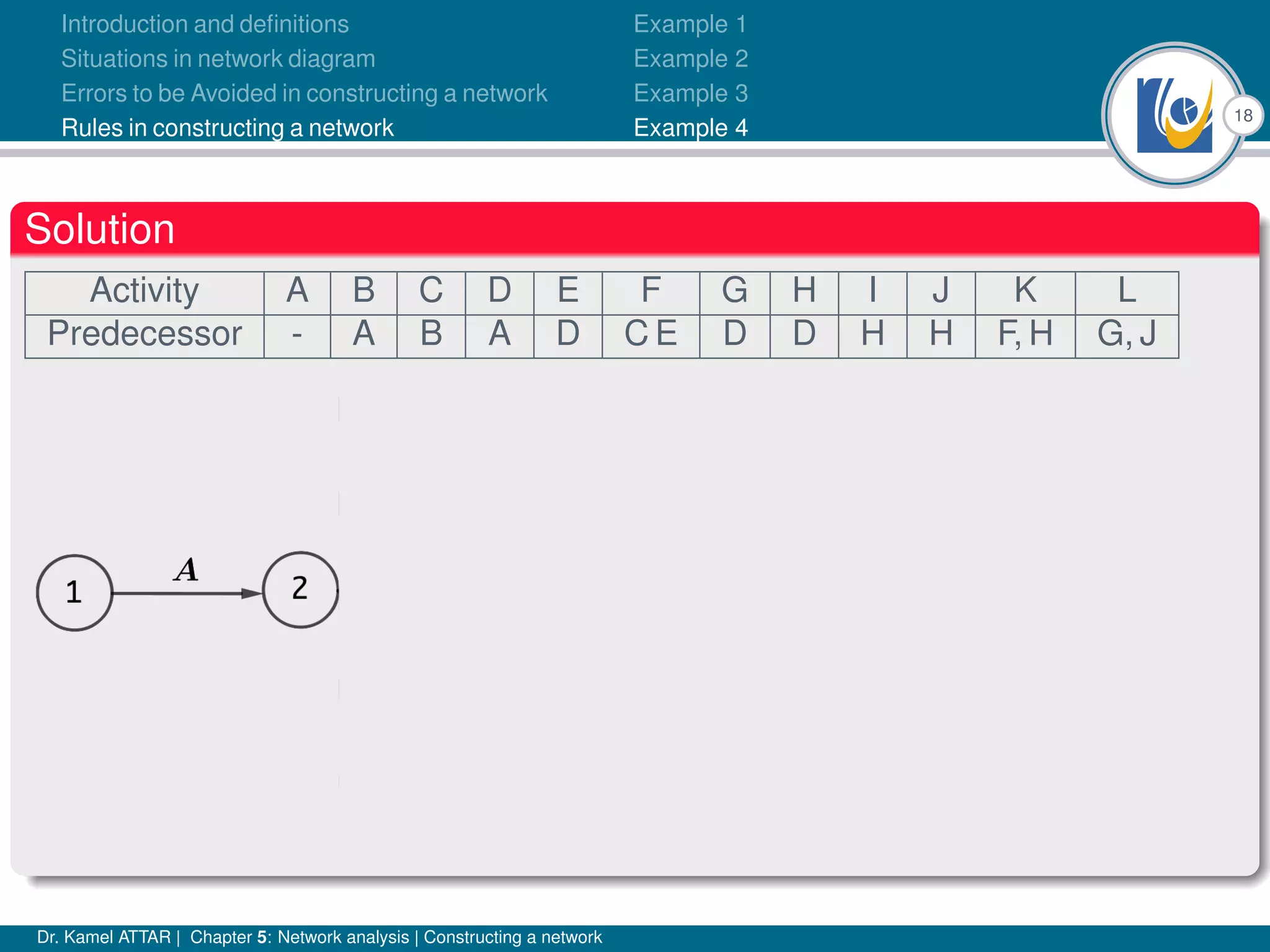
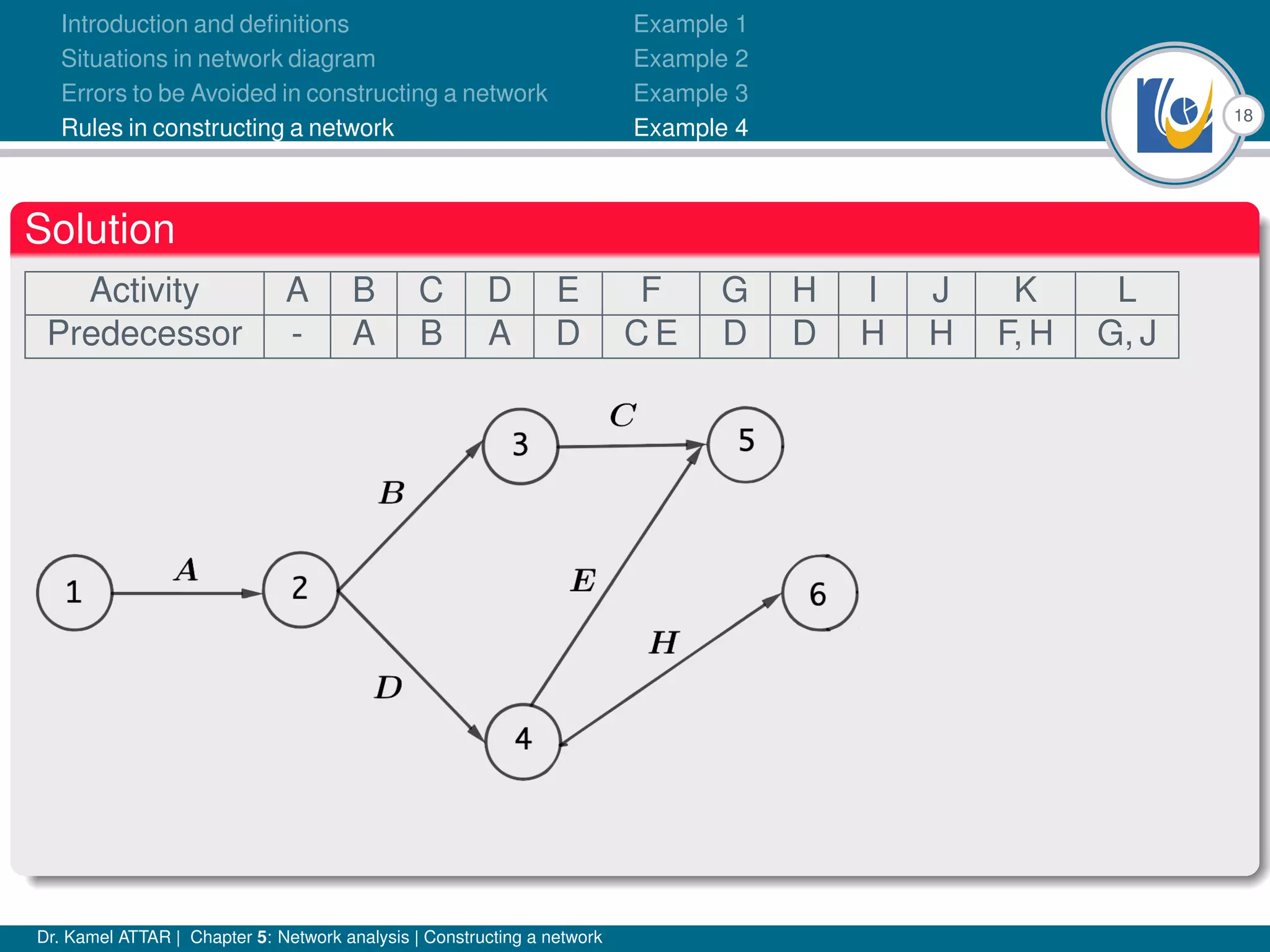
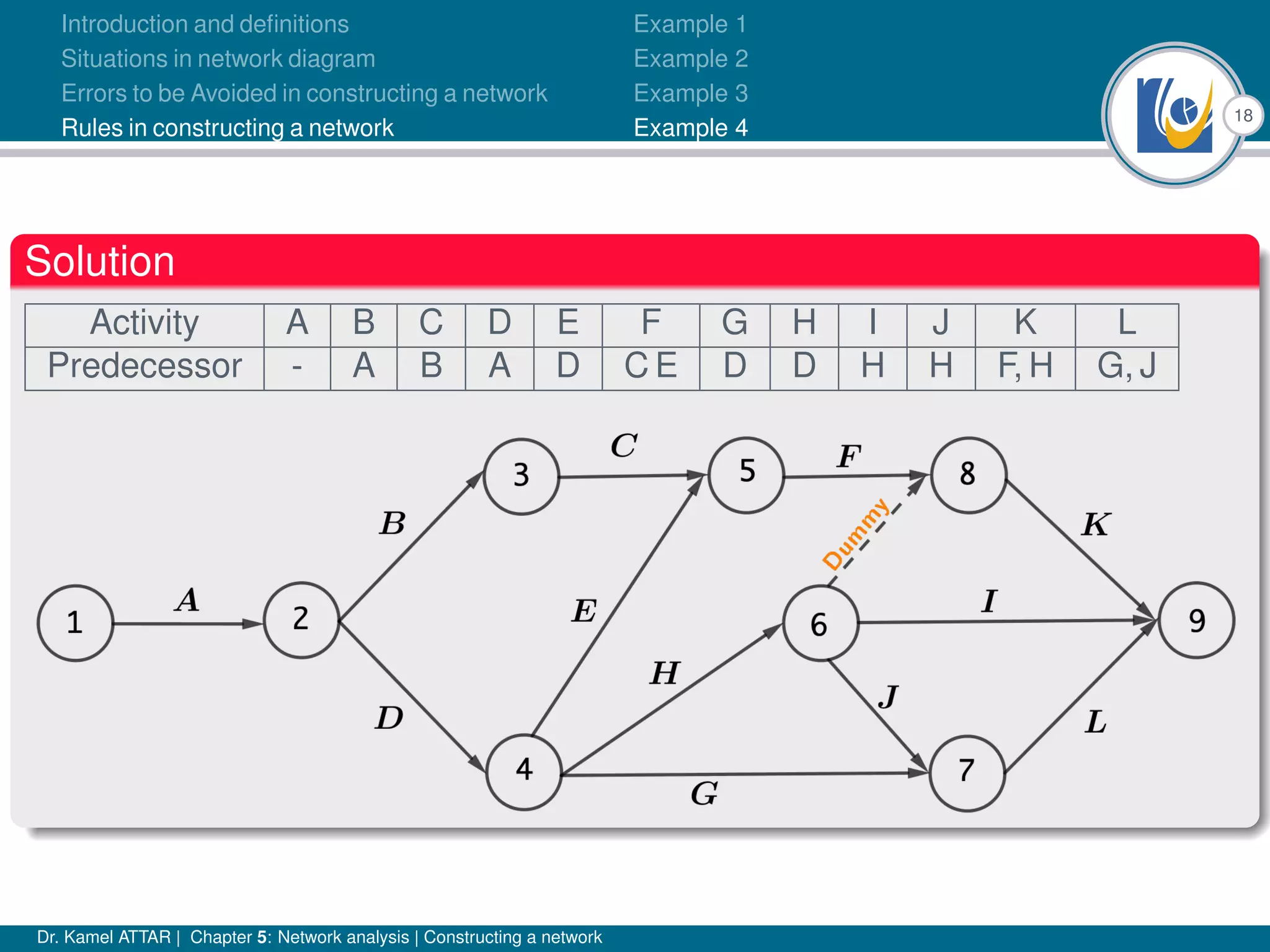
Chapter 5 of Dr. Kamel Attar's work focuses on network analysis in project management, detailing essential definitions, rules, and common errors in constructing activity networks. It emphasizes the importance of planning, scheduling, and controlling projects through graphical representations known as networks, discussing various techniques like PERT and CPM. The chapter also categorizes activities and describes how to avoid logical errors in network diagrams, ensuring effective project execution.